 |
|---|
|
The 1980 Lombard regional election took place on 8 June 1980. The 3rd term of the Regional Council was chosen.
Contents

 |
|---|
|
The 1980 Lombard regional election took place on 8 June 1980. The 3rd term of the Regional Council was chosen.

Election was held under proportional representation with provincial constituencies where the largest remainder method with a Droop quota was used. To ensure more proportionality, remained votes and seats were transferred at regional level and calculated at-large.
The Christian Democracy party was by far the largest. After the election the incumbent president Giuseppe Guzzetti was re-elected at the head of a center-left coalition comprising also the PSI, the PSDI and the PRI.
 | |||||
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/- | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Christian Democracy | 2,240,861 | 38.86 | 34 | ||
| Italian Communist Party | 1,623,352 | 28.15 | 23 | ||
| Italian Socialist Party | 834,111 | 14.46 | 11 | = | |
| Italian Democratic Socialist Party | 260,611 | 4.52 | 3 | = | |
| Italian Social Movement | 251,745 | 4.37 | 3 | = | |
| Italian Liberal Party | 197,301 | 3.42 | 2 | = | |
| Italian Republican Party | 152,605 | 2.65 | 2 | = | |
| Proletarian Democracy | 96,882 | 1.68 | 1 | ||
| Proletarian Unity Party | 86,631 | 1.50 | 1 | ||
| Association for Trieste | 10,001 | 0.17 | 0 | ||
| Milanese List | 3,825 | 0.07 | 0 | ||
| Social Action Christian Party | 2,738 | 0.05 | 0 | ||
| Revolutionary Communist League | 2,590 | 0.04 | 0 | ||
| European Workers' Party | 2,529 | 0.04 | 0 | ||
| Revolutionary Socialist League | 1,086 | 0.02 | 0 | ||
| Total valid votes | 5,766,868 | 80 | |||
| Blank votes | 233,742 | ||||
| Invalid votes (blank included) | 380,286 | ||||
| Total | 6,147,154 | ||||
| Registered voters & turnout | 6,647,073 | 92.48 | |||
Source: Ministry of the Interior
| Province | DC | PCI | PSI | PSDI | MSI | PLI | PRI | DP | PdUP | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milan | 12 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 39 |
| Brescia | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 10 |
| Bergamo | 5 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8 |
| Como | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| Varese | 3 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| Pavia | 2 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5 |
| Cremona | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| Mantua | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| Sondrio | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Total | 34 | 23 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 80 |

The additional-member system (AMS) is a mixed electoral system under which most representatives are elected in single-member districts (SMDs), and the other "additional members" are elected to make the seat distribution in the chamber more proportional to the way votes are cast for party lists. It is distinct from parallel voting in that the "additional member" seats are awarded to parties taking into account seats won in SMDs, which is not done under parallel voting.
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is an apportionment method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in proportional representation among political parties. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods.

Elections in Mauritania encompass four different types: presidential elections, parliamentary elections, regional elections and local elections.

Elections in Spain encompass four different types: general elections, regional elections, local elections, and elections to the European Parliament. General elections and regional elections are typically conducted at the conclusion of the national or regional legislative mandate, which usually spans four years since the previous election. However, early elections can be called in certain circumstances. On the other hand, local council elections and elections to the European Parliament follow fixed dates, although some local government bodies, such as provincial councils, are not directly elected. In most elections, a party-list proportional representation (PR) system is employed, while the Senate utilizes the plurality system.

Bulgaria elects on the national level a head of state—the president—and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term directly by the people. The National Assembly has 240 members elected for a four-year term by proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies with a 4% threshold. Bulgaria has a multi-party system in which often no one party has a chance of gaining power alone and parties must work with each to form governments.

The Sardinian regional election of 2004 took place on 12–13 June 2004.

The 2005 Lombard regional election took place on 3–4 April 2005. The 8th term of the Regional Council was chosen. Roberto Formigoni was re-elected for the third time in a row President, defeating Riccardo Sarfatti.

The 2000 Lombard regional election took place on 16 April 2000. The 7th term of the Regional Council was chosen.

The 1990 Lombard regional election took place on 6 and 7 May 1990. The 5th term of the Regional Council was chosen.

The 1985 Lombard regional election took place on 12 May 1985. The 4th term of the Regional Council was chosen.

The 1975 Lombard regional election took place on 15 June 1975. The 2nd term of the Regional Council was chosen.

The 1970 Lombard regional election took place on 7–8 June 1970. It was the first-ever regional election.

The Sardinian regional election of 1994 took place on 12 and 26 June 1994.
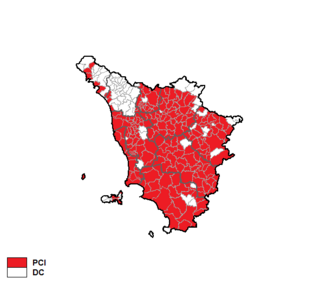
The Tuscan regional election of 1970 took place on 7–8 June 1970. It was the first-ever regional election.
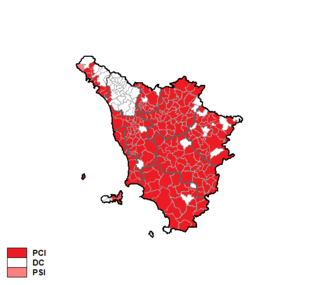
The Tuscan regional election of 1975 took place on 15 June 1975.
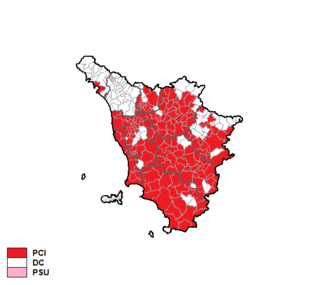
The Tuscan regional election of 1980 took place on 8 June 1980.
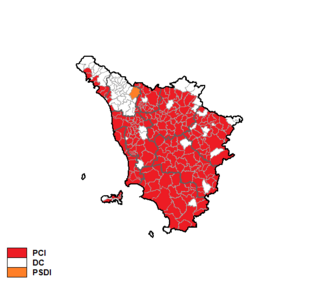
Tuscan regional election of 1985 took place on 12 May 1985.

The Sardinian regional election of 2009 took place on 15–16 February 2009.

The Italian regional elections of 1980 were held on 8 and 9 June. The fifteen ordinary regions, created in 1970, elected their third assemblies.

The Italian regional elections of 1990 were held on 6 and 7 May. The fifteen ordinary regions, created in 1970, elected their fifth assemblies.