
Acacia conniana is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to the southern coast of western Australia.

Acacia effusifolia is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to an area in the Mid West and the Wheatbelt regions of Western Australia.

Acacia repanda is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia sibina is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to parts of western Australia.

Acacia nigripilosa is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia pachyphylla is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia pachypoda is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia profusa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia retrorsa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to western Australia

Acacia robiniae, commonly known as Robin's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia ryaniana is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to an area along the west coast of Australia.
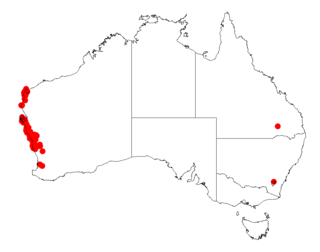
Acacia spathulifolia commonly known as Gold carpet or the Gold carpet wattle is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to coastal parts of western Australia.

Acacia anfractuosa is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia aulacophylla is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to western Australia.
Acacia papulosa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area along the south coast of south western Australia.

Acacia pharangites, commonly known as Wongan gully wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to the Wongan Hills of south western Australia and is listed as endangered according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia roycei is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of western Australia.
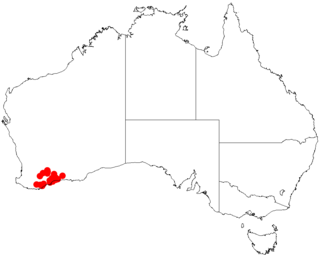
Acacia tetanophylla is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia undosa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia vittata, commonly known as Lake Logue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.




















