Transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic functional group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. Strong acids catalyze the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile. Bases catalyze the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of other enzymes, particularly lipases.
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base. An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.

Oleyl alcohol, or cis-9-octadecen-1-ol, is an unsaturated fatty alcohol with the molecular formula C18H36O or the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)7−CH=CH−(CH2)8OH. It is a colorless oil, mainly used in cosmetics.
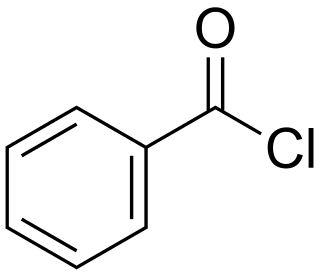
Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula C7H5ClO. It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour, and consists of a benzene ring with an acyl chloride substituent. It is mainly useful for the production of peroxides but is generally useful in other areas such as in the preparation of dyes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and resins.

Trimethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name it has the formula Al2(CH3)6 (abbreviated as Al2Me6 or TMA), as it exists as a dimer. This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industrially important compound, closely related to triethylaluminium.
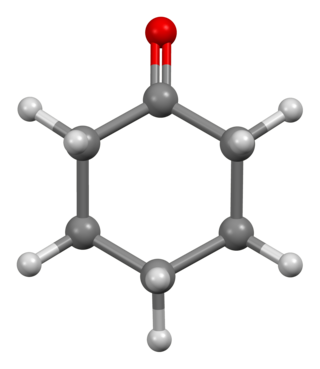
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.

A peroxy acid is an acid which contains an acidic –OOH group. The two main classes are those derived from conventional mineral acids, especially sulfuric acid, and the peroxy derivatives of organic carboxylic acids. They are generally strong oxidizers.
The Ullmann condensation or Ullmann-type reaction is the copper-promoted conversion of aryl halides to aryl ethers, aryl thioethers, aryl nitriles, and aryl amines. These reactions are examples of cross-coupling reactions.
The Bouveault–Blanc reduction is a chemical reaction in which an ester is reduced to primary alcohols using absolute ethanol and sodium metal. It was first reported by Louis Bouveault and Gustave Louis Blanc in 1903. Bouveault and Blanc demonstrated the reduction of ethyl oleate and n-butyl oleate to oleyl alcohol. Modified versions of which were subsequently refined and published in Organic Syntheses.

Itaconic acid, or methylidenesuccinic acid, is an organic compound. This dicarboxylic acid is a white solid that is soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone. Historically, itaconic acid was obtained by the distillation of citric acid, but currently it is produced by fermentation. The name itaconic acid was devised as an anagram of aconitic acid, another derivative of citric acid.
The Hunsdiecker reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry whereby silver salts of carboxylic acids react with a halogen to produce an organic halide. It is an example of both a decarboxylation and a halogenation reaction as the product has one fewer carbon atoms than the starting material and a halogen atom is introduced its place. A catalytic approach has been developed.

Orcinol is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(OH)2. It occurs in many species of lichens including Roccella tinctoria and Lecanora. Orcinol has been detected in the "toxic glue" of the ant species Camponotus saundersi. It is a colorless solid. It is related to resorcinol, 1,3-C6H4(OH)2.
Thiocarbonate describes a family of anions with the general chemical formula CS
3−xO2−
x (x = 0, 1, or 2):

Aminomethyl propanol is an organic compound with the formula H2NC(CH3)2CH2OH. It is colorless liquid that is classified as an alkanolamine. It is a useful buffer and a precursor to numerous other organic compounds.

Diethyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)H. It is a popular reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. Diethyl phosphite is a colorless liquid. The molecule is tetrahedral.
Tetrahydrophthalic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C6H8C2O3. The compound exists as two isomers, this article being focused on the more common cis isomer. It is a precursor to other compounds including the dicarboxylic acid tetrahydrophthalic acid as well the tetrahydrophthalimide, which is a precursor to the fungicide Captan. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
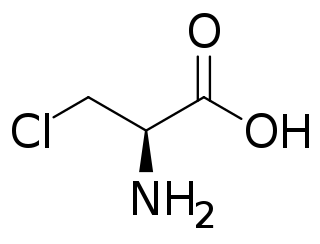
Chloroalanine (3-chloroalanine) is an unnatural amino acid with the formula ClCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a white, water-soluble solid. The compound is usually derived from chlorination of serine. The compound is used in the synthesis of other amino acids by replacement of the chloride. Protected forms of the related iodoalanine are also known.
Glycine methyl ester hydrochloride is the organic compound with the formula [CH3O2CCH2NH3]Cl. A white, water-soluble solid, it is the hydrochloride of the methyl ester of the amino acid glycine.













