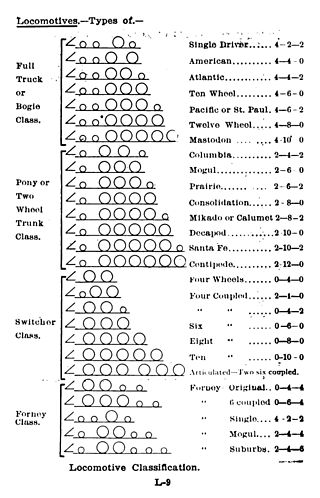
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-10-4 locomotive has two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a Bissel truck, ten coupled driving wheels on five axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles, usually in a bogie. These were referred to as the Texas type in most of the United States, the Colorado type on the Burlington Route, and the Selkirk type in Canada.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-2-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle and no trailing wheels. This type of locomotive is often called a Jervis type, the name of the original designer.
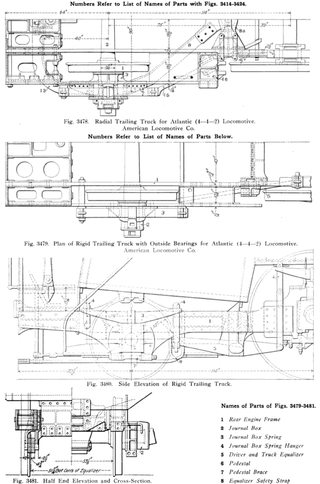
Locomotive classification on the Pennsylvania Railroad took several forms. Early on, steam locomotives were given single-letter classes. As the 26 letters were quickly assigned, that scheme was abandoned for a more complex system. This was used for all of the PRR's steam locomotives, and — with the exception of the final type bought — all electric locomotives also used this scheme.

A 6-4-4-6 steam locomotive, in the Whyte notation for describing locomotive wheel arrangements, is one with six leading wheels, two sets of four driving wheels, and six trailing wheels.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-4-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles. In the United States, this arrangement was named the Reading type, since the Philadelphia and Reading Railroad was the first to use it. In Canada, this type is known as the Jubilee.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle.

The PRR S1 class steam locomotive was a single experimental duplex locomotive of the Pennsylvania Railroad. It was designed to demonstrate the advantages of duplex drives espoused by Baldwin Chief Engineer Ralph P. Johnson. It was the longest and heaviest rigid frame reciprocating steam locomotive that was ever built. The streamlined Art Deco styled shell of the locomotive was designed by Raymond Loewy.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-4-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The type is sometimes named Columbia after a Baldwin 2-4-2 locomotive was showcased at the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition held at Chicago, Illinois.
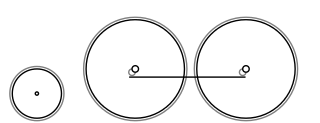
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing truck. On some large locomotives, a booster engine was mounted on the trailing truck to provide extra tractive effort when starting a heavy train and at low speeds on gradients.

In Whyte notation, a 4-6-6-4 is a railroad steam locomotive that has four leading wheels followed by six coupled driving wheels, a second set of six driving wheels and four trailing wheels. 4-6-6-4's are commonly known as Challengers.

The Union Pacific Railroad 9000 Class was a class of 88 steam locomotives, built by ALCO for the Union Pacific between 1926 and 1930.
In Whyte notation, 2-4-4-2 refers to a railroad steam locomotive that has two leading wheels followed by four coupled driving wheels, a second set of four coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels.
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-4-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and no trailing wheels. In most of North America it became known as a Porter.
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 4-8-6 locomotive would have had four leading wheels, eight coupled driving wheels and six trailing wheels.

The Pennsylvania Railroad's class R1 comprised a single prototype electric locomotive constructed in 1934 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA, with the electrical equipment by Westinghouse.
The Pennsylvania Railroad class Q1, #6130, was a single experimental steam locomotive designed for dual service. The locomotive entered service in 1942, and retired in 1949 after accumulating a relatively low 165,000 service miles.

A triplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using three pairs of cylinders powering three sets of driving wheels. Inevitably any such locomotive will be articulated. All the examples that have been produced were of the Mallet type but with one extra set of driving wheels under the tender.
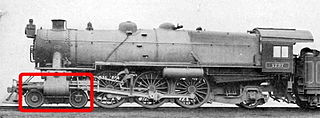
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck. Leading wheels are used to help the locomotive negotiate curves and to support the front portion of the boiler.

A duplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using two pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame; it is not an articulated locomotive. The concept was first used in France in 1863, but was particularly developed in the early 1930s by the Baldwin Locomotive Works, the largest commercial builder of steam locomotives in North America, under the supervision of its then chief engineer, Ralph P. Johnson.















