Related Research Articles

The Quabbin Reservoir is the largest inland body of water in Massachusetts, United States, and was built between 1930 and 1939. Along with the Wachusett Reservoir, it is the primary water supply for Boston, 65 miles (105 km) to the east, and 40 other cities and towns in Greater Boston. The Quabbin also supplies water to three towns west of the reservoir and acts as backup supply for three others. By 1989, it supplied water for 2.5 million people, about 40% of the state's population at the time. It has an aggregate capacity of 412 billion US gallons (1,560 GL) and an area of 38.6 square miles (99.9 km2).
The Boston Water and Sewer Commission (BWSC) serves retail customers with water services in Boston, Massachusetts. It purchases water wholesale from the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA).

The Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA) is a public authority in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts that provides wholesale drinking water and sewage services to 3.1 million people in sixty-one municipalities and more than 5,500 large industrial users in the eastern and central parts of the state, primarily in the Boston area.

Middlesex Fells Reservation, often referred to simply as the Fells, is a public recreation area covering more than 2,200 acres (890 ha) in Malden, Medford, Melrose, Stoneham, and Winchester, Massachusetts, United States. The state park surrounds two inactive reservoirs, Spot Pond and the Fells Reservoir, and the three active reservoirs that are part of the water supply system for the town of Winchester. Spot Pond and the Fells Reservoir are part of the Wachusett water system, one of six primary water systems that feed metropolitan Boston's waterworks. The park is managed by the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation and is part of the Metropolitan Park System of Greater Boston.

The Wachusett Reservoir is the second largest body of water in the state of Massachusetts. It is located in central Massachusetts, northeast of Worcester. It is part of the water supply system for metropolitan Boston maintained by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA). It has an aggregate capacity of 65 billion US gallons (250,000,000 m3) and an area of almost 7 square miles (18 km2). Water from the reservoir flows to the covered Norumbega Storage Facility via the Cosgrove Tunnel and the MetroWest Water Supply Tunnel. The reservoir has a maximum depth of 120 feet (37 m) and a mean depth of 48 feet (15 m).

The Ware River Diversion is a dam on the Ware River. It is part of the Boston, Massachusetts public water supply system, maintained by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA). It is located in Worcester County in the town of Barre, close to its border with Oakham.

The Ware River is a 35.4-mile-long (57.0 km) river in central Massachusetts. It has two forks, its West Branch, which begins in Hubbardston, Massachusetts, and its East Branch, which begins in Westminster, Massachusetts. The Ware River flows southwest through the middle of the state, joins the Quaboag River at Three Rivers, Massachusetts, to form the Chicopee River on its way to the Connecticut River.

The Wachusett Aqueduct is a secondary aqueduct that carries water from the Wachusett Reservoir to the John J. Carroll Water Treatment Plant at Walnut Hill in Marlborough, Massachusetts. It is part of the public water supply system for the communities of Greater Boston that are served by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA), which manages the aqueduct. The aqueduct serves as a standby backup to the Cosgrove Tunnel.

The Quinapoxet River is part of the Nashua River watershed in northern Massachusetts in the United States. It is part of the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority water system supplying drinking water to the greater Boston area.

The Weston Reservoir is part of the greater Boston water supply maintained by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority. It is located in central Weston, with its principal public access point on Ash Street.

The Barre Falls Dam is located on the Ware River in Barre, Massachusetts, about 0.3 miles (0.48 km) below the junction of the river's east and west branches and 13 miles (21 km) northwest of Worcester, Massachusetts.
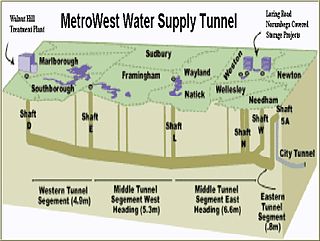
The MetroWest Water Supply Tunnel (MWWST) is an advanced underground aqueduct that supplies potable water to residents of much of Greater Boston. It is part of the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA) water supply system, having entered operation in November 2003.

