Related Research Articles
The Torino scale is a method for categorizing the impact hazard associated with near-Earth objects (NEOs) such as asteroids and comets. It is intended as a communication tool for astronomers and the public to assess the seriousness of collision predictions, by combining probability statistics and known kinetic damage potentials into a single threat value. The Palermo Technical Impact Hazard Scale is a similar, but more complex scale.
(35396) 1997 XF11 (provisional designation 1997 XF11) is a kilometer-sized asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object, Mars-crosser and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group.
2006 RH120 is a tiny near-Earth asteroid and fast rotator with a diameter of approximately 2–3 meters that ordinarily orbits the Sun but makes close approaches to the Earth–Moon system around every twenty years, when it can temporarily enter Earth orbit through temporary satellite capture (TSC). Most recently, it was in Earth orbit from July 2006 to July 2007, during which time it was never more than 0.0116 AU (1.74 million km) from Earth. As a consequence of its temporary orbit around the Earth, it is currently the second smallest asteroid in the Solar System with a well-known orbit, after 2021 GM1. Until given a minor planet designation on 18 February 2008, the object was known as 6R10DB9, an internal identification number assigned by the Catalina Sky Survey.

2007 VK184 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, and estimated to be approximately 130 meters (430 ft) in diameter. It was listed on the Sentry Risk Table with a Torino Scale rating of 1 for a potential impactor in June 2048. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 28 March 2014.
1994 WR12 is an asteroid and near-Earth object approximately 130 meters (430 feet) in diameter. As a member of the Aten group almost all of its orbit is closer to the Sun than Earth is. On 24 November 1994 it passed about 374100 km from the Moon. First imaged at Kitami Observatory on 26 November 1994, it was discovered two nights later by American astronomer Carolyn S. Shoemaker at Palomar Observatory on 28 November 1994. The asteroid then went unobserved from 1994 until it was recovered by Mauna Kea in March 2016. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 2 April 2016.
2010 RF12 is a very small asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo group, that passed between Earth and the Moon on 8 September 2010, at 21:12 UTC, approaching Earth within 79,000 kilometres (49,000 mi) above Antarctica. The asteroid was discovered by the Mount Lemmon Survey near Tucson, Arizona on 5 September 2010 along with 2010 RX30. Based on a short 7-day observation arc from that apparation, it was listed for 12 years on the Sentry Risk Table as the asteroid with the greatest known probability (5%) of impacting Earth. 2010 RF12 was rediscovered in August 2022, and now has a 12-year observation arc and a much better known orbit. As of the December 2022 solution which accounts for nongravitational forces, there is a 1-in-10 chance of an Earth impact on 5 September 2095.
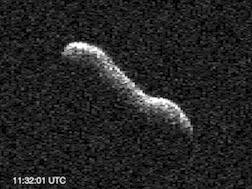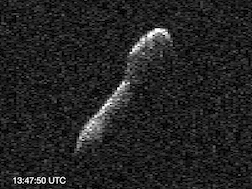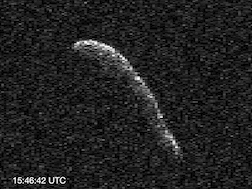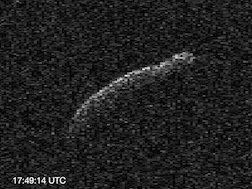
(367789) 2011 AG5, provisional designation 2011 AG5, is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It has a diameter of about 140 meters (460 ft). It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 21 December 2012 and as such it now has a rating of 0 on the Torino Scale. It was recovered in December 2022 extending the observation arc from 4.8 years to 14 years. As of 2023, the distance between the orbits of Earth and 2011 AG5 is 0.0004 AU (60,000 km; 0.16 LD)
(471240) 2011 BT15, provisional designation 2011 BT15, is a stony, sub-kilometer sized asteroid and fast rotator, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It had been one of the objects with the highest impact threat on the Palermo Technical Impact Hazard Scale.
2012 KP24 (also written 2012 KP24) is a Chelyabinsk-sized near-Earth asteroid with an observation arc of only 5 days and has a modestly determined orbit for an object of its size. Around 31 May 2023 ±3 days it will pass between 0.19–24 lunar distances (73,000–9,200,000 km) from Earth. Nominally the asteroid is expected to pass 0.026 AU (3,900,000 km; 10 LD) from Earth and brighten to around apparent magnitude 21.6.
(454101) 2013 BP73, provisional designation 2013 BP73, is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 310 meters (1,020 ft) in diameter.
2011 XC2 (also written 2011 XC2) is a near-Earth asteroid roughly 60–140 meters (200–460 ft) in diameter that passed less than 1 lunar distance from Earth on 3 December 2011.
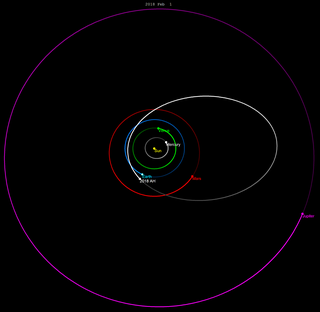
2018 AH is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 100 m (300 ft) in diameter. It was first observed on 4 January 2018, by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) on Mauna Loa and quickly followed-up by many other surveys, with precovery observations found from Pan-STARRS and PTF from the day previous.
1979 XB is a lost asteroid with a short observation arc of 3.9 days that cannot be recovered with targeted observations and awaits serendipitous survey observations. It is classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group and is estimated to be 660 meters in diameter. The unnumbered minor planet has a poorly constrained orbit and has not been observed in 44 years. It has been listed on the Sentry Risk Table since the list started in 2002. With a cumulative Palermo Technical Impact Hazard Scale of −2.72, the poorly known orbit and assumed size place 1979 XB third on an unconstrained listing of the Sentry Risk Table.

