
Apollo is one of the Olympian deities in ancient Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. He is considered to be the most beautiful god and is represented as the ideal of the kouros. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu.

Boeotia, sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes.
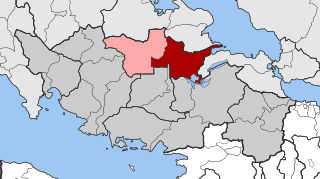
Akraifnia is a former municipality in Boeotia, Greece. It was established in 1997 from the former communities Akraifnio, Kastro and Kokkino. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Orchomenos, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 185.816 km2. Population 2,276 (2021). The seat of the municipality was in Akraifnio. It was named after the ancient city Acraephia.
Akraifnio, before 1933 known as Karditsa (Καρδίτσα), is a village in Boeotia, Greece.
In Greek mythology, Ptous may refer to the following:



