
Coprosma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in New Zealand, Hawaiian Islands, Borneo, Java, New Guinea, islands of the Pacific Ocean to Australia and the Juan Fernández Islands.

Leucopogon is a genus of about 150-160 species of shrubs or small trees in the family Ericaceae, in the section of that family formerly treated as the separate family Epacridaceae. They are native to Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia, the western Pacific Islands and Malaysia, with the greatest species diversity in southeastern Australia. Plants in this genus have leaves with a few more or less parallel veins, and tube-shaped flowers usually with a white beard inside.

Psammisia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Ericaceae. It contains the fruiting bushes commonly called joyapas and is distributed throughout the Neotropics.

Coprosma rhamnoides is an endemic shrub in New Zealand. It forms a small shrub up to 2 m tall. The leaves are very small, simple and variable in shape. The inconspicuous flowers are unisexual and believed to be wind pollinated. It is widespread in occurrence and can be the dominant small leaved divaricating shrub in some locations

Archeria is a small genus of shrubs in the family Ericaceae. As currently circumscribed the group includes six species, all native to southern Australasia. Four of these are endemic to Tasmania, and the other two endemic to New Zealand.

Acrothamnus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Ericaceae. The species, which were formerly included in the genus Leucopogon, occur in eastern Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea and the Pacific. They include:

Archeria racemosa is a species of shrub in the family Ericaceae.

Acrothamnus hookeri, commonly known as the mountain beardheath, is a flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and grows in subalpine regions of southeastern Australia. It is a small upright shrub with oblong-shaped leaves and white flowers.

Gaultheria depressa, commonly known as the mountain snow berry or alpine wax berry, is a small ground-hugging shrub of the heath family Ericaceae native to rocky alpine areas of Tasmania, Australia, and New Zealand.

Pentachondra pumila, also known as carpet heath, is a small alpine shrub in the epacris family (Ericaceae).. It is commonly found in Australia and New Zealand in areas of high rainfall, being known for its small white flowers as well as its red, hollow fruit that grows on branch ends. It is distinguishable as a prostrate, mat-like shrub, growing in rocky or boggy alpine areas. The fruit is edible and is a food source for many species of bird.
Thelymitra colensoi, commonly called Colenso's sun orchid, is a species of orchid in the family Orchidaceae that is endemic to New Zealand. It has a single fleshy, channelled leaf and up to seven pale blue or mauve to pink flowers. It is similar to T. pauciflora but is smaller and less robust than that species.

Leucopogon fraseri is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is native to south-eastern continental Australia and New Zealand, where it is known as Styphelia nesophila, pātōtara, or dwarf mingimingi. It is a prickly, prostrate to trailing or low-growing shrub with egg-shaped leaves, and erect, tube-shaped white flowers usually arranged singly in leaf axils.

Dracophyllum traversii, commonly known as mountain neinei, grass tree, and pineapple tree is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae. It is a deciduous tree endemic to New Zealand. It reaches a height of 0.2–13 m (0.66–42.65 ft) and has leaves which form tufts at the end of its branches. It has a lifespan of between 500 and 600 years.

Dracophyllum fiordense, commonly known as the Fiordland grass tree, is a species of tree or shrub in the heath family, Ericaceae. It is endemic to the South Island of New Zealand. It reaches a height of 1.5–5.0 metres and has tufts of long green leaves at the ends of its branches. Each leaf has a distinctive curled spiral tip. D. fiordense has a pyramid-shaped inflorescence hidden under each clump of leaves, with between 113 and 120 pink flowers on each spike, and later reddish-brown dry fruit; both are around just 2 by 2 mm. It inhabits shrubland, lowland and subalpine forests, and tussock grassland of mountain slopes, gullies, and ridges. Its range covers two main areas: one in Fiordland National Park, and one in the Mount Cook and Westland National Parks.

Dracophyllum subulatum, commonly known as monoao, is a species of tree or shrub in the heath family Ericaceae. It is endemic to the central North Island of New Zealand.
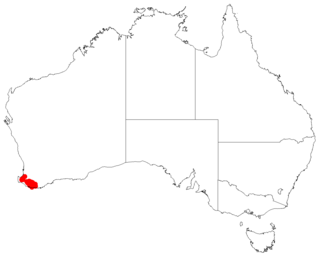
Leucopogon decrescens is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the far south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with hairy young branchlets, spirally arranged, narrowly egg-shaped leaves, and white, bell-shaped flowers often with a pink tinge.

Leucopogon diversifolius is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with more or less glabrous young branchlets, spirally arranged, erect, broadly egg-shaped, elliptic or more or less circular leaves, and white, broadly bell-shaped flowers sometimes with a pink tinge.
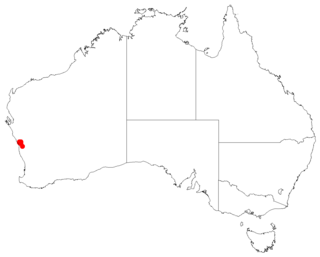
Leucopogon grammatus is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with hairy young branchlets, spirally arranged, erect, egg-shaped leaves, and white, bell-shaped to broadly bell-shaped flowers.

Leucopogon inflexus is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, open shrub with more or less glabrous young branchlets, spirally arranged, erect, egg-shaped to more or less round leaves, and white, bell-shaped, densely bearded flowers.
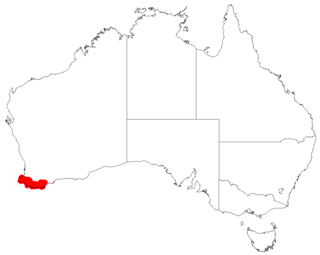
Leucopogon interstans is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with brownish hairs on its young branchlets, erect, narrowly elliptic or narrowly egg-shaped leaves and white or pinkish flowers in groups in upper leaf axils or on the ends of branches.

