2020 CD3 (also CD3 for short) is a tiny near-Earth asteroid (or minimoon) that ordinarily orbits the Sun but makes close approaches to the Earth–Moon system, in which it can temporarily enter Earth orbit through temporary satellite capture (TSC). It was discovered at the Mount Lemmon Observatory by astronomers Theodore Pruyne and Kacper Wierzchoś on 15 February 2020, as part of the Mount Lemmon Survey or Catalina Sky Survey. The asteroid's discovery was announced by the Minor Planet Center on 25 February 2020, after subsequent observations confirmed that it was orbiting Earth.
2009 JF1 is a small near-Earth object that should have passed within 0.3 AU (45 million km) of Earth in 2022. On 5 February 2022 the 2009 observations were remeasured greatly reducing the odds of an impact. On 5 January 2024 it had a 1-in-140,000 chance of impacting Earth. It is estimated to be 10-meters in diameter which would make it smaller than the Chelyabinsk meteor. It has a very short observation arc of 1.2 days and has not been observed since 2009. On 5 January 2024 it was nominally expected to be 0.2 AU (30 million km) from Earth but has an uncertainty region of ±23 million km (0.15 AU). The nominal Earth approach was 14 January 2024 and would have had the asteroid only brightening to apparent magnitude 26 which would have made it too faint for automated surveys to detect. With a Palermo scale rating of -4.41, the odds of impact were 26000 times less than the background hazard level for an asteroid of this size.
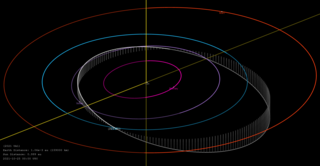
2021 UA1 is a small (~2 meter) near-Earth object that passed about 3047 km from the surface of Earth while passing over Antarctica on 25 October 2021 around 03:07 UT. Given the small size of the asteroid it only reached the brightness of Pluto at around apparent magnitude 14. Since it approached from the direction of the Sun, it was not discovered until 4 hours after closest approach.
2022 AE1 is a Tunguska event-sized asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 70 meters (230 feet) in diameter. It was discovered by the Mount Lemmon Survey on 6 January 2022, when it was 0.09 AU (13 million km) from Earth. On 9 January 2022 with an observation arc of 3 days, it was rated with a Torino scale of 1 for a virtual impactor on 4 July 2023 16:28 UTC. Nominal approach is expected to occur 1 July 2023 01:13 ± 1 day. With a Palermo scale rating of as high as –0.66 at the European Space Agency on 11 January 2022, the odds of impact peaked at about 4.6 times less than the background hazard level. NEODyS was the first risk-page to drop to Torino scale 0 on 12 January 2022 followed by ESA on 13 January 2022, but by January 14 both returned to Torino scale 1. On 14 January 2022 the waxing gibbous moon was as little as 3 degrees from the asteroid delaying observations of the asteroid from January 12–19. On 20 January 2022 with a 16-day observation arc, using JPL #11 the Sentry Risk Table dropped the asteroid to Torino scale 0 and then later that day JPL #12 resulted in it being removed from the risk table.
2022 AP7 is a kilometer-sized Apollo asteroid and potentially hazardous object orbiting between Venus and Jupiter. It was discovered on 13 January 2022 by Scott Sheppard at Cerro Tololo Observatory. Based on its absolute magnitude (H), 2022 AP7 is likely the largest potentially hazardous object identified in the eight years prior to its 2022 discovery.

2023 BU is a near-Earth object that passed 9,967 ± 1 km (6,193.21 ± 0.62 mi) from the centerpoint of Earth around 27 January 2023 00:29 UT. Since Earth's radius is about 6,378 km (3,963 mi), it was expected to pass approximately 3,589 ± 1 km (2,230.10 ± 0.62 mi) from the surface of Earth over the southern tip of South America. It passed at an altitude above low Earth orbit which is 2,000 km (1,200 mi) and below geostationary orbit which is 36,000 km (22,000 mi). The asteroid is about 3–8 meters in diameter and approached Earth from the night sky. It is the fourth closest non-impacting approach known to Earth after 2020 VT4, 2020 QG, and 2021 UA1.
References
- ↑ "MPEC 2023-O01: 2023 NT1". Minor Planet Electronic Circular. Minor Planet Center. 16 July 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2024.
- 1 2 3 "(2023 NT1) – JPL Small-Body Database Browser". ssd.jpl.nasa.gov. Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 19 October 2024.
- ↑ Leonardo De Cosmos (19 July 2023). "La Terra sfiorata da un asteroide di 30 metri, visto in ritardo - Spazio e Astronomia - Ansa.it". Agenzia ANSA (in Italian). Retrieved 6 November 2023.
- ↑ Andrew Griffin (17 July 2023). "Huge asteroid nearly crashes into Earth – and is only spotted days later". The Independent. Retrieved 6 November 2023.
- ↑ Eric Mack. "Hotel-Sized Asteroid Undetected Until Two Days After Close Pass By Earth". Forbes. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ "Horizons Batch for 2044-07-12 Virtual Impactor". JPL Horizons . Retrieved 22 July 2023. (JPL#8/Soln.date: 2023-Jul-21)
- ↑ B. K. Bailey; A. N. Cohen; D. Patel; P. Lubin; M. Boslough; et al. (2023). "Asteroid 2023 NT1: A Cautionary Tale". arXiv: 2310.13112 [astro-ph.EP].