
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value with respect to a change in its argument. Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances.

In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn, form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
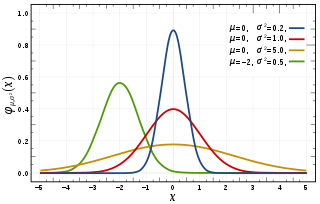
In probability theory, a normaldistribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is

The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of elements, is a tabular display of the chemical elements, which are arranged by atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The structure of the table shows periodic trends. The seven rows of the table, called periods, generally have metals on the left and nonmetals on the right. The columns, called groups, contain elements with similar chemical behaviours. Six groups have accepted names as well as assigned numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18 are the noble gases. Also displayed are four simple rectangular areas or blocks associated with the filling of different atomic orbitals.
The number π is a mathematical constant. It is defined as the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, and it also has various equivalent definitions. It appears in many formulas in all areas of mathematics and physics. The earliest known use of the Greek letter π to represent the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter was by Welsh mathematician William Jones in 1706. It is approximately equal to 3.14159. It has been represented by the Greek letter "π" since the mid-18th century, and is spelled out as "pi". It is also referred to as Archimedes' constant.

In mathematics, the Taylor series of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor's series are named after Brook Taylor who introduced them in 1715.
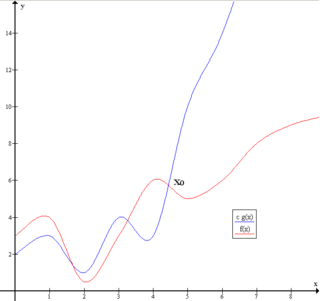
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation.

In mathematics, a Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions depending on space or time into functions depending on spatial or temporal frequency, such as the expression of a musical chord in terms of the volumes and frequencies of its constituent notes. The term Fourier transform refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of space or time.
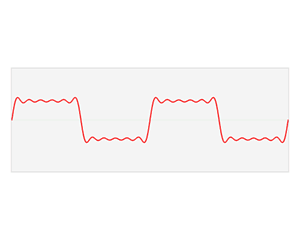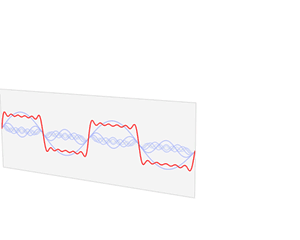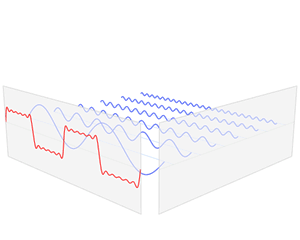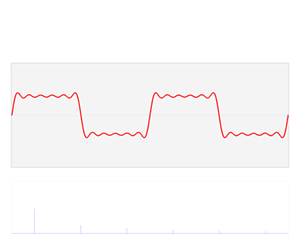
In mathematics, a Fourier series is a periodic function composed of harmonically related sinusoids, combined by a weighted summation. With appropriate weights, one cycle of the summation can be made to approximate an arbitrary function in that interval. As such, the summation is a synthesis of another function. The discrete-time Fourier transform is an example of Fourier series. The process of deriving weights that describe a given function is a form of Fourier analysis. For functions on unbounded intervals, the analysis and synthesis analogies are Fourier transform and inverse transform.

The Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor is an American single-seat, twin-engine, all-weather stealth tactical fighter aircraft developed exclusively for the United States Air Force (USAF). The result of the USAF's Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) program, the aircraft was designed primarily as an air superiority fighter, but also has ground attack, electronic warfare, and signal intelligence capabilities. The prime contractor, Lockheed Martin, built most of the F-22's airframe and weapons systems and conducted final assembly, while Boeing provided the wings, aft fuselage, avionics integration, and training systems.

In mathematics, a function is a binary relation between two sets that associates to each element of the first set exactly one element of the second set. Typical examples are functions from integers to integers, or from the real numbers to real numbers.

The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894-1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system.

Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have alkyl substituents at the 3- or 4-position(s). They are also colored solids, but tend to be soluble in organic solvents.

Petroleum products are materials derived from crude oil (petroleum) as it is processed in oil refineries. Unlike petrochemicals, which are a collection of well-defined usually pure organic compounds, petroleum products are complex mixtures. The majority of petroleum is converted to petroleum products, which includes several classes of fuels.
SHA-2 is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001. They are built using the Merkle–Damgård construction, from a one-way compression function itself built using the Davies–Meyer structure from a specialized block cipher.

Itaconic acid, or methylidenesuccinic acid, is an organic compound. This dicarboxylic acid is a white solid that is soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone. Historically, itaconic acid was obtained by the distillation of citric acid, but currently it is produced by fermentation. The name itaconic acid was devised as an anagram of aconitic acid, another derivative of citric acid.

The 2021 FIA Formula One World Championship is a motor racing championship for Formula One cars which is the 72nd running of the Formula One World Championship. It is recognised by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA), the governing body of international motorsport, as the highest class of competition for open-wheel racing cars. The championship is being contested over twenty-three Grands Prix, which will be held around the world. Drivers and teams are scheduled to compete for the titles of World Drivers' Champion and World Constructors' Champion respectively.

2-Methylthiophene is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3C4H3S. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. It can be produced by Wolff-Kishner reduction of thiophene-2-carboxaldehyde.

2-Methylsuccinic acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH(CH3)CH2CO2H. A white solid, it is the simplest chiral dicarboxylic acid. It is a recurring component of urban aerosols. Salts and esters of 2-methylsuccinic acid are called 2-methylsuccinates.
Methylthiophene may refer to:



