Chestnut Hill Reservoir is a reservoir located in the Chestnut Hill section of Boston, Massachusetts. It was created in 1870 on existing marshes and meadowland to supplement the city’s water needs. A 1.56 mile jogging loop abuts the reservoir. Chestnut Hill Reservoir was taken offline in 1978 as it was no longer needed for regular water supply distribution, but is maintained in emergency backup status. It is recognized today on the National Register of Historic Places and was designated as a Boston Landmark by the Boston Landmarks Commission in 1989.

The Marlborough Brook Filter Beds are a series of water filtration beds near the mouth of Marlborough Brook, where it enters Sudbury Reservoir near the town line between Marlborough and Southborough, Massachusetts. The filter beds were constructed in 1895 as part of the reservoir construction to improve the water quality of Marlborough and Walker Brooks, and are the best-preserved of two such facilities built as part of the public water supply serving Boston and surrounding communities. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.

The Weston Aqueduct is an aqueduct operated by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA). Now part of the MWRA backup systems, it was designed to deliver water from the Sudbury Reservoir in Framingham to the Weston Reservoir in Weston. The 13.5-mile (21.7 km) aqueduct begins at the Sudbury Dam, and passes through the towns of Southborough, Framingham, Wayland, and Weston. In 1990, the route, buildings and bridges of the aqueduct were added to the National Register of Historic Places as the Weston Aqueduct Linear District.

The Framingham Reservoir No. 1 Dam and Gatehouse is a historic water works facility in Framingham, Massachusetts, United States. This complex is located at the end of Framingham Reservoir No. 1, which is also known as the Stearns Reservoir, off Winter Street and north of Long Avenue. Constructed from 1876 to 1878 as part of an expansion of the water supply of the city of Boston, this was designed by its first city architect George A. Clough. The historical purpose of the reservoir, which was located at the confluence of two branches of the Sudbury River, was primarily to control the river's water level, and secondarily to provide reserve supply capacity. The reservoir's reserve capacity was generally used only as a backup supply, as the reservoir's muddy bottom made it a less desirable source than reservoir No. 3 upstream. However the reservoir No. 1 system was nonetheless important due to its role in controlling the flow of the river downstream, and due to the gatehouse which controlled the water flows for all the Framingham reservoirs into the Sudbury Aqueduct. Reservoir No. 1 is no longer maintained as a reserve water source, although it is still owned by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority, successor to the Boston Water Board which oversaw its construction. MWRA retains ownership as the gatehouse contains the connection between Reservoir No. 3 and the Sudbury Aqueudct which remain part of the emergency water systems.

The Sudbury Aqueduct is an aqueduct in Massachusetts. It runs for 16 miles (26 km) from Farm Pond at Waverly Street in Framingham to Chestnut Hill Reservoir in Boston’s Chestnut Hill neighborhood. A later built extension main runs from the Farm Pond gatehouse to the gatehouse at the Stearns Reservoir where additional mains connect to the Brackett and Foss Reservoirs Going east from Framingham, it runs through Sherborn before entering Natick. From Natick it runs east through Wellesley and Needham to the Charles River, which it crosses on the Echo Bridge into Newton. It ends at the Chestnut Hill Reservoir on the Newton side of the Newton-Boston line. The Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA) operates the aqueduct.
The Hultman Aqueduct forms part of the water supply system of eastern Massachusetts, managed by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA). The aqueduct extends from Southborough to Weston, connecting the Cosgrove Tunnel to the distribution network in the Greater Boston area. Opened in 1939, it replaced the Weston Aqueduct. It is now itself a secondary system, having been supplanted as the primary conduit in 2003 by the MetroWest Water Supply Tunnel. From 2009 to 2014, it was rehabilitated and taken offline to repair leaks which were causing losses of at least 400,000 US gallons (1,500,000 L) of water per day in the 1990s.

