
Acacia adenogonia is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia aulacophylla is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia consobrina is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia.
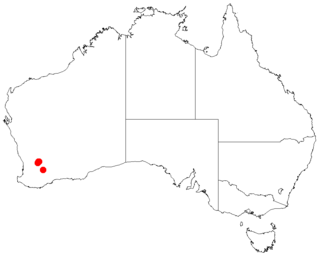
Acacia cowaniana, commonly known as Cowan's wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south west Australia.
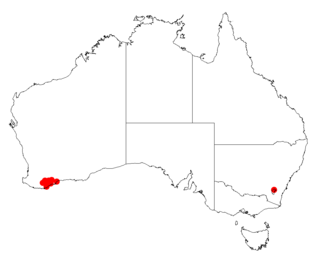
Acacia declinata is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area along the south coast in south western Australia.

Acacia donaldsonii is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemism in an area of south western Australia.

Acacia kenneallyi is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia masliniana, commonly known as Maslin's wattle is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to arid parts of western Australia.

Acacia obesa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is native to a small area of south western Australia.

Acacia ophiolithica is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves where it is endemic to a small area along the south west coast of Australia.
Acacia papulosa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area along the south coast of south western Australia.
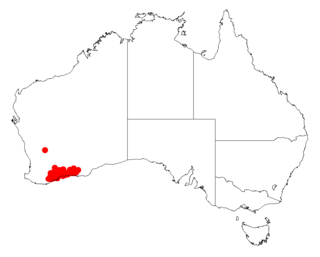
Acacia patagiata, also commonly knowns as salt gully wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia.
Acacia pelophila is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area along the west coast of western Australia.
Acacia perpusilla, commonly known as the King Edward River wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area of north western Australia.

Acacia sericophylla is a shrub or tree commonly known as the desert dogwood, desert oak or cork-bark wattle. To the Indigenous Australian people of the Pilbara, the Nyangumarta peoples, it is known as Pirrkala. The species is of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves.

Acacia speckii is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in central western Australia.

Acacia spongolitica is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia undosa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia vittata, commonly known as Lake Logue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.
Acacia spectrum, also known as Kimberley ghost wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to arid parts of north western Australia.
















