
Rickettsia is a genus of nonmotile, Gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci, bacilli, or threads. The term "rickettsia" has nothing to do with rickets ; the bacterial genus Rickettsia was named after Howard Taylor Ricketts, in honor of his pioneering work on tick-borne spotted fever.

Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a bacterial disease spread by ticks. It typically begins with a fever and headache, which is followed a few days later with the development of a rash. The rash is generally made up of small spots of bleeding and starts on the wrists and ankles. Other symptoms may include muscle pains and vomiting. Long-term complications following recovery may include hearing loss or loss of part of an arm or leg.

The Ixodidae are the family of hard ticks or scale ticks, one of the three families of ticks, consisting of over 700 species. They are known as 'hard ticks' because they have a scutum or hard shield, which the other big family of ticks, the 'soft ticks' (Argasidae), lack. They are ectoparasites of a wide range of host species, and some are vectors of pathogens that can cause human disease.
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. Because individual ticks can harbor more than one disease-causing agent, patients can be infected with more than one pathogen at the same time, compounding the difficulty in diagnosis and treatment. 16 tick-borne diseases of humans are known, of which four have been discovered since 2013.

Dermacentor variabilis, also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. It is one of the best-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms.

Wilhelm "Willy" Burgdorfer was an American scientist born and educated in Basel, Switzerland, considered an international leader in the field of medical entomology. He discovered the bacterial pathogen that causes Lyme disease, a spirochete named Borrelia burgdorferi in his honor.
A rickettsiosis is a disease caused by intracellular bacteria.

Amblyomma is a genus of hard ticks. Some are disease vectors, for example the Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Brazil or ehrlichiosis in the United States.

African tick bite fever (ATBF) is a bacterial infection spread by the bite of a tick. Symptoms may include fever, headache, muscle pain, and a rash. At the site of the bite there is typically a red skin sore with a dark center. The onset of symptoms usually occurs 4–10 days after the bite. Complications are rare, but may include joint inflammation. Some people do not develop symptoms.
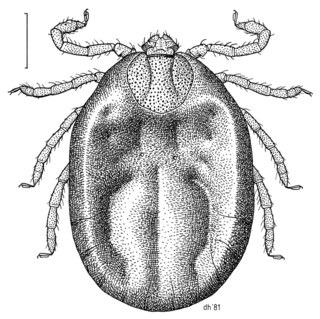
Haemaphysalis longicornis, the Asian longhorned tick, longhorned tick, bush tick, Asian tick, or cattle tick, is a parasitic arachnid belonging to the tick family Ixodidae. The Asian longhorned tick is a known livestock pest, especially in New Zealand, and can transmit a disease called theileriosis to cattle but not to humans. However, the tick has been associated with several other tickborne diseases in humans.
Rickettsia helvetica, previously known as the Swiss agent, is a bacterium found in Dermacentor reticulatus and other ticks, which has been implicated as a suspected but unconfirmed human pathogen. First recognized in 1979 in Ixodes ricinus ticks in Switzerland as a new member of the spotted fever group of Rickettsia, the R. helvetica bacterium was eventually isolated in 1993. Although R. helvetica was initially thought to be harmless in humans and many animal species, some individual case reports suggest that it may be capable of causing a nonspecific fever in humans. In 1997, a man living in eastern France seroconverted to Rickettsia 4 weeks after onset of an unexplained febrile illness. In 2010, a case report indicated that tick-borne R. helvetica can also cause meningitis in humans.

Amblyomma maculatum is a species of tick in the genus Amblyomma. Immatures usually infest small mammals and birds that dwell on the ground; cotton rats may be particularly favored hosts. Some recorded hosts include:

Ornithodoros moubata, commonly known as the African hut tampan or the eyeless tampan, is a species of tick in the family Argasidae. It is an ectoparasite and vector of relapsing fever in humans, and African swine fever in pigs.
Rickettsia monacensis is a tick-borne spotted fever group Rickettsia species.

Amblyomma triguttatum, commonly known as the kangaroo tick, is a species of tick in the genus Amblyomma native to Australia. There are four subspecies, one or more of which might be separate species. The nominate subspecies is a vector for Rickettsia.
Amblyomma patinoi is a species of tick of the genus Amblyomma. The species is associated with the Eastern Cordillera of Colombia. Rickettsia species can habitate A. patinoi endosymbiotically.
Amblyomma interandinum is a species of tick of the genus Amblyomma. The species is associated with the northern part of the Inter-Andean valley of Peru. Rickettsia species can habitate A. interandinum endosymbiotically.
The Asian tortoise tick, is a hard-bodied tick of the genus Amblyomma. The tick is a parasite of tortoises, such as Geochelone elegans, domestic dogs, buffaloes. It is found in India, Sri Lanka and Myanmar. Adult tick is about 3 cm in length.
Amblyomma gervaisi is a hard-bodied tick of the genus Amblyomma. The tick is a parasite of snakes, such as Naja naja, Python molurus species and monitor species such as Varanus ocellatus, Varanus yemenensis, Varanus benghalensis, Varanus griseus and many other Varanus species in southeastern Asia and Asia-minor. They exhibit sexual dimorphism. They can be found in Sri Lanka, India, Yemen, Saudi Arabia. It is a potential vector for Coxiella burnetii.

Amblyomma testudinarium is a hard-bodied tick of the genus Amblyomma. It is found in Indonesia, India, Japan, Thailand, Sri Lanka and Vietnam. Adults parasitize various larger mammals such as buffalo and cattle, whereas nymphs and larvae use mostly larger and medium mammals.












