
The politics of Latvia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the prime minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. The President holds a primarily ceremonial role as Head of State. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament, the Saeima. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. The Economist Intelligence Unit rated Latvia a "flawed democracy" in 2022.
A minority government, minority cabinet, minority administration, or a minority parliament is a government and cabinet formed in a parliamentary system when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in the legislature. It is sworn into office, with or without the formal support of other parties, enabling a government to be formed. Under such a government, legislation can only be passed with the support or consent of enough other members of the legislature to provide a majority, encouraging multi-partisanship. In bicameral legislatures, the term relates to the situation in the chamber whose confidence is considered most crucial to the continuance in office of the government.
From 1989 through 1991, Poland engaged in a democratic transition which put an end to the Polish People's Republic and led to the foundation of a democratic government, known as the Third Polish Republic, following the First and Second Polish Republic. After ten years of democratic consolidation, Poland joined NATO in 1999 and the European Union on 1 May 2004.

The Socialist People's Party of Montenegro is a political party in Montenegro. It is a social-democratic and socially conservative party, that is positioned on the centre-left on the political spectrum with regard to economic matters. It is supportive of accession of Montenegro to the European Union, and was historically supportive of Serbian–Montenegrin unionism.

The Latvian Social Democratic Workers' Party is a social-democratic political party in Latvia and the second oldest existing Latvian political party after the Latvian Farmers' Union. It is currently represented with two seats in the parliament of Latvia as a part of the Union of Greens and Farmers alliance after an absence of 20 years. The party tends to hold a less Russophilic view than fellow social-democratic party "Harmony".

Parliamentary elections were held in Latvia on 5 October 2002. The New Era Party emerged as the largest party in the Saeima, winning 26 of the 100 seats.
A grand coalition is an arrangement in a multi-party parliamentary system in which the two largest political parties of opposing political ideologies unite in a coalition government.

The Social Democratic Party is a centre-left political party in Estonia. It is currently led by Lauri Läänemets. The party was formerly known as the Moderate People's Party. The SDE has been a member of the Party of European Socialists since 16 May 2003 and was a member of the Socialist International from November 1990 to 2017. It is orientated towards the principles of social-democracy, and it supports Estonia's membership in the European Union. From April 2023, the party has been a junior coalition partner in the third Kallas government.

Finnish People's Democratic League was a Finnish political organisation with the aim of uniting those left of the Finnish Social Democratic Party. It was founded in 1944 as the anti-communist laws in Finland were repealed due to the demands of the Soviet Union, and lasted until 1990, when it merged into the newly formed Left Alliance. At its time, SKDL was one of the largest leftist parties in capitalist Europe, with its main member party, the Communist Party of Finland, being one of the largest communist parties west of the Iron Curtain. The SKDL enjoyed its greatest electoral success in the 1958 parliamentary election, when it gained a support of approximately 23 per cent and a representation of 50 MPs of 200 total, making it the largest party in the Eduskunta.

The 1979 Portuguese legislative election took place on 2 December. The election renewed all 250 members of the Assembly of the Republic, 13 seats less than those elected in 1976.

Parliamentary elections were held in Latvia on 2 October 2010. It was the first parliamentary election to be held in Latvia since the beginning of the economic crisis during which Latvia had experienced one of the deepest recessions in the world.
Unity is a liberal-conservative political party in Latvia. It is a member of the New Unity alliance and is positioned on the centre-right on the political spectrum. Since 2017, its chairman of the Main Board has been the former Minister for Economics of Latvia, Arvils Ašeradens, who succeeded former European Commissioner Andris Piebalgs.
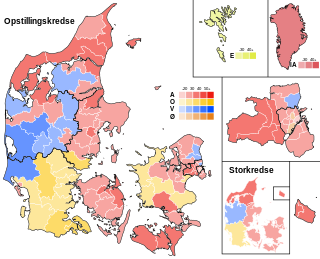
General elections were held in the Kingdom of Denmark on 18 June 2015 to elect the 179 members of the Folketing. 175 members were elected in the Denmark proper, two in the Faroe Islands and two in Greenland. Although the ruling Social Democrats became the largest party in the Folketing and increased their seat count, the opposition Venstre party was able to form a minority government headed by Lars Løkke Rasmussen with the support of the Danish People's Party, the Liberal Alliance and the Conservative People's Party.

Early parliamentary elections were held in Latvia on 17 September 2011, following the country's first parliamentary dissolution referendum held on 23 July 2011. The previous parliamentary election was only held in October 2010.

Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 19 April 2015, with advance voting taking place from 8 to 14 April. The 200 members of the Parliament of Finland were elected with the proportional D'Hondt method.

Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 14 April 2019. For the first time, no party received more than 20% of the vote. The Centre Party, which had been the largest party following the 2015 elections, dropped to fourth place, losing 18 seats and recording its lowest vote share since 1917. The Social Democratic Party saw the biggest gains, winning six more seats and narrowly becoming the largest party for the first time since 1999. The Green League and the Left Alliance also gained five and four seats respectively.
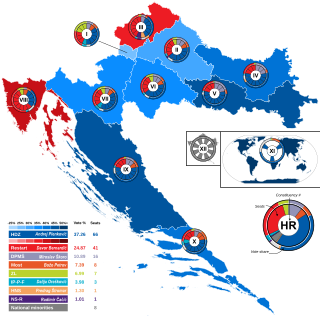
Parliamentary elections were held in Croatia on 5 July 2020. They were the tenth parliamentary elections since the first multi-party elections in 1990 and elected the 151 members of the Croatian Parliament. 140 Members of Parliament were elected from geographical electoral districts in Croatia, three MPs were chosen by the Croatian diaspora and eight MPs came from the ranks of citizens registered as belonging to any of the 22 constitutionally recognized national minorities.
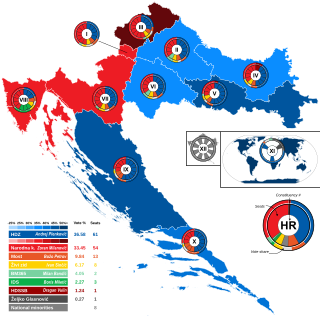
Parliamentary elections were held in Croatia on 11 September 2016, with all 151 seats in the Croatian Parliament up for election. The elections were preceded by a successful motion of no confidence against Prime Minister Tihomir Orešković and his cabinet on 16 June 2016, with 125 MPs voting in favour of the proposal. A subsequent attempt by the Patriotic Coalition to form a new parliamentary majority, with Minister of Finance Zdravko Marić as Prime Minister, failed and the Parliament voted to dissolve itself on 20 June 2016. The dissolution took effect on 15 July 2016, which made it possible for President Kolinda Grabar-Kitarović to officially call for elections on 11 September 2016. These were the ninth parliamentary elections since the 1990 multi-party elections.
The Alliance for the Albanians is a centre-right political party founded in 2015 in North Macedonia by Ziadin Sela.

The Popular Movement of Montenegro, commonly known as simply Popular Movement, is a conservative regionalist political party in Montenegro, formed in February 2021 from the political alliance of the same name. The alliance, which was formed back in May 2020 prior to the August parliamentary election, ran within the common opposition "For the Future of Montenegro" list. The party also seeks to represent Serb ethnic interests. Party founder and current leader is Montenegrin-Serbian businessman Miodrag "Daka" Davidović, who is known as a great benefactor of the Serbian Orthodox Church and a longtime financier of the Montenegrin opposition during the a thirty-year long DPS-led regime in Montenegro. NP has no seats in the national parliament and is yet to contest the elections, its currently operating regionally within the country's second-largest municipality of Nikšić and its surrounding areas.

















