Plurality voting refers to electoral systems in which the candidate in an electoral district who poll more than any other are elected.

First-past-the-post voting is a plurality voting system wherein voters cast a vote for a single candidate, and the candidate with the most votes wins the election. Analogous systems for multi-winner contests are known as plurality block voting or "block voting" systems; both FPTP and block voting are "plurality" systems in that the winner needs only a plurality of the votes and not an absolute majority.
Parallel voting is a type of mixed electoral system in which representatives are voted into a single chamber using two or more different systems, most often first-past-the-post voting (FPTP) with party-list proportional representation (PR). It is the most common form of mixed member majoritarian representation (MMM), which is why these terms are often used synonymously with each other. In some countries, parallel voting is known as the supplementary member (SM) system, while in academic literature it is sometimes called the superposition method within mixed systems.

The Chamber of Deputies is the lower house of the bicameral Italian Parliament, the upper house being the Senate of the Republic. The two houses together form a perfect bicameral system, meaning they perform identical functions, but do so separately. The Chamber of Deputies has 400 seats, of which 392 will be elected from Italian constituencies, and 8 from Italian citizens living abroad. Deputies are styled The Honourable and meet at Palazzo Montecitorio.

The 1987 Italian general election was held in Italy on 14–15 June 1987. This election was the first Italian election in which the distance between the Christian Democrats and the Communists grew significantly instead of decreasing. Two parties that had not previously been in parliament won representation: the Greens with thirteen seats, and the Northern League with two.
A winner-take-all electoral system is one where a voting bloc can win all seats in a legislature or electoral district, denying representation to any political minorities. This system is adopted by many major democracies, including the United Kingdom, as it tends to produce a clear majority in legislatures. When applied using multiple electoral districts to elect an assembly, winner-take-all system provide non-proportional results that often allow for electoral inversions, and they do not require candidates to win an (absolute) majority of the vote to be elected. A less-common but more accurate term is majorizing or majorized representation.

Lombardy elected its first delegation to the Italian Senate on April 18, 1948. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1948 even if, according to the newly established Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its second delegation to the Italian Senate on June 7, 1953. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1953 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its third delegation to the Italian Senate on May 25, 1958. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1958 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its forth delegation to the Italian Senate on April 28, 1963. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1963 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.
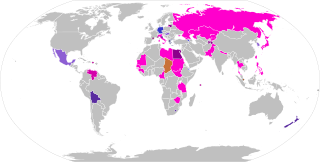
A mixed electoral system or mixed-member electoral system combines methods of majoritarian and proportional representation (PR). The majoritarian component is usually first-past-the-post voting (FPTP/SMP), whereas the proportional component is most often based on party-list PR. The results of the combination may be mixed-member proportional (MMP), where the overall results of the elections are proportional, or mixed-member majoritarian, in which case the overall results are semi-proportional, retaining disproportionalities from the majoritarian component.

Lombardy elected its fifth delegation to the Italian Senate on May 19, 1968. This election was a part of the national Italian general election of 1968 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its sixth delegation to the Italian Senate on May 19, 1972. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1972 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its seventh delegation to the Italian Senate on June 20, 1976. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1976 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its eighth delegation to the Italian Senate on June 3, 1979. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1979 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its tenth delegation to the Italian Senate on June 14, 1987. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1987 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy elected its eleventh delegation to the Italian Senate on April 5, 1992. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1992 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.

Lombardy renewed its delegation to the Italian Senate on March 27, 1994. This election was a part of national Italian general election of 1994 even if, according to the Italian Constitution, every senatorial challenge in each Region is a single and independent race.
Mixed member majoritarian representation (MMM) is type of a mixed electoral system combining majoritarian and proportional methods, where the disproportional results of district contests using a plurality voting system or other, usually first-past-the-post voting, are completely separate from the proportional component. Mixed member majoritarian systems are therefore described as semi-proportional representation, and are usually contrasted with mixed-member proportional representation (MMP) which aims to provide proportional representation via additional compensation ("top-up") seats.
The next Italian general election will occur no later than 22 December 2027, although it may be called earlier as a snap election.















