
Aedes albopictus, from the mosquito (Culicidae) family, also known as the (Asian) tiger mosquito or forest mosquito, is a mosquito native to the tropical and subtropical areas of Southeast Asia. In the past few centuries, however, this species has spread to many countries through the transport of goods and international travel. It is characterized by the white bands on its legs and body.

Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term arbovirus is a portmanteau word. Tibovirus is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last three or four days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and viral hemorrhagic fever may also occur.
La Crosse encephalitis is an encephalitis caused by an arbovirus which has a mosquito vector.
Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE), commonly called Triple E or sleeping sickness, is a disease caused by a zoonotic mosquito-vectored Togavirus that is present in North, Central, and South America, and the Caribbean. EEE was first recognized in Massachusetts, United States, in 1831, when 75 horses died mysteriously of viral encephalitis. Epizootics of EEE in horses have continued to occur regularly in the United States. It can also be identified in donkeys and zebras. Rarely, it can also infect humans. Due to the rarity of the disease, its occurrence can cause economic impact beyond the cost of horses and poultry. EEE is found today in the eastern part of the United States and is often associated with coastal plains. It can most commonly be found in East Coast and Gulf Coast states. In Florida, about one to two human cases are reported a year, although over 60 cases of equine encephalitis are reported. In years in which conditions are favorable for the disease, the number of equine cases is over 200. Diagnosing equine encephalitis is challenging because many of the symptoms are shared with other illnesses and patients can be asymptomatic. Confirmations may require a sample of cerebrospinal fluid or brain tissue, although CT scans and MRI scans are used to detect encephalitis. This could be an indication that the need to test for EEE is necessary. If a biopsy of the cerebrospinal fluid is taken, it is sent to a specialized laboratory for testing.

Aedes aegypti, the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. This mosquito originated in Africa, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
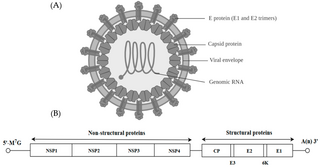
Alphavirus is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the Togaviridae family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphavirus species, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates. Alphaviruses that can infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector. Transmission between species and their vertebrate hosts occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical, and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.

Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus is a mosquito-borne viral pathogen that causes Venezuelan equine encephalitis or encephalomyelitis (VEE). VEE can affect all equine species, such as horses, donkeys, and zebras. After infection, equines may suddenly die or show progressive central nervous system disorders. Humans also can contract this disease. Healthy adults who become infected by the virus may experience flu-like symptoms, such as high fevers and headaches. People with weakened immune systems and the young and the elderly can become severely ill or die from this disease.

The discipline of medical entomology, or public health entomology, and also veterinary entomology is focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Veterinary entomology is included in this category, because many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat, for example, bovine encephalitis. Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public, including local and state officials and other stake holders in the interest of public safety.

Aedes vexans, the inland floodwater mosquito or tomguito, is a cosmopolitan and common pest mosquito.

Mosquito-borne diseases or mosquito-borne illnesses are diseases caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites transmitted by mosquitoes. Nearly 700 million people contract mosquito-borne illnesses each year, resulting in more than a million deaths.

Aedes sollicitans, the eastern saltmarsh mosquito, is a species of mosquito native to the eastern seaboard of the United States and Canada as well as the entire Gulf coast and is also present in the Bahamas and Greater Antilles. While primarily found in coastal areas within a few miles of the coast, it is occasionally found inland in areas with saline pools, the species was reported as far west as Arizona. The species is a prime vector for Eastern equine encephalitis, Venezuelan equine encephalitis and dog heartworm.

Culex quinquefasciatus, commonly known as the southern house mosquito, is a medium-sized mosquito found in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. It is a vector of Wuchereria bancrofti, avian malaria, and arboviruses including St. Louis encephalitis virus, Western equine encephalitis virus, Zika virus and West Nile virus. It is taxonomically regarded as a member of the Culex pipiens species complex. Its genome was sequenced in 2010, and was shown to have 18,883 protein-coding genes.

Aedes canadensis, the woodland pool mosquito, is an aggressive, day biting mosquito that can be a vector of a number of diseases which is found mainly in eastern North America.
Jamestown Canyon encephalitis is an infectious disease caused by the Jamestown Canyon virus, an orthobunyavirus of the California serogroup. It is mainly spread during the summer by different mosquito species in the United States and Canada.

Aedes japonicus, commonly known as the Asian bush mosquito or the Asian rock pool mosquito, was first described by Theobald in 1901 from Tokyo, Japan. They are competent arbovirus vectors known to transmit the West Nile virus as well as Japanese and St. Louis encephalitis. They are listed as an invasive species by the Global Invasive Species Database.

Psorophora ferox is a medium-sized mosquito native to much of North and South America. It inhabits wet woodlands, laying its eggs in temporary pools filled with rainwater. Larvae develop during summer in North America. They are aggressive feeders and give painful bites. The mosquito is reported to be active during both day and night.

Culex nigripalpus is a species of medium-sized, dark, blood-feeding mosquito of the family Culicidae.

Culiseta melanura, the black-tailed mosquito, is a species of mosquito in the family Culicidae. It is found mainly in the eastern and central United States.

Aedes taeniorhynchus, or the black salt marsh mosquito, is a mosquito in the family Culicidae. It is a carrier for encephalitic viruses including Venezuelan equine encephalitis and can transmit Dirofilaria immitis. It resides in the Americas and is known to bite mammals, reptiles, and birds. Like other mosquitoes, Ae. taeniorhynchus adults survive on a combination diet of blood and sugar, with females generally requiring a blood meal before laying eggs.

Aedes infirmatus, informally referred to as the infirm American pointy mosquito or silverback mosquito, is a species of mosquito that is found in woodland environments in parts of Central America, Mexico, and the southern United States, with a type locality in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. In the United States, they have been found as far west as Texas and as far north as New Jersey.
















