
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Its land area is 71,740 km2 (27,699 sq mi). It has a tropical climate and environments ranging from savannas to rainforests. As of the 2023 census, Sierra Leone has a population of 8,908,040. Freetown is both its capital and its largest city. The country is divided into five administrative regions, which are further subdivided into 16 districts.
Sierra Leone first became inhabited by indigenous African peoples at least 2,500 years ago. The Limba were the first tribe known to inhabit Sierra Leone. The dense tropical rainforest partially isolated the region from other West African cultures, and it became a refuge for peoples escaping violence and jihads. Sierra Leone was named by Portuguese explorer Pedro de Sintra, who mapped the region in 1462. The Freetown estuary provided a good natural harbour for ships to shelter and replenish drinking water, and gained more international attention as coastal and trans-Atlantic trade supplanted trans-Saharan trade.

Sir Milton Augustus Strieby Margai was a Sierra Leonean physician and politician who served as the country's head of government from 1954 until his death in 1964. He was titled chief minister from 1954 to 1960, and then prime minister from 1961 onwards. Margai studied medicine in England, and upon returning to his homeland became a prominent public health campaigner. He entered politics as the founder and inaugural leader of the Sierra Leone People's Party. Margai oversaw Sierra Leone's transition to independence, which occurred in 1961. He died in office aged 68, and was succeeded as prime minister by his brother Albert. Margai enjoyed the support of Sierra Leoneans across classes, who respected his moderate style, friendly demeanor, and political savvy.

The Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, along with its main political rival the All People's Congress (APC). It has been the ruling party in Sierra Leone since 4 April 2018. The SLPP dominated Sierra Leone's politics from its foundation in 1951 to 1967, when it lost the 1967 parliamentary election to the APC, led by Siaka Stevens. Originally a centre-right, conservative party, it identifies since 2012 as a centre-left social democratic party, with a centrist tendency.

Siaka Probyn Stevens was the leader of Sierra Leone from 1967 to 1985, serving as Prime Minister from 1967 to 1971 and as President from 1971 to 1985. Stevens' leadership was often characterized by patrimonial rule and self-indulgence, consolidating power by means of corruption and exploitation.

The All People's Congress (APC) is one of the two major political parties in Sierra Leone, the other being its main political rival the Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP). The APC has been the main opposition party in Sierra Leone since 4 April 2018 when Julius Maada Bio of the SLPP won the 2018 presidential elections, though it maintains a majority in parliament.

Julius Maada Wonie Bio is a Sierra Leonean politician who has served as president of Sierra Leone since 4 April 2018. He is a retired brigadier in the Sierra Leone Army and was the military head of state of Sierra Leone from 16 January 1996 to 29 March 1996, in a military junta government known as the National Provisional Ruling Council (NPRC). Bio is the first democratically elected president of Sierra Leone born after Sierra Leone's independence from British colonial rule.
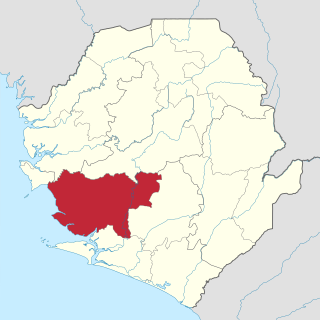
Moyamba District is a district in the Southern Province of Sierra Leone, with a population of 318,064 in the 2015 census. Its capital and largest city is Moyamba. The other major towns include Njala, Rotifunk and Shenge. The district is the largest in the Southern Province by geographical area, occupying a total area of 6,902 km2 (2,665 sq mi) and comprises fourteen chiefdoms.

Brigadier David Lansana was the first prominent Sierra Leonean in the Sierra Leone Military during the colonial era. After Sierra Leone gained independence, he served as Military Attaché to the United States.
Sir Albert Michael Margai was the second prime minister of Sierra Leone and the half-brother of Sir Milton Margai, the country's first Prime Minister. He was also the father of Sierra Leonean politician Charles Margai.

Charles Francis Kondo Margai is a Sierra Leonean politician and constitutional lawyer who served as Attorney General and Minister of Justice of Sierra Leone in 2018.
Brigadier John Amadu Bangura, CBE was a Sierra Leonean who served as Chief of the Defence Staff of the Sierra Leone Armed Forces from 1968 to 1971. Prior to this in 1967, he served as the Sierra Leonean Ambassador of to the United States.

Ernest Bai Koroma is a Sierra Leonean politician who served as the fourth President of Sierra Leone from 17 September 2007 to 4 April 2018.

Paramount Chief Ella Koblo Gulama OBE, GCOR was a Sierra Leonean paramount chief and politician. In 1957, she became the first elected female Member of Parliament in Sierra Leone. She was re-elected in 1962. During the government of Milton Margai, Gulama became Sierra Leone and sub-Saharan Africa's first female Cabinet Minister.

Komeh Gulama Lansana was the wife of Brigadier David Lansana, Force Commander of the Sierra Leone Army until his execution in 1975.
The National Reformation Council, or NRC, was a group of senior military officers with Brigadier Andrew Juxon-Smith as its chairman, who seized control of the Sierra Leone government on March 23, 1967. They suspended the constitution, arresting Brigadier David Lansana, Commander of the Armed Forces.

The Dominion of Sierra Leone was an independent sovereign state with Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state between independence on 27 April 1961 and becoming the Republic of Sierra Leone on 19 April 1971.

The Constitution of Sierra Leone is the supreme law governing Sierra Leone and delineates its frame of government. It entered into force on October 1, 1991, following a popular referendum and approval by President Joseph Momoh. It superseded the 1978 Constitution.
The Sergeants' Coup was a military coup d'état in Sierra Leone that occurred on 18 April 1968 against Chairman of the National Reformation Council (NRC) and acting Governor-General of Sierra Leone Brigadier Andrew Juxon-Smith, who declared himself the interim leader the year prior. The coup was led by Brigadier John Amadu Bangura who briefly ruled as head of state before handing power over to Siaka Stevens, who had won the 1967 general election. Despite Bangura's desire to restore democracy by upholding the results of the election, the coup opened the way for the autocratic rule of Stevens, including the 23-year-long period from 1978-1991 where the All People's Congress was the only legal party in Sierra Leone following the 1978 Sierra Leonean constitutional referendum, a sham election where 97% of the population voted in favor of one-party rule. Despite returning Stevens to power, Bangura was later executed for treason.

The 1967 Sierra Leonean coups d'état were two successive coups in Sierra Leone that took place from March 21 to 23, 1967.













