The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet-Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union during World War II. It began with a Finnish declaration of war and invasion on 25 June 1941 and ended on 19 September 1944 with the Moscow Armistice. The Soviet Union and Finland had previously fought the Winter War from 1939 to 1940, which ended with the Soviet failure to conquer Finland and the Moscow Peace Treaty. Numerous reasons have been proposed for the Finnish decision to invade, with regaining territory lost during the Winter War regarded as the most common. Other justifications for the conflict include Finnish President Risto Ryti's vision of a Greater Finland and Commander-in-Chief Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim's desire to annex East Karelia.

The siege of Leningrad was a prolonged military siege undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of Leningrad on the Eastern Front of World War II. Germany's Army Group North advanced from the south, while the German-allied Finnish army invaded from the north and completed the ring around the city.

The Battle of Narva was a World War II military campaign, lasting from 2 February to 10 August 1944, in which the German Army Detachment "Narwa" and the Soviet Leningrad Front fought for possession of the strategically important Narva Isthmus.

The Northwestern Front was a military formation of the Red Army during the Winter War and World War II. It was operational with the 7th and 13th Armies during the Winter War. It was re-created on 22 June 1941, the first day of the Eastern Front on the basis of the Baltic Special Military District. On 22 June the Front consisted of the 8th, 11th, and 27th Armies, as well as the 5th Airborne Corps and the headquarters of the 65th Rifle Corps.
The Volkhov Front was a major formation of the Red Army during the first period of the Second World War. It was formed as an expediency of an early attempt to halt the advance of the Wehrmacht Army Group North in its offensive thrust towards Leningrad. Initially the front operated to the south of Leningrad, with its flank on Lake Ladoga.

The 7th Army was a Soviet Red Army field army during World War II, primarily against Finland. It was disbanded in 1944.

The Finnish invasion of the Karelian Isthmus refers to a military campaign carried out by Finland in 1941. It was part of what is commonly referred to as the Continuation War. Early in the war Finnish forces liberated the Karelian Isthmus. It had been ceded to the Soviet Union on 13 March 1940, in the Moscow Peace Treaty, which marked the end of the Winter War. Later, in the summer of 1944, the Soviet Union reconquered the southern part of the isthmus in the Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive.

The Narva offensive was an operation conducted by the Soviet Leningrad Front. It was aimed at the conquest of the Narva Isthmus from the German army detachment "Narwa". At the time of the operation, Joseph Stalin, the supreme commander of the Soviet Armed Forces, was personally interested in taking Estonia, viewing it as a precondition to forcing Finland out of the war.
The 11th Rifle Division was a military formation of the Soviet Union's Red Army. Its personnel were involved in the protection of the demarcation line in Pskov, defensive battles against the Army of the Southern Front in Krasnov Novohopersk - Borisoglebsk, against the army and the forces of Estonia, Bulak Balakhovich in Marienburg in defense of Petrograd and as the offensive against Yudenich's troops in Pskov the Luga-Gdov, Yamburg, Narva, Dvina-Rezhitsk directions, the Polish-Soviet war of 1920, in the suppression of the Kronstadt uprising participated in the Soviet-Finnish War and World War II.
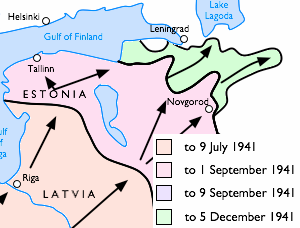
Leningrad strategic defensive operation is the term in Soviet historiography for the defensive operations in the area south of Leningrad by the Red Army and the Soviet Navy during World War II from 10 July to 30 September 1941. The following operations are considered as part of the strategic operation:
The 48th Army was a field army of the Soviet Red Army, active from 1941 to 1945. The army was first formed in August 1941 and fought in the Leningrad Strategic Defensive Operation. The army suffered heavy losses and was disbanded in early September. Its remnants were moved to the 54th Army. Reformed in April 1942 on the Bryansk Front, the army fought in the Maloarkhangelsk Offensive in the winter of 1943. It was sent to the Central Front in March and defended the northern face of the Kursk Bulge. During the summer, it fought in Operation Kutuzov and the Chernigov-Pripyat Offensive. From November, the army fought in the Gomel-Rechitsa Offensive. The army fought in Operation Bagration from June 1944. During the offensive, the army captured Zhlobin and Bobruisk and was on the Narew by early September. During early 1945, the army fought in the East Prussian Offensive and ended the war in East Prussia during May. The army was transferred to Poland in July 1945 and its headquarters was used to form the Kazan Military District in September.
The 1st Army Corps was an army corps of the Soviet Armed Forces. It was formed in 1957 and finally deactivated in 1991. It draws its history from the 1st Rifle Corps, formed in 1922. Troops of the 1st Rifle Corps participated in the Winter War and World War II.
The 109th Rifle Division was a Red Army infantry division that was formed three times, briefly in 1939, during 1942, and again from 1942 to 1946. The first formation of the division was converted to a mechanized division after about nine months. Its second formation served for six months in 1942 in the defense of the fortress of Sevastopol, in the southern sector of the siege lines. After being destroyed there in July, a third division was formed by re-designating an existing rifle division near Leningrad in August, and it successfully held its positions for nearly a year and a half, in spite of shortages of food and supplies due to the German/Finnish siege. The 109th then participated in the Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive that drove the Germans and Finns away from the city and lifted the siege in early 1944, helped drive Finland out of the war in the Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive, and then joined the offensive along the Baltic coast towards Germany. This third formation compiled an admirable record of service, but was disbanded in 1946.
The Red Army's 54th Army was a Soviet field army during the Second World War. It was first formed in the Leningrad Military District in August, 1941, and continued in service in the northern sector of the Soviet-German front until the end of 1944. It spent much of the war attempting to break the German siege of Leningrad, in which it helped to achieve partial success in January, 1943, and complete success one year later. During these operations the soldiers of the 54th served under five different commanders, most notably Col. Gen. Ivan Fedyuninsky in the winter of 1941–42. After helping to drive Army Group North away from Leningrad and into the Baltic states in the first nine months of 1944, the army was deemed surplus to requirements on the narrowing front, and was officially disbanded on the last day of the year.

