
Vidarbha is a geographical region in the west Indian state of Maharashtra. Forming the eastern part of the state, it comprises Amravati and Nagpur divisions. As per the 2011 Census, the region had a population of 23,003,179. The region occupies 31.6% of the total area and is home to 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. Situated in central India, it borders the state of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh to the east, Telangana to the south and Marathwada and Uttar Maharashtra regions of Maharashtra to the west.

The Wainganga is a river in India originating in the Mahadeo Hills in Mundara in Gondwana region near the village Gopalganj in Seoni, Madhya Pradesh. It is a key tributary of the Godavari. The river flows south in a winding course through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, roughly 580 km (360 mi). After joining the Wardha River, the united stream, which is known as the Pranahita River, empties into the Godavari River at Kaleshwaram, Telangana.

The Wardha River, also known as the Varada River, is a major river in Vidarbha, Maharashtra, which originates in the Satpura Range and flows into the Wain ganga river to form the Pranhita river which finally joins the Godavari river.

The Godavari River has its catchment area in seven states of India: Maharashtra, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Odisha. The number of dams constructed in Godavari basin is the highest among all the river basins in India. Nearly 350 major and medium dams and barrages had been constructed in the river basin by the year 2012.

Balaghat district is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in Central India. Its belongs to Jabalpur Division. Balaghat city is Administrative Headquarter of Balaghat District.

Seoni District is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. The town of Seoni is the district's headquarters.

Seoni is a city and a municipality in Seoni district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. This tribal household dominated district was formed in the year 1956.
Pusad is a city in the Yavatmal district located in Vidarbha region of Maharashtra state of India. It is named after the Pus river. Its ancient name was 'Pushpawanti'. Pusad is second largest city of Yavatmal district. For last 20 years Pusad is being tried to be promoted to the stature of district but due to lack of administration of governing bodies it is only a dream of the people.

The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Nagpur was the primary winter capital while Pachmarhi served as the regular summer retreat. It became the Central Provinces and Berar in 1903.
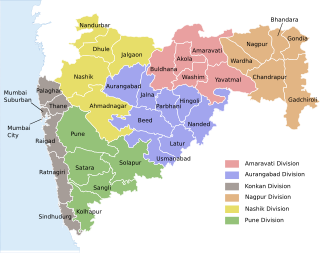
The word Maharashtra, the land of the mainly Marathi-speaking people, appears to be derived from Maharashtri, an old form of Prakrit. Some believe that the word indicates that it was the land of the Mahars and the Rattas, while others consider it to be a corruption of the term 'Maha Kantara', a synonym for 'Dandakaranya'. Maharashtra is the third largest state in India after Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. It covers an area of 307,713 km2 and is bordered by the states of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh to the east, Telangana to the southeast, Karnataka to the south and Goa to the southwest. The state of Gujarat lies to the northwest, with the Union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli sandwiched between the borders. Maharashtra has coastline of 720 km.The Arabian Sea makes up Maharashtra's west coast. Maharashtra consists of two major relief divisions. The plateau is a part of the Deccan tableland and the Konkan coastal strip abutting on the Arabian Sea.

The Painganga River is the chief river of the Buldhana district, Hingoli district, Nanded district, Yavatmal district, Chandrapur district and Washim district in the Maharashtra state in India. It flows along the southeast boundaries of the district in a winding, meandering course. It is deeply entrenched and difficult to navigate. It rises in the Ajantha range and is a major tributary of the Wardha River, the other major river in the district. It is also divided Marathwada and Vidarbha near Umarkhed and Himayatnagar.

The Pranahita River is the largest tributary of Godavari River covering about 34% of its drainage basin conveying the combined waters of the Penganga River, the Wardha River, and the Wainganga River. By virtue of its extensive network of tributaries, the river drains a large part of Vidarbha region in Maharashtra, as well as the southern slopes of the Satpura Range in southeast Madhya Pradesh. It flows along the border of Gadchiroli district in Maharashtra and Komaram Bheem Asifabad district in Telangana. The Pranahita sub-basin is the seventh largest in India, measuring about 109,078 km2, making it larger than the individual basins of significant rivers such as the Narmada River and Kaveri.

The Upper Wardha Dam is an earthfill straight gravity dam across the Wardha River, a tributary of the Godavari River, near Simbhora village in Morshi taluk in Amravati district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The dam provides multipurpose benefits of irrigation, drinking water supply, flood control and hydropower generation.
Bor Tiger Reserve is a wildlife sanctuary which was declared as a tiger reserve in July 2014. It is located near Hingani in Wardha District in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is a home to a variety of wild animals. The reserve covers an area of 138.12 km2 (53.33 sq mi). which includes the drainage basin of the Bor Dam.

The Kanhan River is an important right bank tributary of the Wainganga River draining a large area lying south of Satpura range in central India. Along its 275 km run through the Indian States of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh, it receives its largest tributary - Pench River, a major water source for the metropolis of Nagpur.
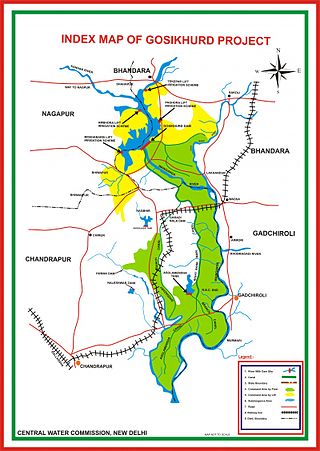
GosiKhurd Irrigation Project also known as Indira Sagar Irrigation Project is one of the major irrigation projects in Godavari basin in Indian state Maharashtra in the Bhandara district on the river Wainganga. The project was launched in 7th Five Year Plan by former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi during 1984. It has been declared as National Irrigation Project by Government of India.
The 2019 Indian floods were a series of floods that affected over thirteen states in late July and early August 2019, due to excessive rains. At least 200 people died and about a million people were displaced. Karnataka and Maharashtra were the most severely affected states. People died but many were rescued with the help of the Indian Navy.
Nagpur broad-gauge Metro is a commuter rail project planned for the city of Nagpur and extending up to adjacent areas of Wardha, Yavatmal, Narkhed, Ramtek, Bhandara, Amravati, Wadsa and Chhindwara in Vidarbha region of Maharashtra, India. This project will be executed by Maharashtra Metro Rail Corporation Limited. According to some Government officials first broad gauge metro will run in December 2023 on Nagpur to Yavatmal line via Wardha.And inauguration will be taken place in hand of Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
The Sur is a river in India. It is a key tributary of the Wainganga. The river flows south in a winding course through the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra.
The 2023 Nagpur Flood was a flooding event that occurred in the city of Nagpur in the Indian State of Maharashtra on September 24, 2023. The flood caused deaths and economic destruction with several hundred people being evacuated in various parts of the city.













