| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2009 in Burkina Faso .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2009 in Burkina Faso .

Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of 274,200 km2 (105,900 sq mi), bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and the Ivory Coast to the southwest. It has a population of 20,321,378. Previously called Republic of Upper Volta (1958–1984), it was renamed Burkina Faso by President Thomas Sankara. Its citizens are known as Burkinabè, and its capital and largest city is Ouagadougou.

The history of Burkina Faso includes the history of various kingdoms within the country, such as the Mossi kingdoms, as well as the later French colonisation of the territory and its independence as the Republic of Upper Volta in 1960.

A transboundary protected area (TBPA) is an ecological protected area that spans boundaries of more than one country or sub-national entity. Such areas are also known as transfrontier conservation areas (TFCAs) or peace parks.

Sudano-Sahelian architecture refers to a range of similar indigenous architectural styles common to the African peoples of the Sahel and Sudanian grassland (geographical) regions of West Africa, south of the Sahara, but north of the fertile forest regions of the coast.

Loropéni is a market town in southern Burkina Faso, lying about 40 kilometres (25 mi) west of Gaoua. Nearby are the medieval stone ruins of Loropéni, added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2009. These ruins of a fortress, which date back at least a thousand years, are the country's first World Heritage site.

The W National Park or W Regional Park is a major national park in West Africa around a meander in the River Niger shaped like the letter W. The park includes areas of the three countries Niger, Benin and Burkina Faso, and is governed by the three governments. Until 2008, the implementation of a regional management was supported by the EU-funded project ECOPAS. The three national parks operate under the name W Transborder Park.. The section of W National Park lying in Benin, measuring over 8,000 km2 (3,100 sq mi), came under the full management of African Parks in June 2020. In Benin, W National Park is contiguous with Pendjari National Park which is also under the management of African Parks.
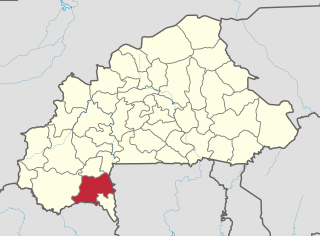
Poni is one of the 45 provinces of Burkina Faso, located in its Sud-Ouest Region.
As of August 2022, there are a total of 1,154 World Heritage Sites located in 167 States Parties, of which 897 are cultural, 218 are natural and 39 are mixed properties. The countries have been divided by the World Heritage Committee into five geographic zones: Africa, Arab States, Asia and the Pacific, Europe and North America, and Latin America and the Caribbean. Italy, with 58 entries, has the highest number of World Heritage Sites.

Burkina Faso is largely wild bush country with a mixture of grass and small trees in varying proportions. The savanna region is mainly grassland in the rainy season and semi desert during the harmattan period. Fauna, one of the most diverse in West Africa, includes the elephant, hippopotamus, buffalo, monkey, lions, crocodile, giraffe, various types of antelope, and a vast variety of bird and insect life. The country has 147 mammal species, 330 aquatic species including 121 species of fish and 2067 different plant species. Of the plant species, the dominant endemic species are shea tree (Butyrospermum parkii) and the baobab, the former plant species has immense economic value to the country.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Burkina Faso:

Loropeni is a department or commune of Poni Province in southern Burkina Faso. Its capital lies at the town of Loropeni.
Gold Mining often plays a significant role in Burkina Faso’s economy. Burkina Faso has become Africa's 4th biggest producer of gold in 2012. Production of mineral commodities is limited to cement, dolomite, gold, granite, marble, phosphate rock, pumice, other volcanic materials, and salt.
Douroula is a town in Burkina Faso. It is the county seat of Douroula Department in the province Mouhoun.

The ruins of Loropéni are a medieval heritage site near the town of Loropéni in southern Burkina Faso. They were added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2009. These ruins are the country's first World Heritage site. The site, which spans 11,130 square metres (119,800 sq ft), includes an array of stone walls that comprised a medieval fortress, the best preserved of ten in the area. They date back at least a thousand years. The settlement was occupied by the Lohron or Kulango people and prospered from the trans-Saharan gold trade, reaching its height between the 14th and 17th centuries AD. It was abandoned in the early 19th century.

Burkina Faso–India relations refers to the international relations that exist between Burkina Faso and India. Burkina Faso maintains an embassy in New Delhi. India maintained an embassy in Ouagadougou from November 1996 until its closure in July 2002. Currently, India maintains an honorary consulate in Ouagadougou, which functions under the jurisdiction of the High Commission of India in Accra, Ghana.
Science and technology in Burkina Faso summarizes developments and trends in this field in Burkina Faso since 2010 and places them in their subregional context.
The Ancient Ferrous Metallurgy Sites of Burkina Faso are a collection of ancient metallurgy sites across five locations in the Nord and Centre-Nord regions of Burkina Faso, used to extract iron from ore. The oldest of these structures are dated from roughly 800 BC, making them the most ancient known examples of metallurgy in Burkina Faso. In 2019, the sites were registered as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO, because of the exemplary evidence of ancient metalworking.