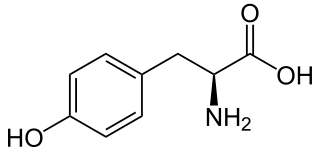
L-Tyrosine or tyrosine or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek tyrós, meaning cheese, as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA.

A catecholamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol and a side-chain amine.
Dopa or DOPA may refer to:
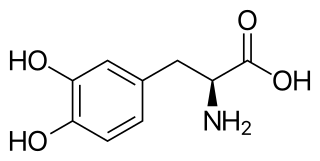
l-DOPA, also known as levodopa and l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is an amino acid that is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize l-DOPA, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid l-tyrosine. l-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, l-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. l-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, and Stalevo. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.

d-DOPA is similar to l-DOPA (levodopa), but with opposite chirality. Levo- and dextro- rotation refer to a molecule's ability to rotate planes of polarized light in one or the other direction. Whereas l-DOPA is moderately effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) and dopamine-responsive dystonia (DRD) by stimulating the production of dopamine in the brain, d-DOPA is biologically inactive.
Tyrosine hydroxylase or tyrosine 3-monooxygenase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of the amino acid L-tyrosine to L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA). It does so using molecular oxygen (O2), as well as iron (Fe2+) and tetrahydrobiopterin as cofactors. L-DOPA is a precursor for dopamine, which, in turn, is a precursor for the important neurotransmitters norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline). Tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the rate limiting step in this synthesis of catecholamines. In humans, tyrosine hydroxylase is encoded by the TH gene, and the enzyme is present in the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral sympathetic neurons and the adrenal medulla. Tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylalanine hydroxylase and tryptophan hydroxylase together make up the family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases (AAAHs).
Dihydroxyphenylalanine may refer to either of two chemical compounds:

4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a stizolobate synthase (EC 1.13.11.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a stizolobinate synthase (EC 1.13.11.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dihydroxyphenylalanine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.11, entry deleted) is a non-existing enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dihydroxyphenylalanine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Rhodobacter sphaeroides is a kind of purple bacterium; a group of bacteria that can obtain energy through photosynthesis. Its best growth conditions are anaerobic phototrophy and aerobic chemoheterotrophy in the absence of light. R. sphaeroides is also able to fix nitrogen. It is remarkably metabolically diverse, as it is able to grow heterotrophically via fermentation and aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Such a metabolic versatility has motivated the investigation of R. sphaeroides as a microbial cell factory for biotechnological applications.

α-Difluoromethyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine is a DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor.
The TH gene codes for the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase.
1-Hydroxycarotenoid 3,4-desaturase is an enzyme with systematic name 1-hydroxy-1,2-dihydrolycopene:acceptor oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phytoene desaturase (neurosporene-forming) is an enzyme with systematic name 15-cis-phytoene:acceptor oxidoreductase (neurosporene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine oxidative deaminase (EC 1.13.12.15, 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine: oxidative deaminase, oxidative deaminase, DOPA oxidative deaminase, DOPAODA) is an enzyme with systematic name 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine:oxygen oxidoreductase (deaminating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
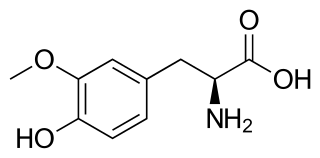
3-O-Methyldopa (3-OMD) is one of the most important metabolites of L-DOPA, a drug used in the treatment of the Parkinson's disease.

Chlorophyllide a and Chlorophyllide b are the biosynthetic precursors of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b respectively. Their propionic acid groups are converted to phytyl esters by the enzyme chlorophyll synthase in the final step of the pathway. Thus the main interest in these chemical compounds has been in the study of chlorophyll biosynthesis in plants, algae and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyllide a is also an intermediate in the biosynthesis of bacteriochlorophylls.









