
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Quasars are usually categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of cosmological origin.

3C 273 is a quasar located at the center of a giant elliptical galaxy in the constellation of Virgo. It was the first quasar ever to be identified and is the visually brightest quasar in the sky as seen from Earth, with an apparent visual magnitude of 12.9. The derived distance to this object is 749 megaparsecs. The mass of its central supermassive black hole is approximately 886 million times the mass of the Sun.

A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the jet makes blazars appear much brighter than they would be if the jet were pointed in a direction away from Earth. Blazars are powerful sources of emission across the electromagnetic spectrum and are observed to be sources of high-energy gamma ray photons. Blazars are highly variable sources, often undergoing rapid and dramatic fluctuations in brightness on short timescales. Some blazar jets appear to exhibit superluminal motion, another consequence of material in the jet traveling toward the observer at nearly the speed of light.

The Perseus cluster is a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Perseus. It has a recession speed of 5,366 km/s and a diameter of 863′. It is one of the most massive objects in the known universe, containing thousands of galaxies immersed in a vast cloud of multimillion-degree gas.

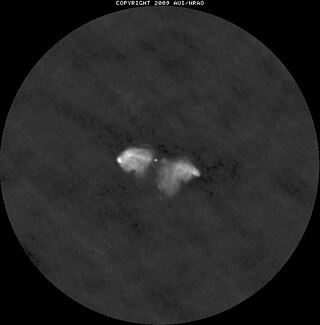
Abell 400 is a galaxy cluster which contains the galaxy NGC 1128 with two supermassive black holes spiraling towards merger.

3C 75 is a binary black hole system in the dumbbell-shaped galaxy NGC 1128 in the galaxy cluster Abell 400. It has four relativistic jets, two coming from each accreting supermassive black hole. It is travelling at 1200 kilometers per second, causing the jets to be swept back. 3C 75 may be X-ray source 2A 0252+060.

3C 295 is a narrow-line radio galaxy located in the constellation of Boötes. With a redshift of 0.464, it is approximately 5 billion light-years from Earth. At time of the discovery of its redshift in 1960, this was the remotest object known.

NGC 1265 is a Fanaroff and Riley class 1 radio galaxy located in the constellation Perseus, a member of the Perseus Cluster.

3C 390.3 is a broad-line radio galaxy located in the constellation Draco. It is also a Seyfert 1 galaxy which is an X-ray source.

3C 66B is an elliptical Fanaroff and Riley class 1 radio galaxy located in the constellation Andromeda. With an estimated redshift of 0.021258, the galaxy is about 300 million light-years away.

3C 79 is a Seyfert Galaxy located in the constellation Aries. The extended emission-line region (EELR) is almost certainly photoionized by the hidden quasar.

Ursa Major B or 3C 244.1 is a radio galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major.
3C 285 is a radio galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is located about 1 bilion light years away. It is a Fanaroff-Riley 2 radio galaxy and is hosted in a disturbed spiral galaxy.
3C 401 is a powerful radio galaxy located in the constellation Draco. It is near the center of a rich cluster of galaxies and dominates the cluster. That is, it is the type-cD galaxy of its cluster. It has a double nucleus, indicating that it is merging with another galaxy.

3C 438 is a Seyfert galaxy and Fanaroff and Riley class II radio galaxy located in the constellation Cygnus. The radio galaxy has two lobes and there is a radio jet leading to the south lobe, which also has a prominent double hot spot. There is age variation across the lobes.

3C 66A is a blazar located in the constellation Andromeda.

3C 147 (B0538+498) is a compact steep-spectrum (CSS) quasar that was discovered in 1964. It is located in the constellation Auriga not far in the sky from the 5th magnitude star Omicron Aurigae.

NGC 3862 is an elliptical galaxy located 300 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. Discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785, NGC 3862 is an outlying member of the Leo Cluster.

NGC 4523 is a Magellanic spiral galaxy located about 35 to 50 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on April 19, 1865. NGC 4523 is a member of the Virgo Cluster. A distance of for NGC 4523 was derived from using yellow supergiants in the galaxy as standard candles.

NGC 547 is an elliptical galaxy and radio galaxy located in the constellation Cetus. It is located at a distance of circa 220 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 547 is about 120,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 1, 1785. It is a member of the Abell 194 galaxy cluster and is included along with NGC 547 in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.



















