
Stenodus leucichthys is a species of freshwater whitefish in the family Salmonidae. In the strict sense its natural distribution is restricted to the Caspian Sea basin. It is now considered extinct in the wild, but survives in cultured stocks. The nelma, a more widespread species of Eurasian and North America, is sometimes considered its subspecies.

Alosa is a genus of fish, the river herrings, in the family Alosidae. Along with other genera in the subfamily Alosinae, they are generally known as shads. They are distinct from other herrings by having a deeper body and spawning in rivers. Several species can be found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Also, several taxa occur in the brackish-water Caspian Sea and the Black Sea basin. Many are found in fresh water during spawning and some are only found in landlocked fresh water.

The Lessepsian migration is the migration of marine species along the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 1869, fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other marine animals and plants were exposed to an artificial passage between the two naturally separate bodies of water, and cross-contamination was made possible between formerly isolated ecosystems. The phenomenon is still occurring today. It is named after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French diplomat in charge of the canal's construction.

The skipjack herring is a North American, migratory, fresh- and brackish water fish species in the herring family Alosidae. The name skipjack shad comes from the fact that it is commonly seen leaping out of the water while feeding. Other common names include blue herring, golden shad, river shad, Tennessee tarpon, and McKinley shad. The skipjack shad is restricted to the Gulf of Mexico drainage basins. Skipjack are found in clear to moderately turbid water in areas with flow. Because they are a migratory species, dams often impede their reproduction. Records suggest that this species was much more abundant in the Upper Mississippi River basin before it was impounded. Currently, skipjack is most abundant in the Upper Mississippi River below the mouth of the Ohio River. They are known as an "early-run" species as they migrate to spawn in the early spring.
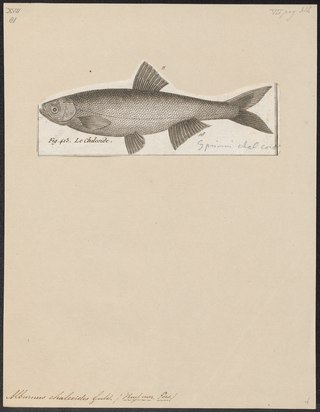
The Danube bleak or Caspian shemaya is a species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae. It is found in Iran, Ukraine, Georgia, Armenia, Slovakia, Moldova, Greece, Czechia, Azerbaijan, Turkiye, Afghanistan, Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Switzerland, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovenia, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.

The allis shad is a widespread Northeast Atlantic species of fish in the Alosidae family. It is an anadromous fish which migrates into fresh water to spawn. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, the western Baltic Sea and the western Mediterranean Sea. In appearance it resembles an Atlantic herring but has a distinctive dark spot behind the gill cover and sometimes a row of up to six spots behind this. It sometimes hybridises with the twait shad. This fish becomes mature when three or more years old and migrates to estuaries, later swimming up rivers to spawn. Populations of this fish have declined due to overfishing, pollution and habitat destruction. Conservation of this species is covered by Appendix III of the Bern Convention and Appendix II and V of the European Community Habitats Directive.

The twait shad or twaite shad is a species of fish in the family Alosidae. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea and is an anadromous fish which lives in the sea but migrates into fresh water to spawn. In appearance it resembles an Atlantic herring but has a row of six to ten distinctive spots on its silvery flanks. They become mature when three or more years old and migrate to estuaries, later swimming up rivers to spawn. Populations of this fish have declined due to overfishing, pollution and habitat destruction. Conservation of this species is covered by Appendix III of the Bern Convention and Appendix II and V of the European Community Habitats Directive.

Alosa macedonica, or the Macedonian shad, is a landlocked species of alosid fish endemic to Greece. Its single natural occurrence is the freshwater Lake Volvi in northern Greece. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Alosa maeotica, known as the Black Sea shad or Azov shad, is a species of Alosid fish endemic to the Sea of Azov and the western part of the Black Sea basin. It is found in Bulgaria, Georgia, Moldova, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine.
Abrau sprat, Clupeonella abrau, is a species of freshwater fish in the family Clupeidae. It is found landlocked in Russia in a single locality, Lake Abrau, located at 70 m above sea level near the Black Sea coast close to Novorossiysk. The lake is small and has been stocked by several alien species, whence the Abrau sprat is considered critically endangered.

Alosa caspia is a species of [[alosid]] fish, one of the species of shad endemic to the Caspian Sea basin.
Stenodus nelma, known alternatively as the nelma, sheefish, siifish, inconnu or connie, is a commercial species of freshwater whitefish in the family Salmonidae. It is widespread in the Arctic rivers from the Kola Peninsula eastward across Siberia to the Anadyr River and also in the North American basins of the Yukon River and Mackenzie River.

Lake Omodeo is an artificial lake in central west Sardinia, Italy.

The blueback herring, blueback shad, or summer shad is an anadromous species of herring from the east coast of North America, with a range from Nova Scotia to Florida. Blueback herring form schools and are believed to migrate offshore to overwinter near the bottom.
Alosa algeriensis, the North African shad, is a Mediterranean species of clupeid fish in the shad genus Alosa.

The Pontic shad, also referred to as the Black Sea shad or Kerch shad, is a species of clupeid fish in the genus Alosa, native to the Black Sea and Sea of Azov basins.
Alosa kessleri, also referred to as the Caspian anadromous shad, the blackback, or the black-spined herring, is a species of alosid fish. It is one of the several species of shad endemic to the Caspian Sea basin.
The Killarney shad, also called the goureen, is a freshwater fish in the family Alosidae, endemic to a single lake in Ireland, Lough Leane in County Kerry. Research has shown that it is a landlocked subspecies of the anadromous, twait shad, arriving in the lake after the Last Glacial Maximum about 10,000 years ago. This fish is at risk from eutrophication and the introduction of alien species of fish to the lake and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it as "critically endangered".
Alosa volgensis, the Volga shad, is a alosid fish, one of the species of shad endemic to the Caspian Sea region.

The Alabama shad is an anadromous species of alosid fish endemic to the United States where it breeds in medium to large flowing rivers from the Mississippi River drainage to the Suwannee River, Florida, as well as some other Gulf coast drainages. The biology of this fish is little known but it has become increasingly rare. The International Union for Conservation of Nature rated it "near threatened" in 2020 and the United States National Marine Fisheries Service has listed it as a Species of Concern. A principal reason for its decline is thought to be the many locks and dams blocking access for the fish to up-river spawning grounds.













