
In organic chemistry, an ethyl group is an alkyl substituent with the formula −CH2CH3, derived from ethane. Ethyl is used in the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry's nomenclature of organic chemistry for a saturated two-carbon moiety in a molecule, while the prefix "eth-" is used to indicate the presence of two carbon atoms in the molecule.

Dimethylethanolamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2OH. It is bifunctional, containing both a tertiary amine and primary alcohol functional groups. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in skin care products for improving skin tone and also taken orally as a nootropic. It is prepared by the ethoxylation of dimethylamine.
Butyronitrile or butanenitrile or propyl cyanide, is a nitrile with the formula C3H7CN. This colorless liquid is miscible with most polar organic solvents.
Butyraldehyde, also known as butanal, is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)2CHO. This compound is the aldehyde derivative of butane. It is a colorless flammable liquid with an unpleasant smell. It is miscible with most organic solvents.

Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula HF. It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield an aqueous solution termed hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils at near room temperature, much higher than other hydrogen halides.
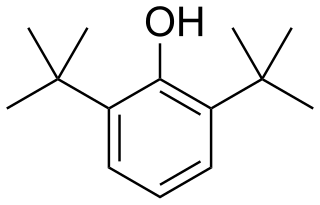
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is an organic compound with the structural formula 2,6-((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH. This colorless solid alkylated phenol and its derivatives are used industrially as UV stabilizers and antioxidants for hydrocarbon-based products ranging from petrochemicals to plastics. Illustrative of its usefulness, it prevents gumming in aviation fuels.

Manganese(II) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula MnSO4·H2O. This pale pink deliquescent solid is a commercially significant manganese(II) salt. Approximately 260,000 tonnes of manganese(II) sulfate were produced worldwide in 2005. It is the precursor to manganese metal and many other chemical compounds. Manganese-deficient soil is remediated with this salt.
Arylide yellow, also known as Hansa yellow and monoazo yellow, is a family of organic compounds used as pigments. They are primarily used as industrial colorants including plastics, building paints and inks. They are also used in artistic oil paints, acrylics and watercolors. These pigments are usually semi-transparent and range from orange-yellow to yellow-greens. Related organic pigments are the diarylide pigments. Overall, these pigments have partially displaced the toxic cadmium yellow in the marketplace. Painters such as Alexander Calder and Jackson Pollock are known to have employed arylide yellow in their artworks.

Strontium sulfate (SrSO4) is the sulfate salt of strontium. It is a white crystalline powder and occurs in nature as the mineral celestine. It is poorly soluble in water to the extent of 1 part in 8,800. It is more soluble in dilute HCl and nitric acid and appreciably soluble in alkali chloride solutions (e.g. sodium chloride).
Undecylenic acid is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CH(CH2)8CO2H. It is an unsaturated fatty acid. It is a colorless oil. Undecylenic acid is mainly used for the production of Nylon-11 and in the treatment of fungal infections of the skin, but it is also a precursor in the manufacture of many pharmaceuticals, personal hygiene products, cosmetics, and perfumes. Salts and esters of undecylenic acid are known as undecylenates.

Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is an important precursor to numerous compounds in organic chemistry. It is also an important pheromone in certain species.
In organic chemistry, 3-hydroxybutanal is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO and the structure H3C−CH(OH)−CH2−CH=O. It is classified as an aldol and the word "aldol" can refer specifically to 3-hydroxybutanal. It is formally the product of the dimerization of acetaldehyde. A thick colorless or pale-yellow liquid, it is a versatile and valuable intermediate with diverse impacts. The compound is chiral although this aspect is not often exploited.

Phthalonitrile is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CN)2, which is an off-white crystal solid at room temperature. It is a derivative of benzene, containing two adjacent nitrile groups. The compound has low solubility in water but is soluble in common organic solvents. The compound is used as a precursor to phthalocyanine and other pigments, fluorescent brighteners, and photographic sensitizers.
In organic chemistry, ammoxidation is a process for the production of nitriles using ammonia and oxygen. It is sometimes called the SOHIO process, acknowledging that ammoxidation was developed at Standard Oil of Ohio. The usual substrates are alkenes. Several million tons of acrylonitrile are produced in this way annually:
Propionitrile, also known as ethyl cyanide and propanenitrile, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CN. It is a simple aliphatic nitrile. The compound is a colourless, water-soluble liquid. It is used as a solvent and a precursor to other organic compounds.

β-Nitrostyrene is an aromatic compound and a nitroalkene used in the synthesis of indigo dye and the slimicide bromo-nitrostyrene.
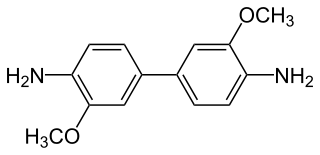
o-Dianisidine is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3O)(H2N)C6H3]2. A colorless or white solid, it is a bifunctional compound derived via the benzidine rearrangement from o-anisidine.
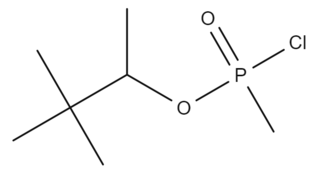
Chlorosoman is a chlorine analog of soman. It is a highly toxic organophosphorus compound and used as the precursor substance for soman nerve agent. Its physical properties are estimated. Soman is insoluble in water, with a boiling point of 223 degrees Celsius and a melting point of -27 degrees Celsius. Chlorosoman is at least 2.5x less toxic than its analogue.
Chlorobenzonitrile may refer to:
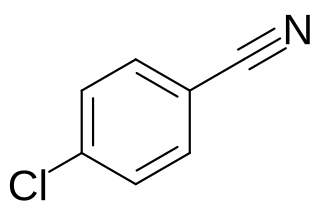
4-Chlorobenzonitrile is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4CN. It is a white solid. The compound, one of three isomers of chlorobenzonitrile, is produced industrially by ammoxidation of 4-chlorotoluene. The compound is of commercial interest as a precursor to pigments.
















