Related Research Articles

The Surf Line is a railroad line that runs from San Diego to Orange County along California's Pacific Coast. It was so named because much of the line is near the Pacific Ocean, within less than 100 feet (30 m) in some places. It is the second busiest passenger rail corridor in the United States after the Northeast Corridor.

The Denver Trolley, formerly known as the Platte Valley Trolley, is a heritage streetcar line in Denver, Colorado, operated by the Denver Tramway Heritage Society. It began service on July 1, 1989.

Chatsworth station is an intermodal passenger transport station in the Los Angeles neighborhood of Chatsworth, United States. It is served by Amtrak Pacific Surfliner inter-city rail service, Metrolink Ventura County Line commuter rail service, and the Metro G Line of the Los Angeles Metro Busway bus rapid transit. The station is also served by Los Angeles Metro Bus and Simi Valley Transit local buses, plus Santa Clarita Transit and LADOT Commuter Express regional express bus routes.

Van Nuys station is an Amtrak and Metrolink train station in the Van Nuys neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, close to the nighborhood of Panorama City. Amtrak's Pacific Surfliner from San Luis Obispo to San Diego, Amtrak's Coast Starlight from Los Angeles to Seattle, Washington, and Metrolink's Ventura County Line from Los Angeles Union Station to East Ventura stop here.

Claremont station is a passenger rail and bus station in Claremont, California, United States. It is served by Metrolink's San Bernardino Line which runs from Los Angeles Union Station to San Bernardino–Downtown. The Mission Revival-Spanish Colonial Revival style station is listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places as Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad Station.

The Fullerton Transportation Center is a passenger rail and bus station located in Fullerton, California, United States.

The San Bernardino Santa Fe Depot is a Mission Revival Style passenger rail terminal in San Bernardino, California, United States. It has been the primary station for the city, serving Amtrak today, and the Santa Fe and Union Pacific Railroads in the past. Until the mid-20th century, the Southern Pacific Railroad had a station 3/4 of a mile away. It currently serves one Amtrak and two Metrolink lines. The depot is a historical landmark listed on the National Register of Historic Places as Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway Passenger and Freight Depot.
Eesti Raudtee or EVR is the national railway infrastructure company of Estonia. It owns a network of 1,191 kilometres (740 mi) of broad gauge railway throughout the country, including the 192 kilometres (119 mi) used by the Elron commuter trains around Tallinn. Its sole shareholder is the Government of Estonia.

San Juan Capistrano station is a train station in San Juan Capistrano, California, United States served by Amtrak, the national railroad passenger system, and Metrolink, a commuter railroad. The station has a single side platform serving the single track of the SCRRA's Orange Subdivision.

Established in 1982, the California Trolley and Railroad Corporation (CTRC) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization to preserve rail transportation in the Santa Clara Valley.

Pomona–North station is a railroad station located in Pomona, California. It is located just west of Garey Avenue and south of Bonita Avenue, and has 225 free parking spaces which are accessible from either Santa Fe Street or Fulton Road. Formerly an intercity train station, it is served by the Metrolink commuter rail system. The extension of the Los Angeles Metro Rail A Line light rail line to Pomona-North is projected to open in 2025.
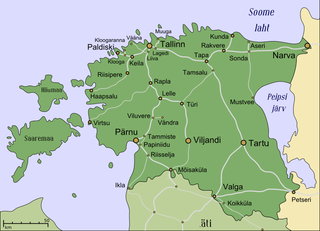
The history of rail transport in Estonia starts in 1870 when a railway line was opened connecting Paldiski, Tallinn, Tapa and Narva; the line extending all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia.

The Philadelphia Belt Line Railroad owns a 2.66-mile (4.28 km) long railroad line running along the Delaware River waterfront in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was created in 1889 to allow any Philadelphia railroad to access the waterfront. The railroad, which does not operate any trains itself, is currently maintained by Conrail Shared Assets Operations and used by CSX Transportation and Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Altrincham Line is a tram line of the Manchester Metrolink running from Manchester to Altrincham in Greater Manchester. Originally a railway line, it was, along with the Bury Line, converted into a tramway during 1991–92, as part of the first phase of the Metrolink system.
References
- ↑ "Ajalugu" (in Estonian). Eesti Raudtee. Archived from the original on 2017-09-23. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
- ↑ "Significant dates in Canadian railway history". Colin Churcher's Railway Pages. 17 March 2006. Archived from the original on 24 April 2006. Retrieved 3 April 2006.
- ↑ Light Rail and Modern Tramway (ISSN 0964-9255), July 1992 and August 1992 issues. Ian Allan Publishing (UK).
- ↑ Light Rail and Modern Tramway (ISSN 0964-9255), September 1992 issue, p. 249. Ian Allan Publishing (UK).
- ↑ Stauss, Ed. "Baltimore's Zig Zag Zig Trolley". Rail Classics (ISSN 0743-9075), September/October 1992 issue, pp. 14–21. Challenge Publications.
- ↑ Satchell, Veront M.; Sampson, Cezley (March 2003). "The rise and fall of railways in Jamaica, 1845–1975". Journal of Transport History. 24 (1): 18.
- ↑ Acott, Kent (18 December 2017). "Joondalup and Mandurah train lines celebrate significant anniversaries". The West Australian. Retrieved 10 July 2023.
- ↑ Johnston, Bob (February 1997). "Amtrak RoadRailers get rolling". Trains . 57 (2): 26–27.
- ↑ "No men allowed". Trains: 46. January 2008.
- ↑ "Historic SEPTA trolleys being replaced by buses for at least a year". www.phillyvoice.com. Retrieved 25 January 2021.