
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. The 4-6-2 locomotive became almost globally known as a Pacific type.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This type of steam locomotive is commonly known as the Mountain type.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of locomotives, 4-6-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels. In France where the type was first used, it is known as the Baltic while it became known as the Hudson in most of North America.

4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, 4-6-0 represents the configuration of four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the absence of trailing wheels. In the mid 19th century, this wheel arrangement became the second most popular configuration for new steam locomotives in the United States, where this type is commonly referred to as a ten-wheeler. As a locomotive pulling trains of lightweight all-wood passenger cars in the 1890–1920s, it was exceptionally stable at near 100 mph (160 km/h) speeds on the New York Central's New York to Chicago Water Level Route and on the Reading Railroad's Camden to Atlantic City, NJ, line. As passenger equipment grew heavier with all steel construction, heavier locomotives replaced the ten-wheeler.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Mogul.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. In the United States and elsewhere, this wheel arrangement is commonly known as a Consolidation, after the Lehigh and Mahanoy Railroad’s Consolidation, the name of the first 2-8-0.
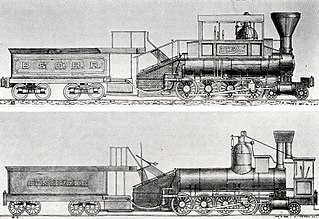
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, usually in a leading truck or bogie, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and no trailing wheels. In North America and in some other countries the type was usually known as the Twelve-wheeler.
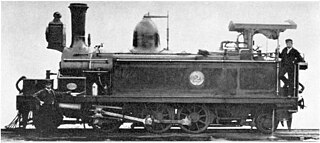
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Prairie.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-12-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, twelve coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels. This arrangement was named the Union Pacific type, after the only railroad to use it, the Union Pacific Railroad.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, 2-6-6-0 is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels and no trailing wheels. The wheel arrangement was principally used on Mallet-type articulated locomotives. Some tank locomotive examples were also built, for which various suffixes to indicate the type of tank would be added to the wheel arrangement, for example 2-6-6-0T for an engine with side-tanks.

The South African Railways Class H 4-10-2T, introduced in 1899, was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
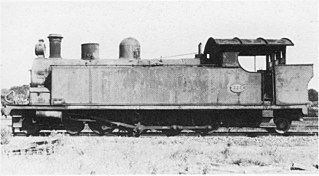
The South African Railways Class H1 4-8-2T of 1903 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.

The South African Railways Class H2 4-8-2T of 1909 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
The South African Railways Class 1 4-8-0 of 1904 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
The South African Railways Class 2C 4-6-2 of 1910 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The South African Railways Class G 4-8-2T of 1904 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.

The South African Railways Class MA 2-6-6-0 of 1909 was a steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Natal Colony.

The Central South African Railways Class E 4-10-2T of 1901 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.

The Natal Government Railways 4-6-2TT Havelock of 1888 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Natal Colony.




















