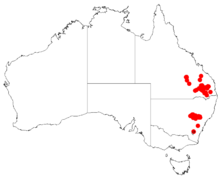
Acacia deanei is a tree native to Australia, which is useful for controlling soil erosion. There are two subspecies: Acacia deanei subsp. deanei and Acacia deanei subsp. paucijuga.

Acacia pravissima, commonly known as Ovens wattle, Oven wattle, wedge-leaved wattle and Tumut wattle, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is an evergreen shrub native to Victoria, the South West Slopes and Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, Australia.

Acacia bakeri, known as the marblewood, white marblewood, Baker's wattle or scrub wattle, is one of the largest of all acacias, growing to 40 m (130 ft) tall. It is a long-lived climax rainforest tree from eastern Australia. Unlike most acacias, fire is not required for seed germination. This tree is considered vulnerable to extinction. Its former habitat is lowland sub tropical rainforest which has been mostly cleared in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Acacia linifolia, known colloquially as white wattle, or flax wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia.

Acacia georgensis, commonly known as Bega wattle or Dr George Mountain wattle, is a species of Acacia native to southeastern Australia. It was one of eleven species selected for the Save a Species Walk campaign in April 2016 when scientists walked 300 km to raise money for collection of seeds to be prepared and stored at the Australian PlantBank at the Australian Botanic Garden Mount Annan.

Acacia nigripilosa is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia havilandiorum, also known as Haviland's wattle or needle wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to an area in South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.

Acacia oshanesii, commonly known as corkwood wattle and irish wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia.
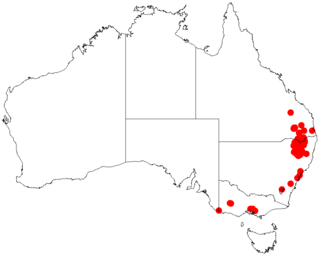
Acacia pruinosa, commonly known as the frosty wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia.

Acacia debilis, commonly known as the spindly wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia.

Acacia hamiltoniana, commonly known as Hamilton's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of eastern Australia.

Acacia juncifolia, commonly known as rush-leaf wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.

Acacia pilligaensis, commonly known as Pillaga wattle or pinbush wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia siculiformis, commonly known as dagger wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia kettlewelliae, commonly known as buffalo wattle, is a tree or shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia kybeanensis, commonly known as kybean wattle or kybeyan wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia linearifolia, commonly known as stringybark wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia sparsiflora, also known as currawong or currawang, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to a large area in eastern Australia.

Acacia rhodoxylon, also known as rosewood, ringy rosewood or spear wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia baeuerlenii is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in eastern Australia.