
Dysderidae, also known as woodlouse hunters, sowbug-eating spiders, and cell spiders, is a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837. They are found primarily in Eurasia, extending into North Africa with very few species occurring in South America. Dysdera crocata is introduced into many regions of the world.

The sac spiders of the family Clubionidae have a very confusing taxonomic history. Once, this family was a large catch-all taxon for a disparate collection of spiders, similar only in that they had eight eyes arranged in two rows and conical anterior spinnerets that touched, and were wandering predators that built silken retreats, or sacs, usually on plant terminals, between leaves, under bark, or under rocks. These are now recognized to include several families, some of which are more closely related to the three-clawed spiders, like lynx and wolf spiders, than to Clubionidae and related families.

Nusatidia is a genus of Asian sac spiders first described by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold in 2001.
Koppe is a genus of liocranid sac spiders first described by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold in 2001.

Psiloderces is a genus of six eyed spiders in the family Psilodercidae, first described by Eugène Simon in 1892.
Pristidia is a genus of Asian sac spiders first described by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold in 2001.
Echinax is a genus of Asian and African corinnid sac spiders first described by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold in 2001.
Medmassa is a genus of corinnid sac spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1887 under the name "Megaera", later renamed because "Megaera" was already in use as a synonym of the reptile genus Trimeresurus.
Kaemis is a genus of woodlouse hunting spiders that was first described by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold in 1993.
Leclercera is a genus of spiders in the family Psilodercidae found in Asia, including Thailand, Nepal, China and the Philippines. It was first described in 1995 by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold, who named it after a fellow collector of Asian spiders. She originally placed under Ochyroceratidae, but it was later moved it to Psilodercidae. It is named for Philippe Leclerc, a collector of spiders in southeast Asia.

Christa Laetitia Deeleman-Reinhold is a Dutch arachnologist. She specializes in spiders from Southeast Asia and Southern Europe, particularly cave-dwelling and tropical spiders. She donated a collection of about 25,000 Southeast Asian spiders, the largest collection of Southeast Asian spiders in existence, to the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden. In addition to numerous articles, she has written the book Forest Spiders of South East Asia (2001).
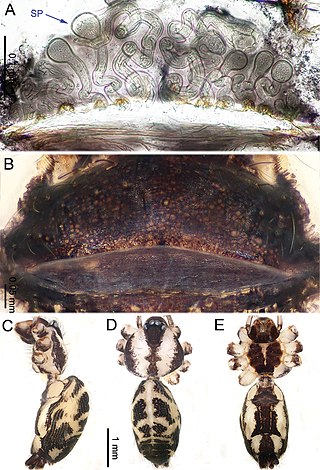
Althepus is a genus of spiders in the family Psilodercidae. It was first described in 1898 by Tamerlan Thorell. As of 2019, it contains 60 species, all from Asia.
Althepus indistinctus is a species of spider of the genus Althepus. It is endemic to Kalimantan in Indonesia.
Althepus javanensis is a species of spider of the genus Althepus. It is endemic to Java in Indonesia.
Althepus dekkingae is a species of spider of the genus Althepus. It is endemic to Java in Indonesia.
Althepus suhartoi is a species of spider of the genus Althepus, named after Suharto. It is endemic to Sumatra in Indonesia.
Althepus tibiatus is a species of spider of the genus Althepus.
Althepus stonei is a species of spider of the genus Althepus.

Psilodercidae is a family of spiders first described as a subfamily of Ochyroceratidae by Machado in 1951 and raised to family rank by J. Wunderlich in 2008. These spiders can be distinguished by the "segestriid positioning" of their six eyes, the absence of leg bristles, strong apical bristles on the cymbium, and several pairs of spermathecae in females.






