
The Intergiro is a competition in the annual multiple stage bicycle race the Giro d'Italia. It was first introduced in 1989 and discontinued in 2005 as a stand alone Jersey. It was reintroduced in 2024 as number colour. In its initial inception, the calculation for the intergiro was similar to that of the general classification, in each stage there is a midway point that the riders passed through a point and where their times were stopped. As the race went, their times were compiled and the person with the lowest time was the leader of the intergiro classification and wore a blue jersey until 2005. When the competition was revived in 2024, it was changed to points-based scoring, with competitors accumulating points at the designated midway point. The rider with the most points is the leader of the Intergiro classification.

Evgeni Valentinovich Berzin is a Russian former road cyclist.

The 1988 Giro d'Italia was the 71st running of the Giro d'Italia, one of cycling's Grand Tour races. The race started in Urbino, on 23 May, with a 9 km (5.6 mi) individual time trial and concluded in Vittorio Veneto, on 12 June, with a 43 km (26.7 mi) individual time trial. A total of 180 riders from 20 teams entered the 21-stage race, which was won by American Andrew Hampsten of the 7-Eleven–Hoonved team. The second and third places were taken by Dutchman Erik Breukink and Swiss Urs Zimmermann, respectively. It was the third time – and second successive year – in the history of the Giro that the podium was occupied solely by non-Italian riders.
The 1984 Giro d'Italia was the 67th running of the Giro. It started in Lucca, on 17 May, with a 5 km (3.1 mi) prologue and concluded in Verona, on 10 June, with a 42 km (26.1 mi) individual time trial. A total of 171 riders from nineteen teams entered the 22-stage race, that was won by Italian Francesco Moser of the Gis Gelati–Tuc Lu team. The second and third places were taken by Frenchman Laurent Fignon and Italian Moreno Argentin, respectively.
The 1985 Giro d'Italia was the 68th running of the Giro. It started in Palermo, on 16 May, with a 6.6 km (4.1 mi) prologue and concluded in Lucca, on 9 June, with a 48 km (29.8 mi) individual time trial. A total of 180 riders from twenty teams entered the 22-stage race, that was won by Frenchman Bernard Hinault of the La Vie Claire team. The second and third places were taken by Italian Francesco Moser and American Greg LeMond, respectively.
The 1981 Giro d'Italia was the 64th running of the Giro. It started in Brescia, on 13 May, with a 6.6 km (4.1 mi) prologue and concluded in Verona, on 7 June, with a 42 km (26.1 mi) individual time trial. A total of 130 riders from thirteen teams entered the 22-stage race, that was won by Italian Giovanni Battaglin of the Inoxpran team. The second and third places were taken by Swede Tommy Prim and Italian Giuseppe Saronni, respectively.
The 1991 Giro d'Italia was the 74th edition of the race. It began on May 26 with a mass-start stage that began and ended in the Italian city of Olbia. The race came to a close in Milan on June 16. Twenty teams entered the race, which was won by the Italian Franco Chioccioli of the Del Tongo-MG Boys Maglificio team. Second and third respectively were the Italians Claudio Chiappucci and Massimiliano Lelli.
The 1990 Giro d'Italia was the 73rd edition of the race. It started off in Bari on May 18 with a 13 km (8.1 mi) individual time trial. The race came to a close with a mass-start stage that began and ended in Milan on June 6. Twenty-two teams entered the race, which was won by the Italian Gianni Bugno of the Château d'Ax–Salotti team. Second and third respectively were the Frenchman Charly Mottet and the Italian rider, Marco Giovannetti. Bugno wore the pink jersey as leader in the general classification from the first to the last stage.
The 1983 Giro d'Italia was the 66th running of the Giro. It started in Brescia, on 12 May, with an 8 km (5.0 mi) prologue and concluded in Udine, on 5 June, with a 40 km (24.9 mi) individual time trial. A total of 162 riders from eighteen teams entered the 22-stage race, that was won by Italian Giuseppe Saronni of the Del Tongo-Colnago team. The second and third places were taken by Italian Roberto Visentini and Spaniard Alberto Fernández, respectively.
The 1986 Giro d'Italia was the 69th running of the Giro d'Italia. The cycling race started in Palermo, on 12 May, with a 1 km (0.6 mi) prologue and concluded in Merano, on 2 June, with a 108.6 km (67.5 mi) mass-start stage. A total of 171 riders from nineteen teams entered the 22-stage race, that was won by Italian Roberto Visentini of the Carrera Jeans–Vagabond team. The second and third places were taken by Italian riders Giuseppe Saronni and Francesco Moser, respectively.
The 1979 Giro d'Italia was the 62nd running of the Giro, one of cycling's Grand Tours. It started in Florence, on 17 May, with an 8 km (5.0 mi) prologue and concluded in Milan, on 6 June, with a 44 km (27.3 mi) individual time trial. A total of 130 riders from thirteen teams entered the 19-stage race, that was won by Italian Giuseppe Saronni of the Scic-Bottecchia team. The second and third places were taken by Italian Francesco Moser and Swede Bernt Johansson, respectively.

