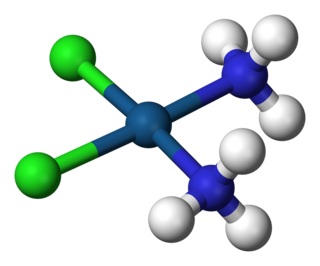
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals, are coordination complexes.

Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands".

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.

1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (Ph2PCH2)2 (Ph = phenyl). It is a commonly used bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Tellurium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula TeCl4. The compound is volatile, subliming at 200 °C at 0.1 mmHg. Molten TeCl4 is ionic, dissociating into TeCl3+ and Te2Cl102−.

In coordination chemistry, hapticity is the coordination of a ligand to a metal center via an uninterrupted and contiguous series of atoms. The hapticity of a ligand is described with the Greek letter η ('eta'). For example, η2 describes a ligand that coordinates through 2 contiguous atoms. In general the η-notation only applies when multiple atoms are coordinated. In addition, if the ligand coordinates through multiple atoms that are not contiguous then this is considered denticity, and the κ-notation is used once again. When naming complexes care should be taken not to confuse η with μ ('mu'), which relates to bridging ligands.

1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene, commonly abbreviated dppf, is an organophosphorus compound commonly used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is related to other bridged diphosphines such as 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe).

Diphenylphosphine, also known as diphenylphosphane, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PH. This foul-smelling, colorless liquid is easily oxidized in air. It is a precursor to organophosphorus ligands for use as catalysts.

1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane (dppm), is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH2(PPh2)2. Dppm, a white, crystalline powder, is used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry as a ligand. It is more specifically a chelating ligand because it is a ligand that can bond to metals with two phosphorus donor atoms. The natural bite angle is 73°.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. While iron adopts oxidation states from Fe(−II) through to Fe(VII), Fe(IV) is the highest established oxidation state for organoiron species. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Organoruthenium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to ruthenium chemical bond. Several organoruthenium catalysts are of commercial interest and organoruthenium compounds have been considered for cancer therapy. The chemistry has some stoichiometric similarities with organoiron chemistry, as iron is directly above ruthenium in group 8 of the periodic table. The most important reagents for the introduction of ruthenium are ruthenium(III) chloride and triruthenium dodecacarbonyl.

A metal-phosphine complex is a coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).
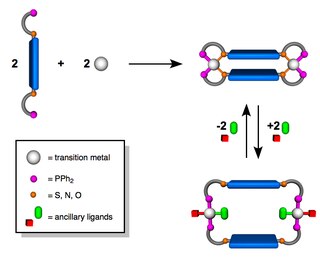
The Weak-Link Approach (WLA) is a supramolecular coordination-based assembly methodology, first introduced in 1998 by the Mirkin Group at Northwestern University. This method takes advantage of hemilabile ligands -ligands that contain both strong and weak binding moieties- that can coordinate to metal centers and quantitatively assemble into a single condensed ‘closed’ structure. Unlike other supramolecular assembly methods, the WLA allows for the synthesis of supramolecular complexes that can be modulated from rigid ‘closed’ structures to flexible ‘open’ structures through reversible binding of allosteric effectors at the structural metal centers. The approach is general and has been applied to a variety of metal centers and ligand designs including those with utility in catalysis and allosteric regulation.
In coordination chemistry and catalysis hemilability refers to a property of many polydentate ligands which contain at least two electronically different coordinating groups, such as hard and soft donors. These hybrid or heteroditopic ligands form complexes where one coordinating group is easily displaced from the metal centre while the other group remains firmly bound; a behaviour which has been found to increase the reactivity of catalysts when compared to the use of more traditional ligands.

trans-Bis(dinitrogen)bis[1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane]molybdenum(0) is a coordination complex with the formula Mo(N2)2(dppe)2. It is a relatively air stable yellow-orange solid. It is notable as being the first discovered dinitrogen containing complex of molybdenum.

Chlorobis(dppe)iron hydride is a coordination complex with the formula HFeCl(dppe)2, where dppe is the bidentate ligand 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane. It is a red-violet solid. The compound has attracted much attention as a precursor to dihydrogen complexes.

Titanium nitrate is the inorganic compound with formula Ti(NO3)4. It is a colorless, diamagnetic solid that sublimes readily. It is an unusual example of a volatile binary transition metal nitrate. Ill defined species called titanium nitrate are produced upon dissolution of titanium or its oxides in nitric acid.
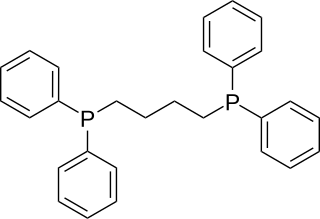
1,4-Bis(diphenylphosphino)butane (dppb) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (Ph2PCH2CH2)2. It is less commonly used in coordination chemistry than other diphosphine ligands such as dppe. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Tris(4-methoxyphenyl)phosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (CH3OC6H4)3P. Several isomers of this formula are known, but the symmetrical derivative with methoxy groups in the 4-position is most studied. The compound is used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.



















