
A turbocharger, colloquially known as a turbo, is a turbine-driven forced induction device that increases an internal combustion engine's efficiency and power output by forcing extra compressed air into the combustion chamber. This improvement over a naturally aspirated engine's power output is due to the fact that the compressor can force more air—and proportionately more fuel—into the combustion chamber than atmospheric pressure alone.

Engine tuning is the adjustment or modification of the internal combustion engine or Engine Control Unit (ECU) to yield optimal performance and increase the engine's power output, economy, or durability. These goals may be mutually exclusive; an engine may be de-tuned with respect to output power in exchange for better economy or longer engine life due to lessened stress on engine components.

Car tuning is the modification of the performance. Most vehicles stay stock for an average driver's expectations and conditions, although tuning has become a way to personalize the characteristics of a vehicle to the owner's preference. Cars may be altered to provide better fuel economy, produce more power, or provide better handling and driving.

The RB engine is a 2.0–3.0 L straight-6 four-stroke gasoline from Nissan, produced from 1985–2004 and will be continuing production in 2019, after a 15 year hiatus.

Power Stroke is a name used by a family of diesel engines for trucks produced by Ford Motor Company since 1994. Along with its use in the Ford F-Series, applications include the Ford E-Series, Ford Excursion, and Ford LCF commercial truck; the name was also used for a diesel engine used in South American production of the Ford Ranger.
Lean-burn refers to the burning of fuel with an excess of air in an internal combustion engine. In lean-burn engines the air:fuel ratio may be as lean as 65:1. The air / fuel ratio needed to stoichiometrically combust fuel, by contrast, is 14.64:1. The excess of air in a lean-burn engine emits far less hydrocarbons. High air–fuel ratios can also be used to reduce losses caused by other engine power management systems such as throttling losses.
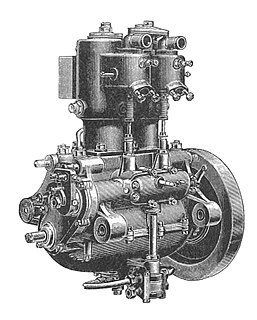
A crankcase is the housing for the crankshaft in a reciprocating internal combustion engine. The enclosure forms the largest cavity in the engine and is located below the cylinder(s), which in a multicylinder engine is usually integrated into one or several cylinder blocks. Crankcases have often been discrete parts, but more often they are integral with the cylinder bank(s), forming an engine block. Nevertheless, the area around the crankshaft is still usually called the crankcase. Crankcases and other basic engine structural components are typically made of cast iron or cast aluminium via sand casting. Today the foundry processes are usually highly automated, with a few skilled workers to manage the casting of thousands of parts.

The Toyota S Series engines are a family of straight-4 engines with displacement from 1.8 L to 2.2 L produced by Toyota Motor Corporation from January 1980 to August 2007. The series has cast iron engine blocks and alloy cylinder heads.

Variable-geometry turbochargers (VGTs),, are a family of turbochargers, usually designed to allow the effective aspect ratio (A:R) of the turbo to be altered as conditions change. This is done because optimum aspect ratio at low engine speeds is very different from that at high engine speeds. If the aspect ratio is too large, the turbo will fail to create boost at low speeds; if the aspect ratio is too small, the turbo will choke the engine at high speeds, leading to high exhaust manifold pressures, high pumping losses, and ultimately lower power output. By altering the geometry of the turbine housing as the engine accelerates, the turbo's aspect ratio can be maintained at its optimum. Because of this, VGTs have a minimal amount of lag, have a low boost threshold, and are very efficient at higher engine speeds. VGTs do not require a wastegate.
Twincharger refers to a compound forced induction system used on some piston-type internal combustion engines. It is a combination of an exhaust-driven turbocharger and a mechanically-driven supercharger, each mitigating the weaknesses of the other. A mechanically-driven supercharger offers exceptional response and low-rpm performance as it does not rely on pressurization of the exhaust manifold. A turbocharger sized to move a large volume of air tends to respond slowly to throttle input while a smaller, faster-responding turbo may fail to deliver suffcient volume through an engines upper RPM range. The unacceptable lag time endemic to a large turbocharger is effectively neutralized when combined with a supercharger which tends to generate substantial boost pressure much faster in response to throttle input. The end result being a zero-lag powerband with high torque at lower engine speeds and increased power at the upper end. Twincharging is therefore desirable for small-displacement motors, especially those with a large operating rpm, since they can take advantage of an artificially broad torque band over a large speed range.
In an internal combustion engine, a crankcase ventilation system (CVS) is a one way, pressure-sensitive passage which allows the natural build up of gases to escape from the crankcase in a controlled manner.
Twin-turbo or biturbo refers to a turbocharged engine in which two turbochargers compress the intake charge. The most common layout features two identical turbochargers in parallel; other twin-turbo layouts include sequential and staged turbocharging, the latter of which is used in diesel auto racing applications.

The PACE Award is an annual award from Automotive News in collaboration with Ernst & Young and through 2016 the Transportation Research Center Inc.. For the 2016-17 awards OESA, the Original Equipment Suppliers Association, will be a sponsor alongside EY. Automotive News and EY founded the award to celebrate innovation, technological advancement and business performance among automotive suppliers. It is given annually since 1995 in a black-tie ceremony the week of the SAE convention in Detroit.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to automobiles:

The VR is a series of twin-turbo DOHC V6 automobile engines from Nissan with displacements varying from 3.0 to 3.8 L. An evolution of the widely successful VQ series, it also draws on developments from the VRH, JGTC, and Nissan R390 GT1 Le Mans racing engines.

A tuned exhaust system is an exhaust system for an internal combustion engine which improves its efficiency by using precise geometry to reflect the pressure waves from the exhaust valve or port back to the valve or port at a particular time in the cycle.
Red Victor 3 is the latest in a line of street legal cars named 'Red Victor' and is the brainchild of British mechanic Andy Frost (Autosports), creator and builder of Red Victor 1 and Red Victor 2. Built in conjunction with Wayne Allman, Jon Webster and Dale Edmonds and Darryl Coleman, the work on the car took three years, and it was completed in June 2012. It completed the Santa Pod Raceway quarter mile track in 6.40s at 225 mph in 2013 and 6.59 seconds at 220 mph in 2012.















