
Agabus was an early follower of Christianity mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles as a prophet. He is traditionally remembered as one of the Seventy Disciples described in Luke 10:1–24.

Didymus the Blind was a Christian theologian in the Church of Alexandria, where he taught for about half a century. He was a student of Origen, and, after the Second Council of Constantinople condemned Origen, Didymus's works were not copied. Many of his writings are lost, but some of his commentaries and essays survive. He was intelligent and a good teacher.

The Dytiscidae – based on the Greek dytikos (δυτικός), "able to dive" – are the predaceous diving beetles, a family of water beetles. They occur in virtually any freshwater habitat around the world, but a few species live among leaf litter. The adults of most are between 1 and 2.5 cm (0.4–1.0 in) long, though much variation is seen between species. The European Dytiscus latissimus and Brazilian Megadytes ducalis are the largest, reaching up to 4.5 cm (1.8 in) and 4.75 cm (1.9 in) respectively. In contrast, the smallest is likely the Australian Limbodessus atypicali of subterranean waters, which only is about 0.9 mm (0.035 in) long. Most are dark brown, blackish, or dark olive in color with golden highlights in some subfamilies. The larvae are commonly known as water tigers due to their voracious appetite. They have short, but sharp mandibles and immediately upon biting, they deliver digestive enzymes into prey to suck their liquefied remains. The family includes more than 4,000 described species in numerous genera.

Theodora is a dramatic oratorio in three acts by George Frideric Handel, set to an English libretto by Thomas Morell. The oratorio concerns the Christian martyr Theodora and her Christian-converted Roman lover, Didymus. It had its first performance at Covent Garden Theatre on 16 March 1750.

The wildlife of Tunisia is composed of its flora and fauna. It has 84 species of mammals and 375 species of birds. Tunisia is well documented for its addax and Dama Gazelle population.

Agabus is a large genus of predatory aquatic beetles in the family Dytiscidae, proposed in 1817 by William Elford Leach and named after Agabus, an early follower of Christianity. The adult beetles are moderate-sized, 5 to 14 mm long. The genus is primarily Holarctic in distribution, with only a few species known from the Afrotropical and Neotropical realms. Three species of Agabus, namely A. clypealis, A. discicollis and A. hozgargantae are endangered according to the IUCN Red List. The division into subgenera is not widely accepted. However, a number of species groups are recognized after the works of David J. Larson and Anders N. Nilsson. The genus is probably polyphyletic or paraphyletic. In a recent study of mitochondrial DNA, Agabus was found paraphyletic with respect to several of the species groups of Platambus, a closely related genus in the tribe Agabini. Lately the taxonomy of the genus has been revised, and some groups of species were transferred from Agabussensu stricto to other genera in the tribe Agabini.
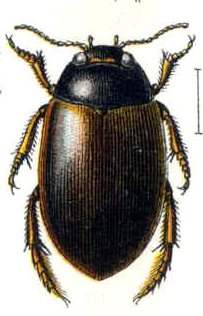
Agabus congener is a species of predatory beetle native to the Palearctic and the Near East. In Europe, it is only found in Andorra, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Great Britain including Shetland, Orkney, Hebrides and Isle of Man, Bulgaria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, mainland Denmark, Estonia, Finland, mainland France, Germany, mainland Greece, the Republic of Ireland, mainland Italy, Kaliningrad, Latvia, Lithuania, Northern Ireland, North Macedonia, mainland Norway, Poland, Russia, Sardinia, Slovakia, mainland Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, the Netherlands and Ukraine.

Agabus melanarius is a species of beetle endemic to Europe, where it is only found in Austria, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Great Britain, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, mainland Denmark, Estonia, Finland, mainland France, Germany, Hungary, mainland Italy, Kaliningrad, Lithuania, Luxembourg, mainland Norway, Poland, Russia except in the East, Sardinia, Slovakia, Sweden, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Ukraine and Yugoslavia.

Agabus striolatus is a species of beetle endemic to Europe, where it is only found in Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Great Britain including Shetland, Orkney, Hebrides and Isle of Man, Croatia, the Czech Republic, mainland Denmark, Estonia, Finland, mainland France, Germany, Hungary, mainland Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia except in the East, Slovakia, Sweden, the Netherlands and Ukraine.

Agabus uliginosus is a species of beetle native to the Palearctic, including Europe, where it is only found in Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Great Britain including Shetland, Orkney, Hebrides and Isle of Man, Croatia, the Czech Republic, mainland Denmark, Estonia, Finland, mainland France, Germany, Hungary, Iceland, mainland Italy, Kaliningrad, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, mainland Norway, Poland, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Ukraine and Yugoslavia.

Agabus undulatus is a species of beetle native to the Palearctic, including Europe, where it is only found in Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Great Britain including Shetland, Orkney, Hebrides and Isle of Man, Bulgaria, Croatia, the Czech Republic, mainland Denmark, Estonia, mainland France, Germany, Hungary, mainland Italy, Kaliningrad, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, mainland Norway, Poland, Russia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland, the Netherlands, and Ukraine.
Predatoroonops is a genus of goblin spiders endemic to the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. The genus is characterized by the extremely modified male chelicerae and long pairs of ventral spines. It is the first fully revised endemic Brazilian genus of spiders, uncovered in 2012 after two and a half years of research at São Paulo's Instituto Butantan.

Agabus paludosus is a species of beetles belonging to the family Dytiscidae.
Agabus ramblae is a species of beetles belonging to the family Dytiscidae. It is found in Spain and North Africa.
Agabus obliteratus is a species in the family Dytiscidae, in the order Coleoptera ("beetles"). It is found in North America.
Agabus infuscatus is a species of predaceous diving beetle in the family Dytiscidae. It is found in North America and the Palearctic.
Agabus griseipennis is a species of predaceous diving beetle in the family Dytiscidae. It is found in North America.
Agabus arcticus is a species of predaceous diving beetle in the family Dytiscidae. It is found in North America and the Palearctic.

Leith Hill SSSI is a 337.9-hectare (835-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest south-east of Dorking in Surrey. The SSSI consists of four wooded areas surrounding Leith Hill.












