
The politics of Latvia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the prime minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. The President holds a primarily ceremonial role as Head of State. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament, the Saeima. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. The Economist Intelligence Unit rated Latvia a "flawed democracy" in 2022.

The Saeima is the parliament of the Republic of Latvia. It is a unicameral parliament consisting of 100 members who are elected by proportional representation, with seats allocated to political parties which gain at least 5% of the popular vote. Elections are scheduled to be held once every four years, normally on the first Saturday of October. The most recent elections were held in October 2022.

A post-legislative referendum was held in Scotland in 1979 to decide whether there was a sufficient support for a Scottish Assembly proposed in the Scotland Act 1978 among the Scottish electorate. This was an act to create a devolved deliberative assembly for Scotland. A majority (51.6%) of voters supported the proposal, but an amendment to the Act stipulated that it would be repealed if less than 40% of the total electorate voted in favour. As there was a turnout of 64% the "Yes" vote represented only 32.9% of the registered electorate, and the act was subsequently repealed.

Latvia elects on the national level a legislature. The Saeima has 100 members, elected for a four-year term by proportional representation with a 5% threshold. An unmodified Sainte-Laguë method is used to allocate seats. The parliamentary elections are held on the first Saturday of October. Locally, Latvia elects municipal councils, consisting of 7 to 60 members, depending on the size of the municipality, also by proportional representation for a four-year term.

The Constitution of Latvia, ratified on February 15, 1922, contains a provision regarding one of the reserve powers of the President of Latvia to initiate the dissolution of the parliament. According to Article 48-50 of the Constitution,
The Irish referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was a vote that was planned but did not occur. The referendum was expected to take place in 2005 or 2006 to decide whether Ireland should ratify the proposed EU Constitution. Following the rejection of the Constitution by voters in the French referendum of May 2005 and the Dutch referendum of June 2005, the planned Irish referendum was postponed indefinitely.

A presidential election was held in the Latvian Saeima on 31 May 2007. The government candidate Valdis Zatlers defeated Aivars Endziņš.

Valdis Zatlers is a Latvian politician and former physician who served as the seventh president of Latvia from 2007 to 2011. He won the Latvian presidential election of 31 May 2007. He became President of Latvia on 8 July 2007 and left office on 7 July 2011 after failing to win reelection for a second term.

The Group for a Switzerland without an army, is a Swiss political advocacy group founded in 1982 by 120 activists in order to abolish the Swiss army. Its roster has varied considerably; as of 2009 its website stated that it consists of about 20,000 members or supporters, consisting largely of pacifists and anti-militarists.

Parliamentary elections were held in Latvia on 2 October 2010. It was the first parliamentary election to be held in Latvia since the beginning of the economic crisis during which Latvia had experienced one of the deepest recessions in the world.

A constitutional referendum was held in Armenia on 27 November 2005. The referendum was on a series of changes to the constitution of Armenia which were backed by the international community. The official results had a high turnout and overwhelming support for the changes. However the opposition and election monitors said that there were serious irregularities with the referendum.

A nationwide referendum was held in Moldova on 5 September 2010 on whether or not the country should amend the Constitution of Moldova to return to direct popular election of the president. Since 2001, the president had been indirectly elected by Parliament, with a supermajority of 61 seats required for election. The voters are asked to answer the following question: "Would you agree with the Constitutional amendment, which would allow the election of the President of the Republic of Moldova by the entire population?" Voters chose one of the proposed options: "Yes (for)" or "No (against)". Of those who had cast their vote, 87.83% chose "Yes". However, the referendum did not pass because only 30.29% of voters turned out, short of the necessary 33% for the referendum to be considered valid.

Indirect presidential elections were held in Latvia on 2 June 2011. Incumbent president Valdis Zatlers was standing again, as well as Andris Bērziņš, a former head of SEB Unibanka ; Bērziņš was nominated by five Saeima members of the Union of Greens and Farmers just two days before the nomination deadline, although the party was assumed to back Zatlers for re-election.
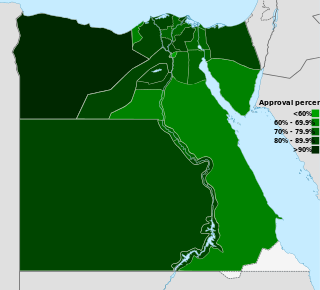
A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt on 19 March 2011, following the 2011 Egyptian revolution. More than 14 million (77%) were in favour, while around 4 million (23%) opposed the changes; 41% of 45 million eligible voters turned out to vote.

A referendum on whether the Saeima should be dissolved early was held in Latvia on 23 July 2011. President Valdis Zatlers used his parliamentary dissolution power for the first time in the history of Latvia. A "yes/no" vote was held and the referendum passed with 94.3% support.

The Reform Party, until April 2012 known as Zatlers' Reform Party, was a centre-right political party in Latvia founded by former President Valdis Zatlers on 23 July 2011. It won 22 seats in the Saeima in the 2011 election.

Early parliamentary elections were held in Latvia on 17 September 2011, following the country's first parliamentary dissolution referendum held on 23 July 2011. The previous parliamentary election was only held in October 2010.

A constitutional referendum on the "Amendments to the Constitution of the Republic of Latvia" was held on 18 February 2012. Proposed amendments included Articles 4, 18, 21, 101 and 104 of the Constitution of Latvia by adding the condition about Russian as the second official language, as well as prescribing two working languages — Latvian and Russian — for self-government institutions. The referendum's question was "Do you support the adoption of the Draft Law "Amendments to the Constitution of the Republic of Latvia" that provides for the Russian language the status of the second official language?"
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.

A constitutional referendum was held in Zambia on 11 August 2016 alongside general elections, a move designed to reduce the cost of the referendum. Voters were asked whether they approve of proposed amendments to the bill of rights and Article 79, which dictates the process of future amendments.













