
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions among voters. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast – or almost all votes cast – contribute to the result and are effectively used to help elect someone. Under other election systems, a bare plurality or a scant majority are all that are used to elect candidates. PR systems provide balanced representation to different factions, reflecting how votes are cast.
National referendums are seldom used in Canada. The first two referendums in 1898 and 1942 saw voters in Quebec and the remainder of Canada take dramatically-opposing stands, and the third in 1992 saw most of the voters take a stand dramatically opposed to that of the politicians in power.

Mixed-member proportional representation is a type of representation provided by some mixed electoral systems which combine local winner-take-all elections with a compensatory tier with party lists, in a way that produces proportional representation overall. Like proportional representation, MMP is not a single system, but a principle and goal of several similar systems. Some systems designed to achieve proportionality are still called mixed-member proportional, even if they generally fall short of full proportionality. In this case, they provide semi-proportional representation.

Electoral reform in New Zealand has been a political issue in the past as major changes have been made to both parliamentary and local government electoral systems.
Canada holds elections for legislatures or governments in several jurisdictions: for the federal (national) government, provincial and territorial governments, and municipal governments. Elections are also held for self-governing First Nations and for many other public and private organizations including corporations and trade unions. Municipal elections can also be held for both upper-tier and lower-tier governments.
The Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform was created by the government of British Columbia, Canada to investigate changes to the provincial electoral system. On October 25, 2004, the citizens' assembly proposed replacing the province's existing first past the post (FPTP) system with BC-STV, a single transferable vote (STV) system. This recommendation was put to the electorate in a referendum in 2005 held during that year's provincial election. The provincial government required the referendum to achieve a super-majority of 60 percent of voters and simple majorities in 60 percent of the 79 districts in order to pass. The second of these thresholds was easily met, with a majority supporting the reform in 77 out of 79 electoral districts, but the overall vote fell short of the 60 percent requirement, with 57.69 percent of the votes in favour. A second referendum in 2009 on adopting the STV system also failed to pass carrying 8 electoral districts and 39.09 percent of the overall vote.

A referendum was held in the Canadian province of British Columbia on May 17, 2005, to determine whether or not to adopt the recommendation of the Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform to replace the existing first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP) with a single transferable vote system (BC-STV). It was held in conjunction with the BC Legislative Assembly election of 2005. Voters were given two ballots at that time: a ballot to vote for a Member of the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia (MLA) in their constituency and a referendum ballot. The referendum received considerable support from the electorate but failed in meeting the 60-percent threshold that had been set. A second referendum was held in 2009.
The Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform was established by the government of the province of Ontario, Canada, in March 2006. Modelled on the British Columbia equivalent, it reviewed the first past the post electoral system currently in use to elect members of the Ontario Legislature, with the authority to recommend an alternative. In May 2007, the assembly recommended, in a decision of 94 to 8, that Ontario adopt a form of mixed member proportional representation (MMP).

A referendum was held on October 10, 2007, on the question of whether to establish a mixed member proportional representation (MMP) system for elections to the Legislative Assembly of Ontario. The vote was strongly in favour of the existing plurality voting or first-past-the-post (FPTP) system.
Electoral reform is a change in electoral systems which alters how public desires are expressed in election results.

The 2019 Prince Edward Island general election was held to elect the members of the 66th General Assembly of Prince Edward Island. The vote in 26 of the 27 districts was held on 23 April 2019, while the vote for the member from Charlottetown-Hillsborough Park was deferred to 15 July due to the death of the Green Party's candidate. However, Charlottetown-Hillsborough Park still voted in a referendum on electoral reform. Natalie Jameson won the deferred election in the district.