The 1987 Giro d'Italia was the 70th edition of the bicycle race. It began on 21 May with a 4 km (2.5 mi) prologue in San Remo, and concluded on 13 June with a 32 km (19.9 mi) individual time trial in Saint-Vincent. A total of 180 riders from 20 teams entered the 22-stage, 3,915 km (2,433 mi)-long race, which was won by Irishman Stephen Roche of the Carrera Jeans–Vagabond team. Second and third places were taken by British rider Robert Millar and Dutchman Erik Breukink, respectively. It was the second time in the history of the Giro that the podium was occupied solely by non-Italian riders. Roche's victory in the 1987 Giro was his first step in completing the Triple Crown of Cycling – winning the Giro d'Italia, the Tour de France, and the World Championship road race in one calendar year – becoming the second rider ever to do so.
The 1992 Giro d'Italia was the 75th edition of the race. It started off in Genoa on 24 May with an 8 km (5.0 mi) individual time trial. The race concluded in Milan with an 66 km (41.0 mi) individual time trial on 14 June. Twenty teams entered the race, which was won by the Spaniard Miguel Induráin of the Banesto team. Second and third respectively were the Italians Claudio Chiappucci and Franco Chioccioli. Indurain's victory in the 1992 Giro was his first step in completing the Giro – Tour double – winning the Giro d'Italia and Tour de France in one calendar year – becoming the sixth rider to accomplish this feat, with the first being Fausto Coppi in 1949.
The 1993 Giro d'Italia,, was the 76th edition of the race. It started off in Porto Azzurro on 23 May with a split stage, with the first leg being a mass-start stage and the latter an individual time trial. The race ended on 13 June with a stage that stretched 166 km (103.1 mi) from Biella to Milan. Twenty teams entered the race, which was won by Miguel Induráin of the Banesto team. Second and third respectively were the Latvian Piotr Ugrumov and the Italian rider, Claudio Chiappucci. Indurain's victory in the 1993 Giro was his first step in completing the Giro – Tour double – winning the Giro d'Italia and Tour de France in one calendar year – becoming the first rider to repeat this feat in consecutive years.
The 1995 Giro d'Italia took place in May and June 1995. It was the 78th edition of the event. The Giro began on 13 May with a stage that began in Perugia and ended Terni. The race came to a close on 4 June with a stage that ended in the Italian city of Milan. The race was won by the Swiss Tony Rominger of the Mapei–GB–Latexco team. Second and third were the Russian rider Evgeni Berzin and Latvian rider Piotr Ugrumov.
The 1996 Giro d'Italia was the 79th edition of the Giro. It began on May 18 with a mass-start stage that began and ended in the Greek capital Athens. The race came to a close on June 9 with a mass-start stage that ended in the Italian city of Milan. Eighteen teams entered the race that was won by the Russian Pavel Tonkov of the Panaria–Vinavil team. Second and third were the Italian rider Enrico Zaina and Spanish rider Abraham Olano.
The 1997 Giro d'Italia was the 80th edition of the Giro. It began on 17 May with a mass-start stage that began and ended in Venice. The race came to a close on 8 June with a mass-start stage that ended in the Italian city of Milan. Eighteen teams entered the race that was won by the Italian Ivan Gotti of the Saeco–Estro team. Second and third were the Russian rider Pavel Tonkov and Italian Giuseppe Guerini.
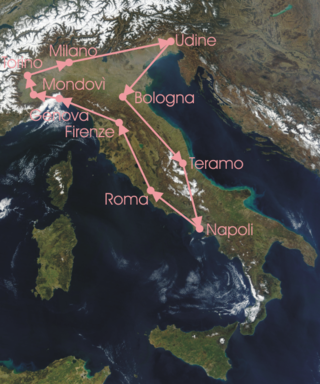
The 1910 Giro d'Italia was the second edition of the Giro d'Italia, a Grand Tour organized and sponsored by the newspaper La Gazzetta dello Sport. The race began on 18 May in Milan with a stage that stretched 388 km (241 mi) to Udine, finishing back in Milan on 5 June after a 277.5 km (172 mi) stage and a total distance covered of 2,987.4 km (1,856 mi). The race was won by the Italian rider Carlo Galetti of the Atala-Continental team, with fellow Italians Eberardo Pavesi and Luigi Ganna coming in second and third respectively.

The 1911 Giro d'Italia was the third edition of the Giro d'Italia, a Grand Tour set up and sponsored by the newspaper La Gazzetta dello Sport. The race began on 18 May in Rome with a stage that stretched 394.1 km (245 mi) to Florence. It was composed of twelve stages that covered a total distance of 3,530.3 km (2,194 mi). The race came to a close back in Rome on 6 June after a 266.9 km (166 mi) stage. The race was won by the Italian rider Carlo Galetti of the Bianchi team. Second and third respectively were the Italian riders Giovanni Rossignoli and Giovanni Gerbi.
The Giro d'Italia is an annual stage race bicycle race primarily held in Italy, while also occasionally passing through nearby countries. The race was first organized in 1909 to increase sales of the newspaper La Gazzetta dello Sport; however it is currently run by RCS Sport. The race has been held annually since its first edition in 1909, except when it was stopped for the two world wars. As the Giro gained prominence and popularity the race was lengthened, and the peloton expanded from primarily Italian participation to riders from all over the world.









