In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix.

Dicarbonyl/L-xylulose reductase, also known as carbonyl reductase II, is an enzyme that in human is encoded by the DCXR gene located on chromosome 17.
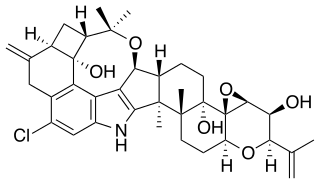
Penitrem A (tremortin) is an indole-diterpenoid mycotoxin produced by certain species of Aspergillus, Claviceps, and Penicillium, which can be found growing on various plant species such as ryegrass. Penitrem A is one of many secondary metabolites following the synthesis of paxilline in Penicillium crostosum. Penitrem A poisoning in humans and animals usually occurs through the consumption of contaminated foods by mycotoxin-producing species, which is then distributed through the body by the bloodstream. It bypasses the blood-brain barrier to exert its toxicological effects on the central nervous system. In humans, penitrem A poisoning has been associated with severe tremors, hyperthermia, nausea/vomiting, diplopia, and bloody diarrhea. In animals, symptoms of penitrem A poisoning has been associated with symptoms ranging from tremors, seizures, and hyperthermia to ataxia and nystagmus.

In enzymology, a (R,R)-butanediol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tryptophan alpha,beta-oxidase (EC 1.3.3.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
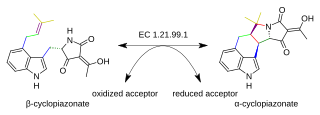
Beta-cyclopiazonate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a thiamine oxidase (EC 1.1.3.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme that is very important in the biosynthesis of amino acids in prokaryotes, fungi, and some higher plants. It forms an early branch point in the metabolic pathway forming lysine, methionine, leucine and isoleucine from aspartate. This pathway also produces diaminopimelate which plays an essential role in bacterial cell wall formation. There is particular interest in ASADH as disabling this enzyme proves fatal to the organism giving rise to the possibility of a new class of antibiotics, fungicides, and herbicides aimed at inhibiting it.

In enzymology, a 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indole 2,3-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,4-diaminopentanoate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-amino-acid dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an L-amino acid oxidase (LAAO) (EC 1.4.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-methyl-L-amino-acid oxidase (EC 1.5.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an opine dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.1.28) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, the FAD dependent oxidoreductase family of proteins is a family of FAD dependent oxidoreductases. Members of this family include Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase EC 1.1.99.5, Sarcosine oxidase beta subunit EC 1.5.3.1, D-amino-acid dehydrogenase EC 1.4.99.1, D-aspartate oxidase EC 1.4.3.1.
D-amino acid dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.4.5.1, DadA) is an enzyme with systematic name D-amino acid:quinone oxidoreductase (deaminating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cannabidiolic acid synthase is an enzyme with systematic name cannabigerolate:oxygen oxidoreductase . It is an oxidoreductase found in Cannabis sativa that catalyses the formation of cannabidiolate, a carboxylated precursor of cannabidiol.

In enzymology, an aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.7.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.