The dual-member mixed proportional (DMP) voting method is a mixed electoral system using a localized list rule to elect two representatives in each district. It is similar to other forms of mixed-member proportional representation but differs in that all representatives are elected locally in small districts, rather than requiring separate list seats to be filled in large regional or nationwide districts. In the first step, one seat in each district is awarded to the candidate with the most votes, as with first-past-the-post voting rules. In the second step, underrepresented parties are assigned secondary seats in the districts in which they won the most votes, which creates an overall proportional result.
The House of Commons Special Committee on Electoral Reform (ERRE) (French: Comité spécial sur la réforme électorale) was a special committee of the House of Commons of Canada established in 2016 during the 42nd Canadian Parliament to investigate reforms to the Canadian electoral system. The formation of "an all-party Parliamentary committee to review... [electoral] reforms" was an election promise by Liberal Party leader Justin Trudeau in the 2015 federal election. After the Liberals won a majority in the election, and Trudeau became Prime Minister of Canada, he indicated the formation of a special committee was a priority in his mandate letter for Minister of Democratic Institutions Maryam Monsef. Shortly after the committee submitted its report to Parliament on December 1, 2016, Monsef was transferred to the position of the Minister of Status of Women and Karina Gould took over the electoral reform file. Shortly after taking her position, Gould announced that the government would no longer be pursuing reform of the electoral system, stating "It has become evident that the broad support needed among Canadians for a change of this magnitude does not exist."
A non-binding referendum on electoral reform was held in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island between 27 October – 7 November 2016. This was the second electoral reform referendum to be held in Prince Edward Island, following a vote to maintain the status quo in 2005. The referendum asked which of five voting systems residents would prefer to use in electing members to the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island. The referendum involved four counts under Instant-runoff voting rules and at the end, mixed member proportional representation was the majority choice with 55.03% support on the final ballot, with support of 52.42% of votes cast.
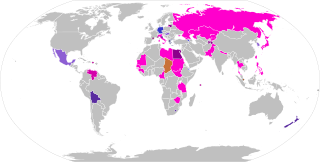
A mixed electoral system is one that uses different electoral systems to elect different seats in a legislature. Most often, this involves a winner-take-all component combined with a proportional component. The results of the combination may be mixed-member proportional (MMP), where the overall results of the elections are proportional, or mixed-member majoritarian, in which case the overall results are semi-proportional, retaining disproportionalities from the majoritarian component. Systems that mix more than two components are sometimes called supermixed.

A referendum on electoral reform took place by mail-in ballot between October 22 and December 7, 2018, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. 61.3 percent of voters supported maintaining the first-past-the-post voting system rather than switching to a proportional representation voting system, which was supported by 38.7 percent of voters. This was British Columbia's third referendum on electoral reform, following ones in 2005 and 2009.
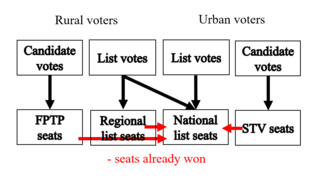
Rural–urban proportional representation (RUP), also called flexible district PR, is a supermixed electoral system which combines the use of single- and multi-member constituencies in a lower tier and top-up seats in an upper tier to meet the different needs of both rural and urban areas, while protecting the objective of proportionality. The term was coined by Fair Vote Canada, which devised a rural–urban system with the intention of meeting the special challenges of Canada's geography, which includes wide-flung, sparsely populated areas.
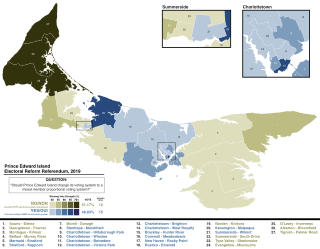
A referendum on electoral reform was held on April 23, 2019, in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island – simultaneously with the 2019 provincial election – to determine if the province should adopt a mixed-member proportional representation voting system (MMP). A narrow majority voted to keep the existing first-past-the-post system. However, the referendum was not binding, as neither the yes or no side received majority support in 60% or more of the province's 27 electoral districts.

Mixed-member majoritarian representation (MMM) is type of a mixed electoral system combining winner-take-all and proportional methods, where the disproportional results of the winner-take-all part are dominant over the proportional component. Mixed member majoritarian systems are therefore categorized under semi-proportional representation, and are usually contrasted with mixed-member proportional representation (MMP) which aims to provide proportional representation compensation ("top-up") seats.

Compensation or correction is an optional mechanism of electoral systems, which corrects the results of one part of the system based on some criterion to achieve a certain result, usually to make it more proportional. There are in general two forms of compensation: vote linkage and seat linkage.









