
Politics of Madagascar takes place in a framework of a semi-presidential representative democratic republic, with a pluralist multi-party system. The President of Madagascar is head of state and the Prime Minister of Madagascar is head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the bicameral parliament, which is composed of the Senate and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.
Constitutional conventions in Australia are significant meetings that have debated the Australian Constitution. The first two gatherings debated Federation and what form of Constitution to adopt, while the following conventions debated amendments to the document.

Madagascar was once divided into six autonomous provinces :
- Antananarivo Province
- Antsiranana Province
- Fianarantsoa Province
- Mahajanga Province
- Toamasina Province
- Toliara Province

Mahajanga was a former province of Madagascar that had an area of 150,023 km2. It had a population of 1,896,000 (2004). Its capital was Mahajanga, the second largest city in Madagascar.

Albert Zafy was a Malagasy politician and educator who served as the fourth President of Madagascar from 1993 to 1996. In 1988, he founded the National Union for Democracy and Development (UNDD).

The Australian republic referendum held on 6 November 1999 was a two-question referendum to amend the Constitution of Australia. The first question asked whether Australia should become a republic, under a bi-partisan appointment model where the president would be appointed by the federal parliament with a two-thirds majority. This was the model that was endorsed by the Constitutional Convention, held in Canberra in February 1998. The second question, generally deemed to be far less important politically, asked whether Australia should alter the Constitution to insert a preamble.
This electoral calendar 2007 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2007 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. Referendums are included, although they are not elections. By-elections are not included.

Herizo Jossicher Razafimahaleo was a politician in Madagascar. He ran for President three times, and he served as Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister from 1997 to 1998.

A constitutional referendum was held in Madagascar on 4 April 2007. The proposed changes, which voters were asked to approve or reject as a whole, included:
The Judged By Your Work Party is a centrist political party in Madagascar.

The current Constitution of Madagascar was, according to the national electoral commission, endorsed by a majority of voters in the constitutional referendum held on 14 November 2010. The new constitution launched the Fourth Republic of Madagascar and was widely seen as an attempt to consolidate and legitimise the rule of Andry Rajoelina and his High Transitional Authority government which was installed after a military-backed coup d'état against President Marc Ravalomanana at the beginning of the ongoing national political crisis. One substantive change from the constitution of the Third Republic was to lower the minimum age for presidential candidates from 40 to 35. This made Rajoelina, aged 36 at the time, eligible to stand in presidential elections.
This national electoral calendar for 2010 lists the national/federal elections held in 2010 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

A constitutional referendum was held in Madagascar on 17 November 2010, in which voters approved a proposal for the state's fourth Constitution. The Malagasy people were asked to answer "Yes" or "No" to the proposed new constitution, which was considered to help consolidate Andry Rajoelina's grip on power. At the time of the referendum, Rajoelina headed the governing Highest Transitional Authority (HAT), an interim junta established following the military-backed coup d'état against then President Marc Ravalomanana in March 2009.

Presidential elections were held in Madagascar on 30 January 1972. Incumbent President Philibert Tsiranana of the Social Democratic Party was the only candidate, and won the approval of 99.7% of voters. However, public unrest led to him handing over power to General Gabriel Ramanantsoa. Ramanantsoa put forward proposals for a five-year transition period during which the National Assembly would be suspended. The plans were approved in a referendum later in the year.

A referendum on military rule was held in Madagascar on 8 October 1972. It followed General Gabriel Ramanantsoa taking power from elected President Philibert Tsiranana in May, and Ramanantsoa's proposals for a five-year transition period during which the National Assembly would be suspended. The plans were approved by 94.43% of voters, with an 84% voter turnout.

A constitutional referendum was held in Madagascar on 21 December 1975. The new constitution created a presidential republic, with the president serving seven-year terms and incumbent President Didier Ratsiraka was to serve the first term without being elected. It also created a High Revolutionary Council to create a "socialist revolution" and a military committee to oversee socio-economic development. Madagascar was transformed into the Democratic Republic of Madagascar. All political parties with the exception of those "loyal to the socialist revolution" were to be banned, and those that were allowed to exist would have to be affiliated with the National Front for the Defense of the Revolution, which was led by Ratsiraka's AREMA party.

A constitutional referendum was held in Madagascar on 19 August 1992. The new constitution created a semi-presidential system and a Senate. It was approved by 73% of voters, with a 65% turnout.

A constitutional referendum was held in Madagascar on 17 September 1995. The proposed amendment would allow the President to appoint and sack the Prime Minister rather than the National Assembly. It was approved by 64% of voters, with a 65% turnout.
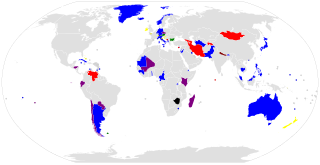
This national electoral calendar for 2013 lists the national/federal elections held in 2013 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
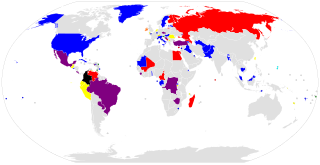
This national electoral calendar for 2018 lists the national/federal elections held in 2018 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.







