Contents
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 2023 History of North Macedonia • Years | ||||
Events in the year 2023 in North Macedonia .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 2023 History of North Macedonia • Years | ||||
Events in the year 2023 in North Macedonia .
Ongoing — COVID-19 pandemic in North Macedonia

Bitola is a city in the southwestern part of North Macedonia. It is located in the southern part of the Pelagonia valley, surrounded by the Baba, Nidže, and Kajmakčalan mountain ranges, 14 kilometres north of the Medžitlija-Níki border crossing with Greece. The city stands at an important junction connecting the south of the Adriatic Sea region with the Aegean Sea and Central Europe, and it is an administrative, cultural, industrial, commercial, and educational centre. It has been known since the Ottoman period as the "City of Consuls", since many European countries had consulates in Bitola.

The Balkans, corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.
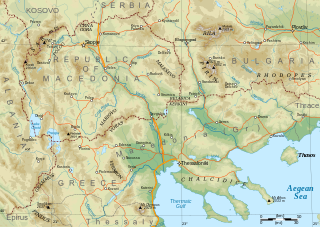
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid-19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: all of North Macedonia, large parts of Greece and Bulgaria, and smaller parts of Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately 67,000 square kilometres (25,869 sq mi) and has a population of around five million. Greek Macedonia comprises about half of Macedonia's area and population.
The history of North Macedonia encompasses the history of the territory of the modern state of North Macedonia.

Ohrid is a city in North Macedonia and is the seat of the Ohrid Municipality. It is the largest city on Lake Ohrid and the eighth-largest city in the country, with the municipality recording a population of over 42,000 inhabitants as of 2002. Ohrid is known for once having 365 churches, one for each day of the year, and has been referred to as the "Jerusalem of the Balkans". The city is rich in picturesque houses and monuments, and tourism is predominant. It is located southwest of Skopje, west of Resen and Bitola. In 1979 and in 1980, respectively, Ohrid and Lake Ohrid were accepted as Cultural and Natural World Heritage Sites by UNESCO. Ohrid is one of only 40 sites that are part of UNESCO's World Heritage that are Cultural as well as Natural sites.

Struga is a town and popular tourist destination situated in the south-western region of North Macedonia, lying on the shore of Lake Ohrid. The town of Struga is the seat of Struga Municipality.

Prilep is the sixth-largest city in North Macedonia. According to 2021 census, it had a population of 63,308.

The Church of Saint Sophia is a church in Ohrid, North Macedonia. The church is one of the most important monuments of North Macedonia, housing architecture and art from the Middle Ages.

The Macedonian Orthodox Church – Archdiocese of Ohrid, or simply the Macedonian Orthodox Church (MOC) or the Archdiocese of Ohrid (AO), is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in North Macedonia. The Macedonian Orthodox Church claims ecclesiastical jurisdiction over North Macedonia, and is also represented in the Macedonian diaspora. The primate of the Macedonian Orthodox Church is Stefan Veljanovski, the Metropolitan of Skopje and Archbishop of Ohrid and Macedonia.

Onufri, Onouphrios of Neokastro or Onouphrios Argytes, was a 16th century Archpriest of Elbasan and the most important painter of Orthodox murals and icons in the early post-Byzantine era in Albania. He founded a school of painting in Berat and extended his influence as far afield as Kastoria. Trained in Venice, he infused Albanian icon painting with the artistic climate of the Italian Renaissance. His works reveal a great degree of originality and ecclesiastically combined post-Byzantine and Gothic elements. Onufri's works played a decisive role in the following trends of Albanian art, up to the 19th century.

Strumica is the largest city in southeastern North Macedonia, near the Novo Selo-Petrich border crossing with Bulgaria. About 54,676 people live in the region surrounding the city. It is named after the Strumica River which runs through it. The city of Strumica is the seat of Strumica Municipality.
The Serbian mafia, or Serbian organized crime, are various criminal organizations based in Serbia or composed of ethnic Serbs in the former Yugoslavia and Serbian diaspora. The organizations are primarily involved in smuggling, arms trafficking, drug trafficking, human trafficking, assassinations, heists, assault, protection rackets, murder, money laundering and illegal gambling. Ethnic Serb organized crime groups are organized horizontally; higher-ranked members are not necessarily coordinated by any leader. According to criminologists and law enforcement authorities, the Serbian mafia is the most powerful in Europe.

The Serbs are one of the constitutional ethnic groups of North Macedonia, numbering about 24,000 inhabitants.

The Liberation Army of Chameria is a reported paramilitary organization founded in 2001 that is active in the northwestern Greek region of Epirus. The group is reportedly linked to the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA) and National Liberation Army (NLA), both ethnic Albanian militant groups.

The Albanian National Army is an Albanian paramilitary organization which operates in North Macedonia, Serbia and Kosovo. The group opposes the Ohrid Framework Agreement which ended the 2001 insurgency in Macedonia between members of the National Liberation Army and Macedonian security forces.

The Bulgarians in Albania live mostly in the areas of Mala Prespa, Gollobordë and Gora. Ethnic identity can be fluid among Albania's Slavophonic population, who might identify as Albanian, Bulgarian or Macedonian, depending on the circumstances. Between 2001 and 2016, around 4,470 Albanian nationals applied for a Bulgarian citizenship and over 2,600 of them were granted one. The Bulgarian minority was recognized by the Albanian government in October 2017. In the 2023 Albania census, 7,057 people declared themselves to be Bulgarians making them the largest Slavophone population in Albania.

Law enforcement in North Macedonia is the responsibility of the Police of the Republic of North Macedonia.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the north. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's population of 1.83 million. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Roma, Serbs, Bosniaks, Aromanians and a few other minorities.

Kolonjë is a municipality in Korçë County, southeastern Albania. It was created in 2015 by the merger of the former municipalities Barmash, Çlirim, Ersekë, Leskovik, Mollas, Novoselë, Qendër Ersekë and Qendër Leskovik. The seat of the municipality is the town Ersekë. The total population is 11,070, in a total area of 865 km2 (334 sq mi). It is an ethnographic region.

In early July 2022, protests began in Skopje, North Macedonia. The protests were triggered by Bulgaria–North Macedonia negotiations surrounding the accession of the latter into the European Union.