
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature.

Contrails or vapor trails are line-shaped clouds produced by aircraft engine exhaust or changes in air pressure, typically at aircraft cruising altitudes several miles above the Earth's surface. Contrails are composed primarily of water, in the form of ice crystals. The combination of water vapor in aircraft engine exhaust and the low ambient temperatures that exist at high altitudes allows the formation of the trails. Impurities in the engine exhaust from the fuel, including sulfur compounds provide some of the particles that can serve as nucleation sites for water droplet growth in the exhaust. If water droplets form, they might freeze to form ice particles that compose a contrail. Their formation can also be triggered by changes in air pressure in wingtip vortices or in the air over the entire wing surface. Contrails, and other clouds directly resulting from human activity, are collectively named homogenitus.

A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a deviation in their course at a right angle to the wind shear direction.

Altocumulus is a middle-altitude cloud genus that belongs mainly to the stratocumuliform physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual elements being larger and darker than those of cirrocumulus and smaller than those of stratocumulus. However, if the layers become tufted in appearance due to increased airmass instability, then the altocumulus clouds become more purely cumuliform in structure. Like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, altocumulus signifies convection. A sheet of partially conjoined altocumulus perlucidus is sometimes found preceding a weakening warm front, where the altostratus is starting to fragment, resulting in patches of altocumulus perlucidus between the areas of altostratus. Altocumulus is also commonly found between the warm and cold fronts in a depression, although this is often hidden by lower clouds.

A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the whole being at a lower height, usually below 2,000 metres (6,600 ft). Weak convective currents create shallow cloud layers because of drier, stable air above preventing continued vertical development. Historically, in English, this type of cloud has been referred to as a twain cloud for being a combination of two types of clouds.

A nimbostratus cloud is a multi-level, amorphous, nearly uniform and often dark grey cloud that usually produces continuous rain, snow or sleet but no lightning or thunder.

Cirrocumulus is one of the three main genus-types of high-altitude tropospheric clouds, the other two being cirrus and cirrostratus. They usually occur at an altitude of 5 to 12 km. Like lower-altitude cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, cirrocumulus signifies convection. Unlike other high-altitude tropospheric clouds like cirrus and cirrostratus, cirrocumulus includes a small amount of liquid water droplets, although these are in a supercooled state. Ice crystals are the predominant component, and typically, the ice crystals cause the supercooled water drops in the cloud to rapidly freeze, transforming the cirrocumulus into cirrostratus. This process can also produce precipitation in the form of a virga consisting of ice or snow. Thus, cirrocumulus clouds are usually short-lived. They usually only form as part of a short-lived transitional phase within an area of cirrus clouds and can also form briefly as a result of the breaking up of part of a cumulonimbus anvil.

A supercell is a thunderstorm characterized by the presence of a mesocyclone: a deep, persistently rotating updraft. For this reason, these storms are sometimes referred to as rotating thunderstorms. Of the four classifications of thunderstorms, supercells are the overall least common and have the potential to be the most severe. Supercells are often isolated from other thunderstorms, and can dominate the local weather up to 32 kilometres (20 mi) away. They tend to last 2–4 hours.
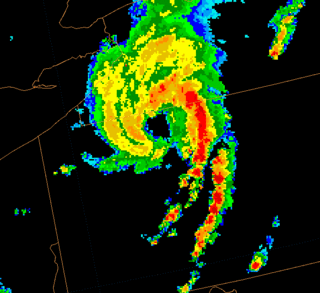
A squall line, or more accurately a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS), is a line of thunderstorms, often forming along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front. Linear thunderstorm structures often contain heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and occasionally tornadoes or waterspouts. Particularly strong straight-line winds can occur where the linear structure forms into the shape of a bow echo. Tornadoes can occur along waves within a line echo wave pattern (LEWP), where mesoscale low-pressure areas are present. Some bow echoes can grow to become derechos as they move swiftly across a large area. On the back edge of the rainband associated with mature squall lines, a wake low can be present, on very rare occasions associated with a heat burst.

