Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as activation immunotherapies, while immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as suppression immunotherapies. Immunotherapy is under preliminary research for its potential to treat various forms of cancer.
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are a family of proteins produced by cells in response to exposure to stressful conditions. They were first described in relation to heat shock, but are now known to also be expressed during other stresses including exposure to cold, UV light and during wound healing or tissue remodeling. Many members of this group perform chaperone functions by stabilizing new proteins to ensure correct folding or by helping to refold proteins that were damaged by the cell stress. This increase in expression is transcriptionally regulated. The dramatic upregulation of the heat shock proteins is a key part of the heat shock response and is induced primarily by heat shock factor (HSF). HSPs are found in virtually all living organisms, from bacteria to humans.

Wasps in the family Pompilidae are commonly called spider wasps, spider-hunting wasps, or pompilid wasps. The family is cosmopolitan, with some 5,000 species in six subfamilies. Nearly all species are solitary, and most capture and paralyze prey, though members of the subfamily Ceropalinae are kleptoparasites of other pompilids, or ectoparasitoids of living spiders.
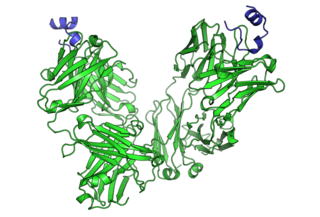
Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology (immuno-oncology) and a growing subspecialty of oncology.

Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antimicrobials which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators.

The Chinese red-headed centipede, also known as the Chinese red head, is a centipede from East Asia. It averages 20 cm (8 in) in length and lives in damp environments.

Arginylglycylaspartic acid (RGD) is the most common peptide motif responsible for cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM), found in species ranging from Drosophila to humans. Cell adhesion proteins called integrins recognize and bind to this sequence, which is found within many matrix proteins, including fibronectin, fibrinogen, vitronectin, osteopontin, and several other adhesive extracellular matrix proteins. The discovery of RGD and elucidation of how RGD binds to integrins has led to the development of a number of drugs and diagnostics, while the peptide itself is used ubiquitously in bioengineering. Depending on the application and the integrin targeted, RGD can be chemically modified or replaced by a similar peptide which promotes cell adhesion.

Psalmotoxin (PcTx1) is a spider toxin from the venom of the Trinidad tarantula Psalmopoeus cambridgei. It selectively blocks Acid Sensing Ion Channel 1-a (ASIC1a), which is a proton-gated sodium channel.
SNX-482 is a toxin from the tarantula Hysterocrates gigas. It acts as a high-affinity blocker of R-type Ca2+ (Cav2.3) channels, but at higher concentrations it can also block other Ca2+ channels and Na+ channels.

Guangxitoxin, also known as GxTX, is a peptide toxin found in the venom of the tarantula Plesiophrictus guangxiensis. It primarily inhibits outward voltage-gated Kv2.1 potassium channel currents, which are prominently expressed in pancreatic β-cells, thus increasing insulin secretion.
Hanatoxin is a toxin found in the venom of the Grammostola spatulata tarantula. The toxin is mostly known for inhibiting the activation of voltage-gated potassium channels, most specifically Kv4.2 and Kv2.1, by raising its activation threshold.
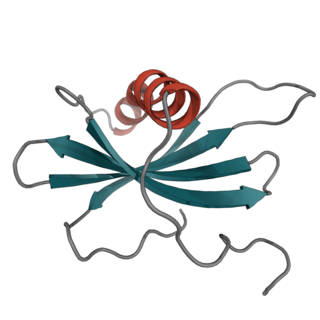
Affimer molecules are small proteins that bind to target proteins with affinity in the nanomolar range. These engineered non-antibody binding proteins are designed to mimic the molecular recognition characteristics of monoclonal antibodies in different applications. These affinity reagents have been optimized to increase their stability, make them tolerant to a range of temperatures and pH, reduce their size, and to increase their expression in E.coli and mammalian cells.
The pathophysiology of a spider bite is due to the effect of its venom. A spider envenomation occurs whenever a spider injects venom into the skin. Not all spider bites inject venom – a dry bite, and the amount of venom injected can vary based on the type of spider and the circumstances of the encounter. The mechanical injury from a spider bite is not a serious concern for humans. Some spider bites do leave a large enough wound that infection may be a concern. However, it is generally the toxicity of spider venom that poses the most risk to human beings; several spiders are known to have venom that can cause injury to humans in the amounts that a spider will typically inject when biting.

Cyrtopholis is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892.
Tolerogenic dendritic cells are heterogenous pool of dendritic cells with immuno-suppressive properties, priming immune system into tolerogenic state against various antigens. These tolerogenic effects are mostly mediated through regulation of T cells such as inducing T cell anergy, T cell apoptosis and induction of Tregs. Tol-DCs also affect local micro-environment toward tolerogenic state by producing anti-inflammatory cytokines.

Wasabi receptor toxin (WaTx) is the active component of the venom of the Australian black rock scorpion Urodacus manicatus. WaTx targets TRPA1, also known as the wasabi receptor or irritant receptor. WaTx is a cell-penetrating toxin that stabilizes the TRPA1 channel open state while reducing its Ca2+-permeability, thereby eliciting pain and pain hypersensitivity without the neurogenic inflammation that typically occurs in other animal toxins.
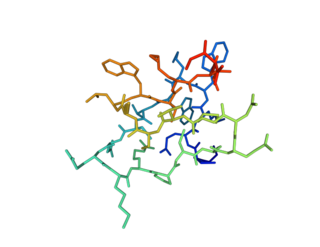
GiTx1 (β/κ-theraphotoxin-Gi1a) is a peptide toxin present in the venom of Grammostola iheringi. It reduces both inward and outward currents by blocking voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels, respectively.
Protoxin-I, also known as ProTx-I, or Beta/omega-theraphotoxin-Tp1a, is a 35-amino-acid peptide neurotoxin extracted from the venom of the tarantula Thrixopelma pruriens. Protoxin-I belongs to the inhibitory cystine knot (ICK) family of peptide toxins, which have been known to potently inhibit voltage-gated ion channels. Protoxin-I selectively blocks low voltage threshold T-type calcium channels, voltage gated sodium channels and the nociceptor cation channel TRPA1. Due to its unique ability to bind to TRPA1, Protoxin-I has been implicated as a valuable pharmacological reagent with potential applications in clinical contexts with regards to pain and inflammation

Grammostola mechanotoxin #4, also known as M-theraphotoxin-Gr1a (M-TRTX-Gr1a), is a neurotoxin isolated from the venom of the spider Chilean rose tarantula Grammostola spatulate. This amphiphilic peptide, which consists of 35 amino acids, belongs to the inhibitory cysteine knot (ICK) peptide family. It reduces mechanical sensation by inhibiting mechanosensitive channels (MSCs).
Acanthoscurria simoensi is a species of tarantula spider found in Guyana, French Guiana, and Brazil, first described from French Guiana in 2000. The species has been traded in the exotic pet hobby as "Para Mongo Zebra” under spurious scientific names such as 'fracta'. The common name partly relates to the colouration where the females of the species have dark bodies with light coloured linear markings on legs. Notably, like in many other tarantulas with strong sexual dimorpsim, adult males of the species have a different general appearance with a more rusty metallic colouration and comparatively weak linear markings on the legs.












