
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as structure for other biomolecules. Carbon is primarily fixed through photosynthesis, but some organisms use a process called chemosynthesis in the absence of sunlight.
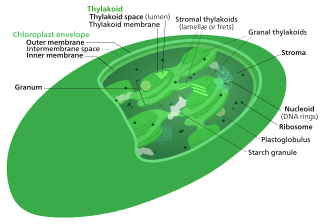
The Calvin cycle,light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase,dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into glucose. The Calvin cycle is present in all photosynthetic eukaryotes and also many photosynthetic bacteria. In plants, these reactions occur in the stroma, the fluid-filled region of a chloroplast outside the thylakoid membranes. These reactions take the products of light-dependent reactions and perform further chemical processes on them. The Calvin cycle uses the chemical energy of ATP and reducing power of NADPH from the light dependent reactions to produce sugars for the plant to use. These substrates are used in a series of reduction-oxidation reactions to produce sugars in a step-wise process; there is no direct reaction that converts several molecules of CO2 to a sugar. There are three phases to the light-independent reactions, collectively called the Calvin cycle: carboxylation, reduction reactions, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration.

Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes that occur in animals. It takes part in gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, the glyoxylate cycle, amino acid synthesis, fatty acid synthesis and the citric acid cycle.

Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) encoded by the gene PC is an enzyme of the ligase class that catalyzes the physiologically irreversible carboxylation of pyruvate to form oxaloacetate (OAA).
Holocarboxylase synthetase ), also known as protein—biotin ligase, is a family of enzymes. This enzyme is important for the effective use of biotin, a B vitamin found in foods such as liver, egg yolks, and milk. In many of the body's tissues, holocarboxylase synthetase activates other specific enzymes by attaching biotin to them. These carboxylases are involved in many critical cellular functions, including the production and breakdown of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (also known as PEP carboxylase, PEPCase, or PEPC; EC 4.1.1.31, PDB ID: 3ZGE) is an enzyme in the family of carboxy-lyases found in plants and some bacteria that catalyzes the addition of bicarbonate (HCO3−) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to form the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate and inorganic phosphate:

Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (ATP) (EC 4.1.1.49, phosphopyruvate carboxylase (ATP), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, phosphopyruvate carboxykinase (adenosine triphosphate), PEP carboxylase, PEP carboxykinase, PEPCK (ATP), PEPK, PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvic carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvic carboxykinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (ATP), phosphopyruvate carboxykinase, ATP:oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (transphosphorylating)) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (transphosphorylating; phosphoenolpyruvate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.3, PCC) catalyses the carboxylation reaction of propionyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. PCC has been classified both as a ligase and a lyase. The enzyme is biotin-dependent. The product of the reaction is (S)-methylmalonyl CoA.

Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase catalyzes the ATP-dependent synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate from glutamine or ammonia and bicarbonate. This enzyme catalyzes the reaction of ATP and bicarbonate to produce carboxy phosphate and ADP. Carboxy phosphate reacts with ammonia to give carbamic acid. In turn, carbamic acid reacts with a second ATP to give carbamoyl phosphate plus ADP.
The enzyme Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase, or AIR carboxylase (EC 4.1.1.21) is involved in nucleotide biosynthesis and in particular in purine biosynthesis. It catalyzes the conversion of 5'-phosphoribosyl-5-aminoimidazole ("AIR") into 5'-phosphoribosyl-4-carboxy-5-aminoimidazole ("CAIR") as described in the reaction:
In enzymology, a 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a biotin—[acetyl-CoA-carboxylase] ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a biotin carboxylase (EC 6.3.4.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a biotin-[methylcrotonoyl-CoA-carboxylase] ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a geranoyl-CoA carboxylase (EC 6.4.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a urea carboxylase (EC 6.3.4.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [acetyl-CoA carboxylase] kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Bisphosphate may refer to:











