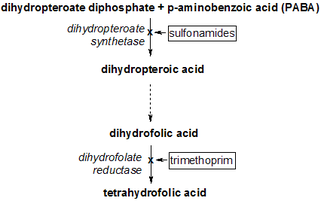
Dihydropteroate synthase is an enzyme classified under EC 2.5.1.15. It produces dihydropteroate in bacteria, but it is not expressed in most eukaryotes including humans. This makes it a useful target for sulfonamide antibiotics, which compete with the PABA precursor.
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.

Riboflavin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the final reaction of riboflavin biosynthesis. It catalyzes the transfer of a four-carbon unit from one molecule of 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine onto another, resulting in the synthesis of riboflavin and 5-amino-6-ribitylamino-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione:
The enzyme dihydroneopterin aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme (sometimes called a cofactor) involved in redox reactions in methanogens, in many Actinomycetota, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative with an absorption maximum at 420 nm—hence its name. The coenzyme is a substrate for coenzyme F420 hydrogenase, 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase and methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase.
In enzymology, a GTP cyclohydrolase IIa (EC 3.5.4.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an IMP cyclohydrolase (EC 3.5.4.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 2-amino-4-hydroxy-6-hydroxymethyldihydropteridine diphosphokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a riboflavin kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

8-Azaguanine is a purine analog with the chemical formula C4H4N6O. It has been widely studied for its biological activity. It shows antineoplastic activity and has been used in the treatment of acute leukemia.
Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase (EC 2.1.2.2, 2-amino-N-ribosylacetamide 5'-phosphate transformylase, GAR formyltransferase, GAR transformylase, glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase, GAR TFase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate:2-amino-N-ribosylacetamide ribonucleotide transformylase) is an enzyme with systematic name 10-formyltetrahydrofolate:5'-phosphoribosylglycinamide N-formyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
DNA photolyase, N-terminal is an evolutionary conserved protein domain. This domain binds a light harvesting chromophore that enhanced the spectrum of photolyase or cryptochrome light absorption, i.e. an antenna. It adopts the rossmann fold.
2,5-diamino-6-(ribosylamino)-4(3H)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate reductase (EC 1.1.1.302, 2,5-diamino-6-ribosylamino-4(3H)-pyrimidinone 5'-phosphate reductase, MjaRED, MJ0671 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 2,5-diamino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin synthase (EC 4.3.1.32, FO synthase) and 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil—L-tyrosine 4-hydroxyphenyl transferase (EC 2.5.1.147) are two enzymes always complexed together to achieve synthesis of FO, a precursor to Coenzyme F420. Their systematic names are 5-amino-5-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-6-(D-ribitylimino)-5,6-dihydrouracil ammonia-lyase (7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin-forming) and 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil:L-tyrosine, 4-hydroxyphenyl transferase respectively. The enzymes catalyse the following chemical reactions:
2-phospho-L-lactate transferase is an enzyme with systematic name (2S)-lactyl-2-diphospho-5'-guanosine:7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin 2-phospho-L-lactate transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
'ARFB, ArfB or arfB may refer to:
6-phospho-3-hexuloisomerase is an enzyme with systematic name D-arabino-hex-3-ulose-6-phosphate isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine is a metabolite in the purine metabolism, formed by the hydrolysis of GTP by GTP cyclohydrolase II. Alternatively two separate enzymes can carry out this reaction, initially GTP cyclohydrolase IIa hydrolyses the 8,9 bond to form 2-Amino-5-formylamino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one, followed by de-formylation by 2-amino-5-formylamino-6-ribosylaminopyrimidin-4(3H)-one 5'-monophosphate deformylase. 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine is deaminated by Diaminohydroxyphosphoribosylaminopyrimidine deaminase to form 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil.
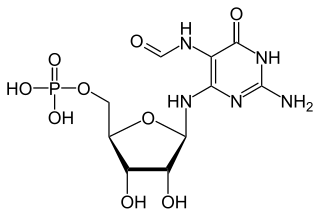
2-Amino-5-formylamino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one is a metabolite in the riboflavin biosynthesis pathway. It is formed from GTP by the enzyme GTP cyclohydrolase IIa which catalyzes the hydrolysis of the 8,9 bond in the guanine group and loss of the beta and gamma phosphate groups. The molecule is deformylated by 2-amino-5-formylamino-6-ribosylaminopyrimidin-4(3H)-one 5'-monophosphate deformylase as the second step in the archaeal riboflavin biosynthetic pathway.












