| Amabiliidae | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Cestoda |
| Order: | Cyclophyllidea |
| Family: | Amabiliidae Braun, 1900 |
| Genera | |
The Amabiliidae are a family of tapeworms. It contains four genera and 23 species. [1]
| Amabiliidae | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Cestoda |
| Order: | Cyclophyllidea |
| Family: | Amabiliidae Braun, 1900 |
| Genera | |
The Amabiliidae are a family of tapeworms. It contains four genera and 23 species. [1]
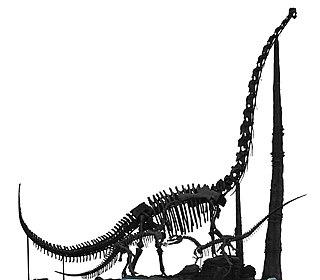
Chuanjiesaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaurs from the middle Jurassic Period. They lived in what is now China. The type species, Chuanjiesaurus anaensis, was first described by Fang, Pang, Lü, Zhang, Pan, Wang, Li and Cheng in 2000. Fossils of the species were found in the village of Chuanjie, Lufeng County, Yunnan Province, and are named after the location where the fossils were discovered. Holtz gave a length of 25 meters.

Lamponidae is a family of spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1893. It contains about 200 described species in 23 genera, most of which are endemic to Australia, with the genus Centrocalia endemic to New Caledonia, and two Lampona species also occurring in New Zealand where it is commonly known as the "White Tail" spider. Lampona papua is endemic to New Guinea, where two otherwise Australian species also occur.

Raphicerus is a genus of small antelopes of the tribe Neotragini.

The elongated shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. It lives in the forests of central, northern, and eastern Sulawesi from 200 to 2000 meters elevation.

The long-tailed mole is a species of mole in the family Talpidae. It is found in China, Vietnam and Myanmar.

Day's shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to India. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The tree bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae and the only species in the genus Ardops. It is found in Dominica, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Montserrat, Netherlands Antilles, Saint Lucia, Saba and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.

The yellow-bellied weasel is a species of weasel that inhabits pine forests in central and eastern Asia.
Fauna Europaea is a database of the scientific names and distribution of all living multicellular European land and fresh-water animals. It serves as a standard taxonomic source for animal taxonomy within the Pan-European Species directories Infrastructure (PESI). As of June 2020, Fauna Europaea reported that their database contained 235,708 taxon names and 173,654 species names.
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined.
Nitrospirae is a phylum of bacteria. It includes multiple genera, such as Nitrospira, the largest. The first member of this phylum, Nitrospira marina, was discovered in 1985. The second member, Nitrospira moscoviensis, was discovered in 1995.

The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates is a list of highly endangered primate species selected and published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Species Survival Commission (SSC) Primate Specialist Group (PSG), the International Primatological Society (IPS), Global Wildlife Conservation (GWC), and Bristol Zoological Society (BZS). The IUCN/SSC PSG worked with Conservation International (CI) to start the list in 2000, but in 2002, during the 19th Congress of the International Primatological Society, primatologists reviewed and debated the list, resulting in the 2002–2004 revision and the endorsement of the IPS. The publication was a joint project between the three conservation organizations until the 2012–2014 list when BZS was added as a publisher. The 2018–2020 list was the first time Conservation International was not among the publishers, replaced instead by GWC. The list has been revised every two years following the biannual Congress of the IPS. Starting with the 2004–2006 report, the title changed to "Primates in Peril: The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates". That same year, the list began to provide information about each species, including their conservation status and the threats they face in the wild. The species text is written in collaboration with experts from the field, with 60 people contributing to the 2006–2008 report and 85 people contributing to the 2008–2010 report. The 2004–2006 and 2006–2008 reports were published in the IUCN/SSC PSG journal Primate Conservation,, since then they have been published as independent publications.

Grevillea irrasa is a shrub species which is endemic to New South Wales in Australia. It has a spreading to erect habit, growing 1.5–3 metres high. Flowers appear between August and January in its native range. These are red, apricot or pink.

Grevillea parvula , commonly known as Genoa grevillea, is a species of the plant genus Grevillea. It is native to the states of Victoria and New South Wales in Australia.

Grevillea polychroma , commonly known as Tullach Ard grevillea, is a species of the plant genus Grevillea. It is endemic to the state of Victoria in Australia. The taxon was first formally described as a subspecies of Grevillea brevifolia in 2000. It was promoted to species status in 2005. The species is listed as "Rare in Victoria" on the Department of Sustainability and Environment's Advisory List of Rare Or Threatened Plants In Victoria.
Grevillea monslacana, commonly known as Lake Mountain grevillea, is a shrub species which is endemic to mountainous areas of eastern Victoria in Australia. It grows to 2 metres in height. The species, which was first formally described in 2000, is listed as "Rare in Victoria" on the Victorian Department of Sustainability and Environment's Advisory List of Rare Or Threatened Plants In Victoria. It was previously known as the Lake Mountain form of Grevillea victoriae.
Grevillea epicroca is a shrub species that is endemic to south-eastern New South Wales in Australia. It grows up to 2.5 metres high and produces clusters of red flowers between November and May in the species' native range. It was first formally described by Val Stajsic and Bill Molyneux, their description published in Flora of Australia in 2000.
Grevillea dunlopii is a species of plant in the protea family that is endemic to Australia. The species grows as a shrub to about 2 m in height and has white flowers. It occurs in the vicinity of Mount Gilruth, on the sandstone Arnhem Land plateau of the tropical Top End of the Northern Territory, where it grows on sandy soils. The specific epithet dunlopii honours Clyde Dunlop, curator of the Northern Territory Herbarium in Darwin.

Protea venusta, the cascade sugarbush or creeping beauty, is a flower-bearing shrub belonging to the genus Protea. It is endemic to South Africa.
Tatria is a genus of tapeworms in the family Amabiliidae. It contains at least 15 known species and is the largest genus in the Amabiliidae family.