A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient. Warm fronts lie within broader troughs of low pressure than cold fronts, and move more slowly than the cold fronts which usually follow because cold air is denser and less easy to remove from the Earth's surface. This also forces temperature differences across warm fronts to be broader in scale. Clouds ahead of the warm front are mostly stratiform, and rainfall defiantly increases as the front approaches. Fog can also occur preceding a warm frontal passage. Clearing and warming is usually rapid after frontal passage. If the warm air mass is unstable, thunderstorms may be embedded among the stratiform clouds ahead of the front, and after frontal passage thundershowers may continue. On weather maps, the surface location of a warm front is marked with a red line of semicircles pointing in the direction of travel.

Cloud physics is the study of the physical processes that lead to the formation, growth and precipitation of atmospheric clouds. These aerosols are found in the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere, which collectively make up the greatest part of the homosphere. Clouds consist of microscopic droplets of liquid water, tiny crystals of ice, or both. Cloud droplets initially form by the condensation of water vapor onto condensation nuclei when the supersaturation of air exceeds a critical value according to Köhler theory. Cloud condensation nuclei are necessary for cloud droplets formation because of the Kelvin effect, which describes the change in saturation vapor pressure due to a curved surface. At small radii, the amount of supersaturation needed for condensation to occur is so large, that it does not happen naturally. Raoult's law describes how the vapor pressure is dependent on the amount of solute in a solution. At high concentrations, when the cloud droplets are small, the supersaturation required is smaller than without the presence of a nucleus.

In meteorology, Altocumulus castellanus or Altocumulus castellatus (ACCAS) is a cloud type named for its tower-like projections that billow upwards from the base of the cloud. The base of the cloud can form as low as 2,000 metres, or as high as 6,000 metres. They are very similar to cumulus congestus clouds, but at a higher level and with the cloud heaps joined at the base.

Cumulus congestus clouds, also known as towering cumulus, are a form of cumulus that can be based in the low or middle height ranges. They achieve considerable vertical development in areas of deep, moist convection. They are an intermediate stage between cumulus mediocris and cumulonimbus, sometimes producing showers of snow, rain, or ice pellets. Precipitation that evaporates before reaching the surface is virga.

A fallstreak hole is a large gap, usually circular or elliptical, that can appear in cirrocumulus or altocumulus clouds. The holes are caused by supercooled water in the clouds suddenly evaporating, and may be triggered by passing aircraft.

Cirrocumulus lacunosus also known as Cirrocumulus lacunar or Cirrocumulus lacunaris is a type of cirrocumulus cloud. The term lacunosus is from Latin, meaning "full of hollows". Cirrocumulus lacunosus is a relatively rare cloud form that occurs as a layer of cloud with circular holes in it. Formation is commonly attributed to a cool layer mixing with a warmer, higher layer of the atmosphere. These holes normally have frayed edges, and they are often arranged in a manner that resembles a net or a honeycomb.

A castellanus is a cloud that displays at least in its upper part cumuliform protuberances having the shape of turrets that give a crenellated aspect. Some of these turrets are higher than they are wide; they have a common base and seem to be arranged in a line. The castellanus characteristic is particularly obvious when the clouds are observed from the side.

Altocumulus stratiformis is the most common species of the Altocumulus genus of clouds. They tend to form broad layers of individual, cell-like clumps, often separated from each other, though they sometimes can coagulate into a larger individual cloud. They often have a vertical extent of less than 500 m. Due to their formation dynamics, they are commonly associated with the imminent arrival of precipitation.

Altocumulus volutus is a type of altocumulus cloud. This cloud type has the appearance of a single, small, horizontal, rolling line, it is relatively rare compared with its counterpart stratocumulus volutus, This cloud does not attach to any other cloud. It may or may not appear with altocumulus clouds of different species. When found in a thunderstorm, it forms when cold air from a thunderstorm's downdraft makes the already present warm and moist air rise, expanding and cooling as it rises. It then condenses, although the most likely scenario is that it condenses into a shelf cloud or roll cloud, rather than an altocumulus volutus cloud. When found in environments where it is not associated with a thunderstorm, it forms because of wind shear.

Perlucidus is a cloud variety that generally appears in only two cloud types, with those cloud types being altocumulus and stratocumulus, this cloud variety is easily recognizable, with its appearance being small gaps showing up in one of the cloud types that it shows up in, which let higher clouds be seen This cloud variety forms when shallow convection starts in a cloud layer that did not previously have perlucidus variety characteristics, the gaps that make the sky visible in these clouds indicate regions where air is sinking, this cloud variety may appear either as a translucent cloud or an opaque cloud



















