
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries which run down the forearm. In some individuals, the bifurcation occurs much earlier and the ulnar and radial arteries extend through the upper arm. The pulse of the brachial artery is palpable on the anterior aspect of the elbow, medial to the tendon of the biceps, and, with the use of a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer, often used to measure the blood pressure.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh.

The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve that originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also a contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm.

In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
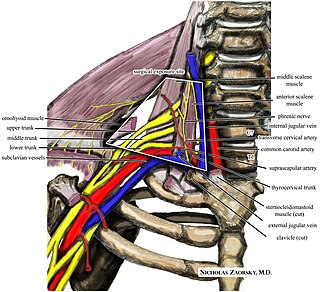
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition in which there is compression of the nerves, arteries, or veins in the superior thoracic aperture, the passageway from the lower neck to the armpit, also known as the thoracic outlet. There are three main types: neurogenic, venous, and arterial. The neurogenic type is the most common and presents with pain, weakness, paraesthesia, and occasionally loss of muscle at the base of the thumb. The venous type results in swelling, pain, and possibly a bluish coloration of the arm. The arterial type results in pain, coldness, and pallor of the arm.

In medicine, Allen's test or the Allen test is a medical sign used in physical examination of arterial blood flow to the hands. It was named for Edgar Van Nuys Allen, who described the original version of the test in 1942.

An arterial line is a thin catheter inserted into an artery.

The cubital fossa, chelidon or inside of elbow is the area on the anterior side of the upper part between the arm and forearm of a human or other hormid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow when in standard anatomical position.
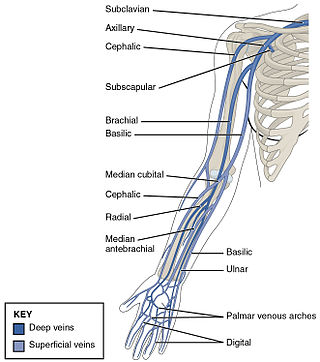
In human anatomy, the brachial veins are venae comitantes of the brachial artery in the arm proper. Because they are deep to muscle, they are considered deep veins. Their course is that of the brachial artery : they begin where radial veins and ulnar veins join. They end at the inferior border of the teres major muscle. At this point, the brachial veins join the basilic vein to form the axillary vein.

The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.
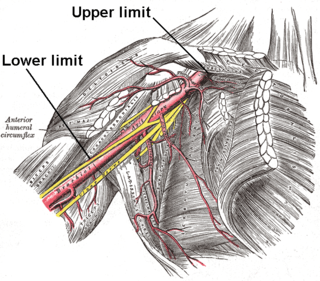
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arterial aneurysm.

The ulnar veins are venae comitantes of the ulnar artery. They drain the superficial venous palmar arch. They arise in the hand and terminate by uniting with the radial veins to form the brachial veins. They mostly drain the medial aspect of the forearm. They receive the venae comitantes of the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries near the elbow, as well as a large branch from the median cubital vein. The ulnar veins are larger than the radial veins.
A peripheral vascular examination is a medical examination to discover signs of pathology in the peripheral vascular system. It is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with leg pain suggestive of a cardiovascular pathology.

The medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm is a sensory branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus derived from the ventral rami of spinal nerves C8-T1. It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the medial forearm and skin overlying the olecranon. It descends through the (upper) arm within the brachial fascia alongside the basilic vein, then divides into an anterior branch and a posterior branch upon emerging from the brachial fascia; the two terminal branches travel as far distally as the wrist.
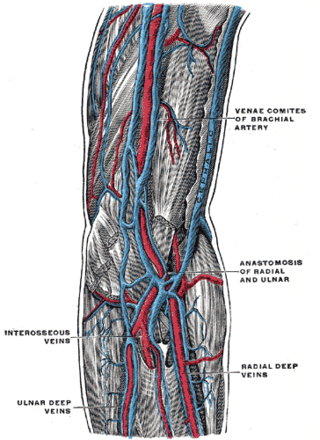
Vena comitans is Latin for accompanying vein and is also known as a satellite vein. It refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes.

The deep artery of arm is a large artery of the arm which arises from the brachial artery. It descends in the arm before ending by anastomosing with the radial recurrent artery.















