
Acacia isoneura is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia multispicata, commonly known as spiked wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.
Acacia stanleyi, commonly known as Stanley's rock wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia tetraneura is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia dentifera, commonly known as tooth-bearing acacia, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia hastulata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to an area in south western Australia.

Acacia merrickiae is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to a small area of south western Australia.
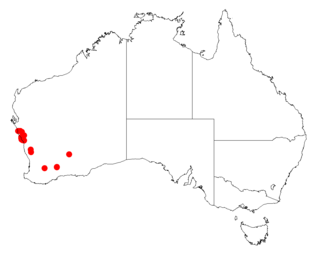
Acacia oxyclada is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to western Australia.
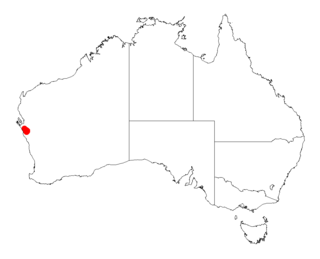
Acacia plautella is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to a small area along the coast of western Australia.

Acacia profusa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia robiniae, commonly known as Robin's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia simulans is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.
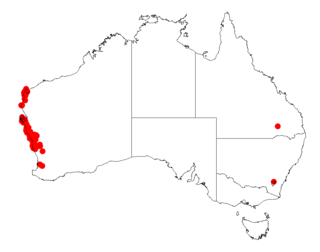
Acacia spathulifolia commonly known as Gold carpet or the Gold carpet wattle is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to coastal parts of western Australia.

Acacia eremaea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area in western Australia.
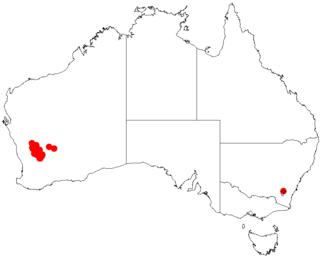
Acacia obtecta is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia.
Acacia pelophila is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area along the west coast of western Australia.

Acacia subsessilis is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of western Australia.

Acacia vittata, commonly known as Lake Logue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia warramaba is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia gracilenta is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north Australia.



















