Related Research Articles

Lecturer is an academic rank within many universities, though the meaning of the term varies somewhat from country to country. It generally denotes an academic expert who is hired to teach on a full- or part-time basis. They may also conduct research.
Maastricht University is a public research university in Maastricht, Netherlands. Founded in 1976, it is the second youngest of the thirteen Dutch universities.

Hacettepe University is a leading state university in Ankara, Turkey. It was established on 8 July 1967. By URAP 2019, it is ranked first among the Turkish universities.
Honorary titles in academia may be conferred on persons in recognition of contributions by a non-employee or by an employee beyond regular duties. This practice primarily exists in the UK and Germany, as well as in many in the universities and colleges of United States, Australia, Hong Kong, Taiwan, China, New Zealand, Japan, Denmark, and Canada.
The following summarizes basic academic ranks in the French higher education system. Most academic institutions are state-run and most academics with permanent positions are civil servants, and thus are tenured.
Professors in the United States commonly occupy any of several positions of teaching and research within a college or university. In the U.S., the word "professor" informally refers collectively to the academic ranks of assistant professor, associate professor, or professor. This usage differs from the predominant usage of the word professor internationally, where the unqualified word professor only refers to "full professors." The majority of university lecturers and instructors in the United States, as of 2015, do not occupy these tenure-track ranks, but are part-time adjuncts, or more commonly referred as college teachers.
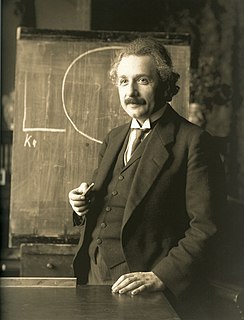
Professor is an academic rank at universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, professor derives from Latin as a "person who professes". Professors are usually experts in their field and teachers of the highest rank.
Academic ranks in the United States are the titles, relative importance and power of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel held in academia.
This article describes the academic positions and ranks in Sweden.
Academic personnel, also known as faculty member or member of the faculty or academics or academic staff, are vague terms that describe teachers or research staff of a school, college, university or research institute. In British and Australian/New Zealand English "faculty" usually refers to a sub-division of a university, not to the employees, as it can also do in North America. Universities, community colleges and even some secondary and primary schools use the terms faculty and professor. Other institutions may likewise use the term faculty.
Academic ranks in Germany are the titles, relative importance and power of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel held in academia.

Academic ranks in the United Kingdom are the titles, relative seniority and responsibility of employees in universities. In general the country has three academic career pathways: one focused on research, one on teaching, and one that combines the two.
Academic ranks in Hungary are the titles, relative importance and power of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel held in academia.
Academic ranks in Norway are the system of merit-based ranks used by academic employees in academia. Similar to the British rank system, the Norwegian rank system is broadly divided into three pathways, a combined research and teaching career pathway, a research career pathway and a teaching career pathway.
Academic ranks in India are the titles, relative importance and power of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel held in academia.
Academic ranks in Portugal and Brazil are the titles, relative importance and power of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel held in academia.
Academic ranks in Russia are the conferred titles, indicating relative importance and power of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel in Russian academia and scientific institutions. The rank “certifies” the demonstrated ability of an individual to function in the specific academic position(s).
Academic ranks in Denmark are the positions and titles of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel held in academia at Danish institutions, and the relations between them.
Academic ranks in Malaysia are the titles, relative importance and power of professors, researchers, and administrative personnel held in academia. Generally, Malaysia uses Commonwealth academic ranks. However, there are universities using their own academic titles.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "ศาสตราจารย์ (professor)" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ "clinical professor ศาสตราจารย์คลินิก" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ "emeritus professor ศาสตราจารย์กิตติคุณ, ศาสตราจารย์เกียรติคุณ" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-19. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ "adjunct professor ศาสตราจารย์วุฒิคุณ" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-09. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ "chair professor ศาสตรเมธาจารย์, ศาสตราจารย์อาวุโส" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ "distinguished professor ศาสตราจารย์พิศิษฐ์" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ ศาสตราจารย์กิตติมศักดิ์ (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. 2008-01-12. Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ "distinguished scholar ศาสตราภิชาน" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ "research professor กิตติเมธี" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- 1 2 3 "visiting professor ศาสตราจารย์อาคันตุกะ, ศาสตราจารย์รับเชิญ" (in Thai). Royal Institute of Thailand. n.d. Archived from the original on 2014-04-09. Retrieved 2014-04-10.