The 310th Rifle Division was a standard Red Army rifle division formed on July 15, 1941 in Kazakhstan before being sent to the vicinity of Leningrad, where it spent most of the war, sharing a similar combat path with its "sister", the 311th Rifle Division. The soldiers of the division fought until early 1944 to, first, hold open some sort of lifeline to the besieged city, then to break the siege and drive off the besieging German forces. They then participated in the offensive that drove Germany's Finnish allies out of the war. Finally, the division was redeployed to take the fight to the German heartland in the winter and spring of 1945. It ended the war north of Berlin with a very creditable combat record for any rifle division.
The 49th Rifle Division was a Soviet Army infantry division, formed three times. First formed as a territorial division in 1931, the 49th Rifle Division's first formation became a regular division by 1939 and fought in the Winter War. For its actions during the war, it was awarded the Order of the Red Banner. However, the 49th Rifle Division was wiped out during the first ten days of Operation Barbarossa. Its second formation occurred in December 1941 and fought at Stalingrad, Kursk, the Vistula-Oder Offensive and the Battle of Berlin. The second formation was disbanded in 1946. The division was reformed in 1955 by renaming the 295th Rifle Division and became the 49th Motor Rifle Division in 1957.

The 314th Rifle Division was a standard Red Army rifle division formed on July 15, 1941 at Petropavlovsk in northern Kazakhstan, before being sent to the vicinity of Leningrad, in the 7th Separate Army east of Lake Ladoga, facing the Finnish Army in East Karelia for more than a year. In consequence the division saw relatively uneventful service on this mostly quiet front until the autumn of 1942, when it was moved south to face German Army Group North, and took a leading role in Operation Iskra, which finally drove a land corridor through to besieged Leningrad in January 1943; a year later it also served prominently in the offensive that broke the enemy siege for good. During the summer the division played a role in the offensive that drove Finland out of the war. Following this, the 314th spent a few months fighting in the Baltic States, before being reassigned southwards to 1st Ukrainian Front to take the fight into Poland and then into the German heartland in the winter and spring of 1945. It ended the war in Czechoslovakia with a distinguished record of service.
The 11th Rifle Corps was a corps of the Red Army, formed twice.

The Battle of Porlampi, also known as the Battle of Porlammi, was a military engagement fought between the Finnish Army and Red Army from 30 August to 1 September 1941 on the Karelian Isthmus. The battle was fought near the town of Porlampi during the second month of the Continuation War. The battle was a Finnish victory and effectively ended the reconquest of Karelia.
The 177th Rifle Division was formed as an infantry division of the Red Army south of Leningrad in March 1941, based on the shtat of September 13, 1939. As Army Group North advanced on Leningrad the division, still incomplete, was rushed south to the Luga area. In mid-July it helped provide the initial resistance to the LVI Motorized Corps which set up the counterstroke at Soltsy, the first significant check of the German drive on Leningrad. In August the German offensive was intensified and the defenders of Luga were encircled and forced to escape northward, losing heavily in the process. A remnant of the 177th reached Leningrad, where it received enough replacements to again be marginally combat-effective. In October to was moved to the Neva River line as part of the Eastern Sector Operational Group. After briefly coming under command of 55th Army it was moved across Lake Ladoga to join 54th Army. It remained in this Army, as part of Volkhov Front, almost continuously until early 1944, serving west of the Volkhov River. It took part in the winter offensive that finally drove Army Group North away from Leningrad and earned a battle honor for the liberation of Lyuban, where part of it had been raised in 1941. Following this victory it was reassigned to 2nd Shock Army in Leningrad Front, and took part in the unsuccessful efforts to retake the city of Narva, before being removed to the Reserve of the Supreme High Command in April for further rebuilding and replenishment. It returned to the fighting front at the beginning of May in 21st Army facing Finland. At the outset of the final offensive against Finland it was in 23rd Army in the Karelian Isthmus. During this operation it advanced through the central part of the isthmus against determined Finnish resistance. The division remained facing Finland until early 1945, when it was moved to Latvia and spent the remainder of the war containing the German forces trapped in Courland, eventually assisting in clearing the region after the German surrender in May. It was moved to the Gorkii Military District in August, and was disbanded there in April 1946.