
Dixville Notch is an unincorporated community in Dixville township, Coos County, New Hampshire, United States. The population of the township, all of whom live in Dixville Notch, was 4 as of the 2020 census. The village is known for being the first place to declare its results during the New Hampshire presidential primary. It is located in the northern part of the state, approximately 20 miles (32 km) south of the border with the Canadian province of Quebec. The village is situated at about 1,800 feet (550 m) above sea level at the base of mountains.

Krzysztof Bosak is a far-right Polish politician. He serves as the Deputy Marshal of the Sejm of the Republic of Poland. He was a member of the Sejm for the League of Polish Families from 2005 to 2007 and has been a member of the Sejm again since 2019 for the Confederation. Bosak was the chairman of the All-Polish Youth from 2005 to 2006 and was one of the founders and the current chairman of the National Movement. He was a candidate for president in 2020.

The National Movement is a Polish far-right ultranationalist political party. It is led by Krzysztof Bosak. It claims spiritual descendance from the prewar movement of Roman Dmowski, the National Democracy, which was also commonly called the National Movement.

Presidential primaries and caucuses were organized by the Democratic Party to select the 3,979 pledged delegates to the 2020 Democratic National Convention held on August 17–20 to determine the party's nominee for president in the 2020 United States presidential election. The elections took place in all 50 U.S. states, the District of Columbia, five U.S. territories, and through Democrats Abroad, and occurred between February 3 and August 11.
Presidential primaries and caucuses of the Republican Party took place in many U.S. states, the District of Columbia, and five U.S. territories from February 3 to August 11, 2020, to elect most of the 2,550 delegates to send to the Republican National Convention. Delegates to the national convention in other states were elected by the respective state party organizations. The delegates to the national convention voted on the first ballot to select Donald Trump as the Republican Party's nominee for president of the United States in the 2020 election, and selected Mike Pence as the vice-presidential nominee.

Presidential elections were held in Poland on 28 June 2020. As no candidate received a majority of the vote, a second round was held on 12 July, in which incumbent president Andrzej Duda, running with the support of Law and Justice, faced off against Civic Platform vice-chairman and Mayor of Warsaw Rafał Trzaskowski. In the second round Duda was re-elected for a second term with 51% of the vote, becoming the first incumbent to win re-election since Aleksander Kwaśniewski in 2000.

The 2020 United States presidential election in California was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. California voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate Kamala Harris, the junior senator from California. In the 2020 election, California had 55 electoral votes in the Electoral College, the most of any state. Biden won by a wide margin, as was expected; however, California was one of six states where Trump received a larger percentage of the two-party vote than he did in 2016. This election also marked the first time since 2004 that the Republican candidate won more than one million votes in Los Angeles County due to increased turnout.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Illinois was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Illinois voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump of Florida, and his running mate, Vice President Mike Pence of Indiana, against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden of Delaware, and his running mate, Senator Kamala Harris of California. Illinois had 20 votes in the Electoral College. Prior to the 2020 election, all news organizations predicted Illinois was a state that Biden would win, or otherwise considered a safe blue state.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Indiana was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Indiana voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Indiana has 11 electoral votes in the Electoral College.
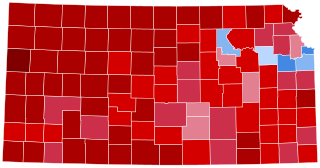
The 2020 United States presidential election in Kansas was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Kansas voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump of Florida, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence of Indiana against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden of Delaware, and his running mate Senator Kamala Harris of California. Kansas has six electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2020 United States presidential election in New York was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. New York voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. New York had 29 electoral votes in the Electoral College. Trump announced that Florida would be his home state for this election, rather than New York as it had been previously. This was the first presidential election in New York to allow no-excuse absentee voting.
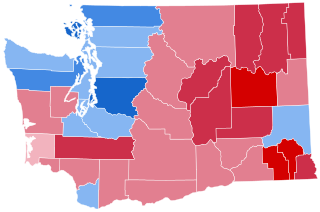
The 2020 United States presidential election in Washington was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 U.S. states plus the District of Columbia participated. Washington voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Washington has 12 electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Virginia was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Virginia voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Virginia has 13 electoral votes in the Electoral College.
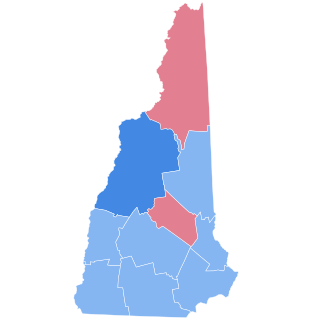
The 2020 United States presidential election in New Hampshire was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states and the District of Columbia participated. New Hampshire voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominees, incumbent President Donald Trump and Vice President Mike Pence, against the Democratic Party's nominees, former Vice President Joe Biden and his running mate, Senator Kamala Harris. New Hampshire has four electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The Confederation Liberty and Independence, frequently shortened to just Confederation, is a far-right political alliance in Poland. It was initially founded in 2018 as a political coalition for the 2019 European Parliament election in Poland, although it was later expanded into a political party in order to circumvent the 8% vote threshold for coalitions to enter the national parliament. It won 11 seats in the Sejm after the 2019 Polish parliamentary election. Its candidate for the 2020 Polish presidential election was Krzysztof Bosak, who placed fourth among eleven candidates.
The Confederation of the Polish Crown, often shortened to The Crown, is a monarchist and far-right political party in Poland. It is led by Grzegorz Braun.

Paweł Juliusz Skutecki is a Polish politician, journalist, anti-vax activist, and former deputy in the Sejm from 2015 to 2019.

Krzysztof Tołwiński is a Polish agrarian politician, farmer, and former deputy minister of the treasury from September to November 2007. In 2010 he became a deputy in the Sejm from the Białystok constituency. He replaced Krzysztof Putra who died in the Smolensk air disaster. He ran for election in 2019 starting from the Confederation list but was not elected. He was a candidate in the 2019–20 Confederation presidential primary.
Presidential elections will be held in Poland on 4, 11 or 18 May 2025, though they can be held earlier should the office become vacated as a result of death, resignation or removal from office of the incumbent. Due to constitutional term limits limiting a president to serve only two terms, incumbent president Andrzej Duda is ineligible for re-election. Presidential elections in Poland must take place on a day free from work between 75 and 100 days before the term ends.



