The Sudbury Reservoir is an emergency backup Boston metropolitan water reservoir in Massachusetts, located predominantly in Southborough and Marlborough, with small sections in Westborough and Framingham. It was created when the Sudbury Dam was constructed to impound the Stony Brook branch of the Sudbury River; no part of the reservoir lies in the town of Sudbury. Nearly 5,000 acres (2,000 ha) in the Sudbury Reservoir watershed are administered by the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation as a limited-access public recreation area.

The John J. Carroll Water Treatment Plant (CWTP) is a water treatment plant operated since 2005 by the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA) to treat water bound for Greater Boston. The plant is located at the town lines of Marlborough, Northborough, and Southborough, Massachusetts.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Derrick Henry (May 2, 2010). "Ruptured Pipe Cuts Water in Boston". The New York Times . Retrieved 2016-08-20.
- 1 2 "Boil water order is lifted for 2M in Boston area". Archived from the original on 7 May 2010. Retrieved 4 May 2010.
- ↑ "Obama Declares Mass. Emergency For Water Break". WBUR.org. 2010-05-03. Retrieved 2016-08-20.
- ↑ "MWRA Water Main Break Triggers State Of Emergency | WCVB Home – WCVB Home". Thebostonchannel.com. 2010-05-02. Archived from the original on 2012-03-20. Retrieved 2016-08-20.
- ↑ Levenson, Michael; Daley, Beth (2010-05-02). "A 'catastrophic' rupture hits region's water system". The Boston Globe .
- ↑ "Hope of fix within days". Archived from the original on May 7, 2010.
- 1 2 "MWRA homepage" . Retrieved 2010-05-02.
- ↑ Levenson, Michael; Daley, Beth (2010-05-02). "A 'catastrophic' rupture hits region's water system". The Boston Globe .
- ↑ "Mwra - Mwra Water Main Break Requires Water Ban, Boil Water Order". Mwra.state.ma.us. Retrieved 2016-08-20.
- ↑ Finucane, Martin; Daley, Beth; Guilfoil, John M.; Teehan, Sean; Castello, Caitlin (May 1, 2010). "'Boil-water' order issued for nearly 2 million in Mass". The Boston Globe . Archived from the original on 3 May 2010. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- ↑ "EMERGENCY WATER NOTICE | Starting May 1, 2010 - Updated Regularly". MWRA.com. Retrieved 2016-08-20.
- ↑ "Coakley to review water price gouging allegations - Local News Updates - MetroDesk - The Boston Globe". Archived from the original on 2010-05-05. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ↑ "Bottled water still available at stores in eastern Massachusetts - Quincy, MA - The Patriot Ledger". Archived from the original on 2010-05-09. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- 1 2 Boil water order: What you need to know, NECN Comcast Network, May 2, 2010.
- 1 2 Weston water main break not worst-case, NECN Comcast Network, May 2, 2010.
- ↑ Boil-water order remains in effect, but progress reported on water main break, Daily News Tribune , by Glen Johnson of the Associated Press, May 2, 2010.
- ↑ Malone, Scott (May 4, 2010). "Boil-water ban lifted for Boston area". Reuters. Retrieved 7 May 2010.
- ↑ Tests confirm it — water was OK to drink all weekend Boston.com, May 5, 2010
- ↑ "Multi-agency Response to a Major Water Pipe Break : A Massachusetts Case Study and Evaluation : Final Report" (PDF). Amwa.net. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-08-20. Retrieved 2016-08-20.
- ↑ Pantic, Zorica. "MWRA MetroWest Water Supply Tunnel Shaft 5A Pipe Break—Pipe Failure Scenario Report" (PDF). Mwra.state.ma.us. Retrieved 4 June 2013.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ LeBlanc, Steve. "Report: Bolt Failure Caused 2010 Weston Water Main Break". Associated Press. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- ↑ Daley, Beth (26 May 2011). "Wrong studs led to water main break, report says". The Boston Globe . Retrieved 4 June 2013.