Related Research Articles

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.

In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

In human anatomy, the splenic vein is a blood vessel that drains blood from the spleen, the stomach fundus and part of the pancreas. It is part of the hepatic portal system.

In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the large intestine. It usually terminates when reaching the splenic vein, which goes on to form the portal vein with the superior mesenteric vein (SMV).

In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. There are usually three large upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver, as well as a number (6-20) of lower hepatic veins. All hepatic veins are valveless.

The coronary sinus is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begins at the junction of the great cardiac vein, and oblique vein of the left atrium. It receives multiple tributaries. It passes across the backside of the heart along a groove between left atrium and left ventricle, then drains into the right atrium at the orifice of the coronary sinus.
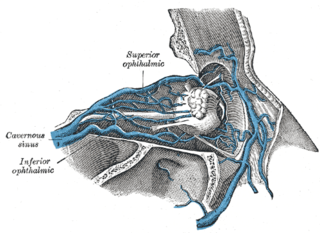
The superior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. It is formed by the union of the angular vein, and supraorbital vein. It passes backwards within the orbit alongside the ophthalmic artery, then exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to drain into the cavernous sinus.

The inferior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. It begins from a venous network in the front of the orbit, then passes backwards through the lower orbit. It drains several structures of the orbit. It may end by splitting into two branches, one draining into the pterygoid venous plexus and the other ultimately into the cavernous sinus.

The rectal venous plexus is the venous plexus surrounding the rectum. It consists of an internal and an external rectal plexus. It is drained by the superior, middle, and inferior rectal veins. It forms a portosystemic (portocaval) anastomosis. This allows rectally administered medications to bypass first pass metabolism.

In human anatomy, the cerebral veins are blood vessels in the cerebral circulation which drain blood from the cerebrum of the human brain. They are divisible into external and internal groups according to the outer or inner parts of the hemispheres they drain into.

The dorsal venous network of the hand is a venous network on the dorsum (backside) of hand. It is formed by the dorsal metacarpal veins, a dorsal digital vein from the radial side of the index finger and one from the ulnar side of the little finger, and both dorsal digital veins of the thumb. The venous network gives rise to the cephalic vein and the basilic vein; an accessory cephalic vein may arise from it as well.

The vorticose veins, referred to clinically as the vortex veins, are veins that drain the choroid of the eye. There are usually 4-5 vorticose veins in each eye, with at least one vorticose vein per each quadrant of the eye. Vorticose veins drain into the superior ophthalmic vein, and inferior ophthalmic vein.

The cystic veins drain venous blood from the gallbladder and the cystic duct. The cystic veins either drain into various branches and tributaries of the hepatic portal vein.

The left gastric vein is a vein that derives from tributaries draining the lesser curvature of the stomach.
The esophageal veins drain blood from the esophagus to the azygos vein, in the thorax, and to the inferior thyroid vein in the neck. It also drains, although with less significance, to the hemiazygos vein, posterior intercostal vein and bronchial veins.

The vaginal venous plexus is a group of veins draining blood from the vagina. It lies around the sides of the vagina. Its blood eventually drains into the internal iliac veins.

The deep palmar arch, an arterial network is accompanied by a pair of venae comitantes which constitute the deep venous palmar arch. It receives the veins corresponding to the branches of the arterial arch: the palmar metacarpal veins.

A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 663 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 663 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)