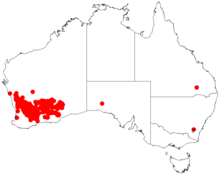
Acacia cyclops, commonly known as coastal wattle, cyclops wattle, one-eyed wattle, red-eyed wattle, redwreath acacia, western coastal wattle, rooikrans, rooikrans acacia, is a coastal shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae. Native to Australia, it is distributed along the west coast of Western Australia as far north as Leeman, and along the south coast into South Australia. The Noongar peoples of Western Australia know the plant as wilyawa or woolya wah.

Acacia saligna, commonly known by various names including coojong, golden wreath wattle, orange wattle, blue-leafed wattle, Western Australian golden wattle, and, in Africa, Port Jackson willow, is a small tree in the family Fabaceae. Native to Australia, it is widely distributed throughout the south west corner of Western Australia, extending north as far as the Murchison River, and east to Israelite Bay. The Noongar peoples know the tree as Cujong.
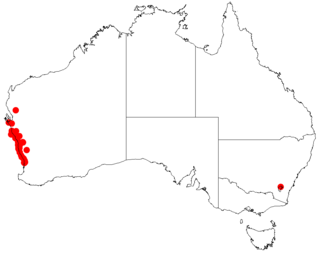
Acacia xanthina, commonly known as white stemmed wattle, is a coastal shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia citrinoviridis, commonly known as black mulga, river jam, milhan or wantan, is a tree in the family Fabaceae that is native to western Australia.

Acacia coolgardiensis, commonly known as sugar brother or spinifex wattle, is a shrub in the family Fabaceae. Endemic to Western Australia, it is widely distributed in the semi-arid spinifex country from Carnarvon to Kalgoorlie.

Acacia coriacea, commonly known as river jam, wirewood, desert oak, wiry wattle or dogwood, is a tree in the family Mimosoideae of family Fabaceae. Indigenous Australians know the plant as Gunandru.

Acacia kempeana, commonly known as wanderrie wattle, witchetty bush or granite wattle, is a shrub in subfamily Mimosoideae of family Fabaceae that is endemic to arid parts of central and western Australia.

Acacia tetragonophylla, commonly known as curara, kurara or dead finish, is a tree in the family Fabaceae that is endemic to arid and semi-arid parts of central and western Australia.

Acacia sclerosperma, commonly known as limestone wattle or silver bark wattle, is a tree in the family Fabaceae. Endemic to Western Australia, it occurs on floodplains and along water-courses throughout the arid north-west corner of the State.

Acacia quadrimarginea, commonly known as granite wattle or spreading wattle, is a tree in the family Mimosaceae. Endemic to Western Australia, it occurs through arid south-central Western Australia. It is common on granite, but also occurs on sand and clay, and is often seen along creeklines in rocky hills.
Acacia ramulosa var. linophylla, commonly known as bowgada, wanderry mulga, horse mulga or sometimes wanyu, is a subspecies of the tree species Acacia ramulosa, with which it shares several common names. While the parent species is found throughout arid Australia, this subspecies is much more restricted, being found only on loose red sand in south central Western Australia and sporadically in South Australia. The species was formally named Acacia linophylla until 2001, when it was recognised as a variety of Acacia ramulosa.

Acacia glaucoptera, commonly known as flat wattle or clay wattle, is a species of Acacia which is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia.

Acacia truncata, commonly known as the angle leaved wattle or west coast wattle, is a coastal shrub in the family Fabaceae, with a native distribution along the southwest coast of Western Australia. A specimen of this wattle was part of an early European botanical collection, perhaps the first from Australia.

Acacia bivenosa, commonly known as two-nerved wattle, two-veined wattle or hill umbrella bush, is a species of Acacia found in northern Australia.

Acacia olgana, commonly known as Kata Tjuta wattle or Mount Olga wattle, is a shrub or tree in the genus Acacia that is found in central Australia.

Acacia stenoptera, commonly known as narrow-winged wattle, is a species of wattle that is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia.

Acacia lasiocalyx, commonly known as silver wattle or shaggy wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae.

Acacia celastrifolia, commonly known as the glowing wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to Western Australia.

Acacia melleodora, commonly known as scented wax wattle, waxy wattle, honey wattle or honey scented wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to arid parts of central Australia.

Acacia calcicola is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is native to parts of central Australia. Common names for this species include; shrubby wattle, shrubby mulga, myall-gidgee, northern myall and grey myall. Indigenous Australians the Pitjantjatjara peoples know the tree as ikatuka, the Warlpiri know it as jirlarti and the Arrernte know it as irrakwetye.