Contents
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1881 List of years in Argentina | ||||
Events in the year 1881 in Argentina.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1881 List of years in Argentina | ||||
Events in the year 1881 in Argentina.
The peso is the currency of Argentina since 1992, identified within Argentina by the symbol $ preceding the amount in the same way as many countries using peso or dollar currencies. It is subdivided into 100 centavos and then Central Bank introduced new issues with peso subdivisions like 1, 2, 5 and 10. Due to rapid inflation, coins are not used. Same situation occurs with 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1,000 and 2,000 peso banknotes, these banknotes are no longer printed, but they are still valid. Its ISO 4217 code is ARS. It replaced the austral at a rate of 10,000 australes to one peso.

Alejo Julio Argentino Roca Paz was an army general and statesman who served as President of Argentina from 1880 to 1886 and from 1898 to 1904. Roca is the most important representative of the Generation of '80 and is known for directing the Conquest of the Desert, a series of military campaigns against the indigenous peoples of Patagonia sometimes considered a genocide.
Postal codes in Argentina are called códigos postales. Argentina first implemented a four-digit postal code system in 1958, aiming to improve mail distribution efficiency. However, it wasn't until 1998 that the more detailed and comprehensive Código Postal Argentino (CPA) system was launched, significantly enhancing both accuracy and efficiency in mail delivery. Until 1998 Argentina employed a four-digit postal code for each municipality, with the first digit representing a region in the country, except in the case of the city of Buenos Aires. The unique codes became the base for the newer system, officially called CPA.

The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Argentina.
The real was the currency of Argentina until 1881. From 1822, it was subdivided into 10 décimos. The sol was also issued during this period and was equal to the real, whilst the peso was worth 8 reales and the escudo was worth 16 reales.
The peso moneda nacional was the currency of Argentina from 5 November 1881 to 1 January 1970, the date in which the peso ley 18.188 was issued to the Argentine public. It was subdivided into 100 centavos, with the argentino worth 5 pesos. The peso was introduced to replace the Argentine peso moneda corriente at a rate of $+m⁄c 25 = m$n 1.

The peso moneda corriente was a non-convertible Argentine paper currency which circulated between 9 January 1826, and 4 November 1881. It was worth eight reales. Its symbol was $m/c. It was also known as the peso papel.

Argentine postage stamps were first issued in 1858 by the Argentine Confederation and nationally by the new Republic's National Postal Service in 1862. Due to the continuing civil wars, a number of provinces and territories, particularly in the then-remote far north and far south, continued to issue their own postage brands and stamps for some time, afterwards; some of these issues have since become collectors' items.
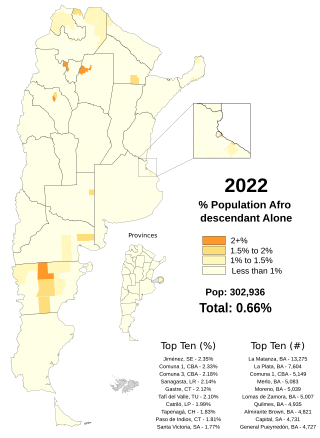
Afro-Argentines, also known as Black Argentines, are Argentines who have predominantly or total Sub-Saharan African ancestry. The Afro-Argentine population is the result of people being brought over during the transatlantic slave trade during the centuries of Spanish domination in the region and immigration.

Gabino Ezeiza, nicknamed Negro, was an Argentine musician. Ezeiza was one of the greatest performers in the art of the payada. He became renowned, both in his native land and in Uruguay, after a memorable encounter with Oriental payador Juan de Nava, who carried at the time a certain halo of invincibility. This celebrated contest was held in the city of Paysandú on July 23, 1884, in front of one of the largest crowds ever to gather for a payada duel.

Juan de Dios Filiberto was an Argentine violinist, conductor, poet and composer who became prominent in the Argentine tango genre.

Gabino Coria Peñaloza was an Argentine poet and lyricist.
Ricardo Roberto Francia was an Argentine musician, cellist, and music arranger.

The Argentine Civil Wars were a series of civil conflicts of varying intensity that took place through the territories of Argentina from 1814 to 1853. Beginning concurrently with the Argentine War of Independence (1810–1818), the conflict prevented the formation of a stable governing body until the signing of the Argentine Constitution of 1853, followed by low-frequency skirmishes that ended with the Federalization of Buenos Aires. The period saw heavy intervention from the Brazilian Empire that fought against state and provinces in multiple wars. Breakaway nations, former territories of the viceroyalty, such as the Banda Oriental, Paraguay and the Upper Peru were involved to varying degrees. Foreign powers such as the British and French empires put heavy pressure on the fledgling nations at times of international war.

The State of Buenos Aires was a secessionist republic resulting from the overthrow of the Argentine Confederation government in the Province of Buenos Aires on 11 September 1852. The State of Buenos Aires was never explicitly recognized by the Confederation; it remained, however, independent under its own government and constitution. Buenos Aires rejoined the Argentine Confederation after the former's victory at the Battle of Pavón in 1861.

There are various allegorical representations of Argentina or associated in any way with Argentina. There is not, however, a national personification with its own name, like Marianne from France, or Hispania from Spain, but sculptures and engravings representing liberty, republic, motherland or other concepts that have been used officially by the Argentine state.
Events from the year 1942 in Argentina
The content below lists down the events in the year 1884 in Argentina.

José Santiago Albarracín 1 was an Argentine soldier who fought on the Unitarian side in many engagements in the Argentine Civil Wars, especially in the struggles against Chacho Peñaloza.

Wenceslao Paunero was a 19th-century Argentine General, politician and diplomat of Uruguayan origin. He was born within the Banda Oriental and would go on to be a major member of the Unitarian Party. He was also the Minister of War and Navy of Argentina and the provisional Governor of Córdoba.