
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to pregnancy, underlying conditions worsened by the pregnancy or management of these conditions. This can occur either while she is pregnant or within six weeks of resolution of the pregnancy. The CDC definition of pregnancy-related deaths extends the period of consideration to include one year from the resolution of the pregnancy. Pregnancy associated death, as defined by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), are all deaths occurring within one year of a pregnancy resolution. Identification of pregnancy associated deaths is important for deciding whether or not the pregnancy was a direct or indirect contributing cause of the death.

Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases. Disease and disability are affected by environmental factors, genetic predisposition, disease agents, and lifestyle choices, and are dynamic processes that begin before individuals realize they are affected. Disease prevention relies on anticipatory actions that can be categorized as primal, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.
Disease management is defined as "a system of coordinated healthcare interventions and communications for populations with conditions in which patient self-care efforts are significant."
There are more than 720,000 estimated global suicide deaths every year. Suicide affects every demographic, yet there are some populations that are more impacted than others. For example, among 15–29 year olds, suicide is much more prominent; this being the third leading cause of death within this age group.

The social determinants of health (SDOH) are the economic and social conditions that influence individual and group differences in health status. They are the health promoting factors found in one's living and working conditions, rather than individual risk factors that influence the risk or vulnerability for a disease or injury. The distribution of social determinants is often shaped by public policies that reflect prevailing political ideologies of the area.
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term chronic is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV which allow these individuals to live while managing symptoms.

Prevalence of tobacco use is reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), which focuses on cigarette smoking due to reported data limitations. Smoking has therefore been studied more extensively than any other form of consumption.
Healthy People is a program of a nationwide health-promotion and disease-prevention goals set by the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The goals were first set in 1979 "in response to an emerging consensus among scientists and health authorities that national health priorities should emphasize disease prevention". The Healthy People program was originally issued by the Department of Health, Education and Welfare. This first issue contained "a report announcing goals for a ten-year plan to reduce controllable health risks. In its section on nutrition, the report recommended diets with fewer calories; less saturated fat, cholesterol, salt, and sugar; relatively more complex carbohydrates, fish and poultry; and less red meat." Though this recommended diet consisted of more processed foods rather than fresh produce, the report advised for consumers to "be wary of processed foods". The goals were subsequently updated for Healthy People 2000, Healthy People 2010, Healthy People 2020 and Healthy People 2030.

In medicine, rural health or rural medicine is the interdisciplinary study of health and health care delivery in rural environments. The concept of rural health incorporates many fields, including wilderness medicine, geography, midwifery, nursing, sociology, economics, and telehealth or telemedicine.

Healthcare in Europe is provided through a wide range of different systems run at individual national levels. Most European countries have a system of tightly regulated, competing private health insurance companies, with government subsidies available for citizens who cannot afford coverage. Many European countries offer their citizens a European Health Insurance Card which, on a reciprocal basis, provides insurance for emergency medical treatment insurance when visiting other participating European countries.

The World Health Organization defines health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being". Average life expectancy at birth was 78.7 in 2017. Heart diseases are responsible for the greatest number of deaths in the United States.
Healthcare reform in the United States has had a long history. Reforms have often been proposed but have rarely been accomplished. In 2010, landmark reform was passed through two federal statutes: the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), signed March 23, 2010, and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, which amended the PPACA and became law on March 30, 2010.

In the United States, health insurance coverage is provided by several public and private sources. During 2019, the U.S. population was approximately 330 million, with 59 million people 65 years of age and over covered by the federal Medicare program. The 273 million non-institutionalized persons under age 65 either obtained their coverage from employer-based or non-employer based sources, or were uninsured. During the year 2019, 89% of the non-institutionalized population had health insurance coverage. Separately, approximately 12 million military personnel received coverage through the Veteran's Administration and Military Health System.
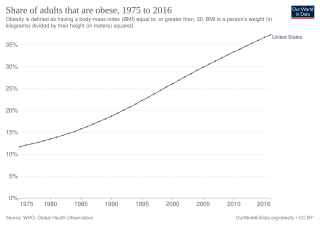
Obesity is common in the United States and is a major health issue associated with numerous diseases, specifically an increased risk of certain types of cancer, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cardiovascular disease, as well as significant increases in early mortality and economic costs.
The healthcare reform debate in the United States has been a political issue focusing upon increasing medical coverage, decreasing costs, insurance reform, and the philosophy of its provision, funding, and government involvement.
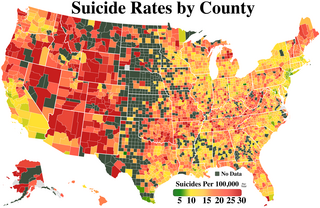
Suicide is a major national public health issue in the United States. The country has one of the highest suicide rates among wealthy nations. In 2020, there were 45,799 recorded suicides, up from 42,773 in 2014, according to the CDC's National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). On average, adjusted for age, the annual U.S. suicide rate increased 30% between 2000 and 2020, from 10.4 to 13.5 suicides per 100,000 people. From 2000 to 2020, more than 800,000 people died by suicide in the United States. Males represented 78.7% of all suicides between 2000 and 2020. In 2022, a record high 49,500 people died by suicide. The 2022 rate was the highest level since 1941, at 14.3 per 100,000 persons. This rate was surpassed in 2023, when it increased to over 14.7 per 100,000 persons.

In the United States, healthcare is largely provided by private sector healthcare facilities, and paid for by a combination of public programs, private insurance, and out-of-pocket payments. The U.S. is the only developed country without a system of universal healthcare, and a significant proportion of its population lacks health insurance. The United States spends more on healthcare than any other country, both in absolute terms and as a percentage of GDP; however, this expenditure does not necessarily translate into better overall health outcomes compared to other developed nations. Coverage varies widely across the population, with certain groups, such as the elderly and low-income individuals, receiving more comprehensive care through government programs such as Medicaid and Medicare.
The social determinants of health in poverty describe the factors that affect impoverished populations' health and health inequality. Inequalities in health stem from the conditions of people's lives, including living conditions, work environment, age, and other social factors, and how these affect people's ability to respond to illness. These conditions are also shaped by political, social, and economic structures. The majority of people around the globe do not meet their potential best health because of a "toxic combination of bad policies, economics, and politics". Daily living conditions work together with these structural drivers to result in the social determinants of health.
Health care finance in the United States discusses how Americans obtain and pay for their healthcare, and why U.S. healthcare costs are the highest in the world based on various measures.
An infection rate or incident rate is the probability or risk of an infection in a population. It is used to measure the frequency of occurrence of new instances of infection within a population during a specific time period.











