| Accessory cephalic vein | |
|---|---|
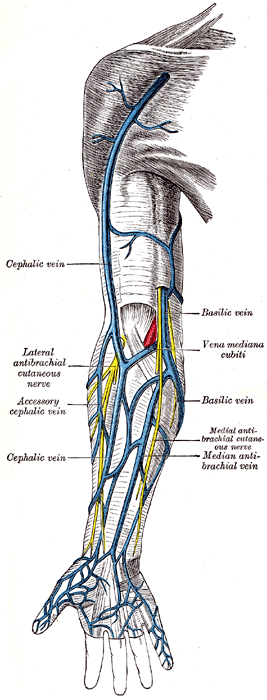 Superficial veins of the upper limb (accessory cephalic vein labeled at center left) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Dorsal venous network of hand |
| Drains to | Cephalic vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena cephalica accessoria |
| TA98 | A12.3.08.017 |
| TA2 | 4966 |
| FMA | 22970 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The accessory cephalic vein is a variable vein that passes along the radial border of the forearm to join the cephalic vein [1] distal/inferior to the elbow. It may arise from a dorsal forearm venous plexus, or from the ulnar/medial side of the dorsal venous network of hand. [2] In some cases the accessory cephalic springs from the cephalic above the wrist and joins it again higher up. A large oblique branch frequently connects the basilic and cephalic veins on the back of the forearm.[ citation needed ]