
The Salton Sea is a shallow, landlocked, highly saline body of water in Riverside and Imperial counties at the southern end of the U.S. state of California. It lies on the San Andreas Fault within the Salton Trough, which stretches to the Gulf of California in Mexico.
Anostomus is a small genus of fish in the family Anostomidae found in South America. They are found in the Orinoco and Amazon Basin, as well as various rivers in the Guianas. The genus currently contains five described species. Petulanos was until recently included here.

The rainbow trout is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout(O. m. irideus) or Columbia River redband trout (O. m. gairdneri) that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead.

The Chinook salmon is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name chavycha (чавыча).

Carl Henry Eigenmann was a German-American ichthyologist of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, who, along with his wife Rosa Smith Eigenmann, and his zoology students is credited with identifying and describing for the first time 195 genera containing nearly 600 species of fishes of North America and South America. Especially notable among his published papers are his studies of the freshwater fishes of South America, the evolution and systematics of South American fishes, and for his analysis of degenerative evolution based on his studies of blind cave fishes found in parts of North America and in Cuba. His most notable works are The American Characidae (1917–1929) and A revision of the South American Nematognathi or cat-fishes (1890), in addition to numerous published papers such as "Cave Vertebrates of North America, a study of degenerative evolution" (1909) and "The fresh-water fishes of Patagonia and an examination of the Archiplata-Archelenis theory" (1909).

A fish is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays.
Scolomys ucayalensis, also known as the long-nosed scolomys or Ucayali spiny mouse is a nocturnal rodent species from South America. It is part of the genus Scolomys within the tribe Oryzomyini. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru in various different habitats in the Amazon rainforest.

The California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW), formerly known as the California Department of Fish and Game (CDFG), is a state agency under the California Natural Resources Agency. The Department of Fish and Wildlife manages and protects the state's wildlife, wildflowers, trees, mushrooms, algae and native habitats (ecosystems). The department is responsible for regulatory enforcement and management of related recreational, commercial, scientific, and educational uses. The department also prevents illegal poaching.
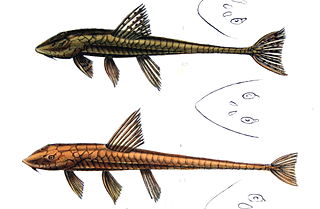
Loricariichthys is a genus of catfishes of the family Loricariidae.
Scolomys melanops, also known as the short-nosed scolomys, South American spiny mouse, Ecuadorian spiny mouse, or gray spiny mouse, is a species of rodent in the genus Scolomys of family Cricetidae. It is a forest mouse and was thought to be endemic to Ecuador but it is now known to have a wider distribution, being also present in part of Peru.
Scolomys is a genus of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of the family Cricetidae. Some evidence suggests that it is related to Zygodontomys. It is characterized, among other traits, by spiny fur. It contains two species, S. melanops and S. ucayalensis.

Ageneiosus is a genus of driftwood catfishes found mostly in South America with one species extending into Central America.
Moro Cojo Estuary State Marine Reserve (SMR) is a marine protected area established to protect the wildlife and habitats in Moro Cojo Slough. Moro Cojo Slough is located inland from Monterey Bay on the central coast of California, directly south of the more widely known Elkhorn Slough. The area covers 0.46 square miles (1.2 km2). The SMR protects all marine life within its boundaries. Fishing and take of all living marine resources is prohibited.

Natural Bridges State Marine Reserve (SMR) is a marine protected area located at the northern edge of Santa Cruz, California, approximately 75 miles (121 km) south of San Francisco. The SMR covers 0.58 square miles (1.5 km2). The SMR protects all marine life within its boundaries. Fishing or other removal of any living marine resource is prohibited.

Ageneiosus inermis is a species of driftwood catfish of the family Auchenipteridae. It can be found throughout South America, from Colombia and Venezuela to Uruguay and northern Argentina.

Ageneiosus militaris is a species of driftwood catfish of the family Auchenipteridae. It can be found in the La Plata River basin in South America.
Ageneiosus pardalis is a species of driftwood catfish of the family Auchenipteridae. It can be found in the Maracaibo Lake.
Ageneiosus polystictus is a species of driftwood catfish of the family Auchenipteridae. It can be found on the Amazon basin.
The Puduari River is a river in the state of Amazonas, Brazil. It is a tributary of the Rio Negro.
Loricariichthys ucayalensis is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Ucayali River basin, for which it is named, in the upper Amazon River drainage in Peru. The species reaches 22 centimetres (8.7 in) in total length and is believed to be a facultative air-breather.











